|
Russian Minister Of Foreign Affairs
The Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Russian Federation is a high-ranking Russian government official who heads the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Russian Federation. The foreign minister is one of the five so-called 'presidential' ministers, along with the ministers of defense, interior, emergencies and justice. Although they are members of the Cabinet, they are directly subordinate to the President. The foreign minister, like other presidential ministers, is nominated and appointed by the President after consultation with the Federation Council (whereas non-presidential ministers are nominated by the Prime Minister and appointed by the President after approval by the State Duma). The foreign minister is also a permanent member of the Russian Security Council. Tsardom of Russia Russian Empire Provisional Government Russian SFSR (1917–1991) Russian Federation (1991–present) See also * Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Russia) * List of Soviet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergey Lavrov
Sergey Viktorovich Lavrov (russian: Сергей Викторович Лавров, ; born 21 March 1950) is a Russian diplomat and politician who has served as the Minister of Foreign Affairs (Russia), Foreign Minister of Russia since 2004. Lavrov served as the Permanent Representative of Russia to the United Nations from 1994 to 2004. Early life and education Lavrov was born on 21 March 1950 in Moscow, to an Armenians in Tbilisi, Armenian father from Tbilisi, Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic, Georgian SSR, and a Russians, Russian mother from Noginsk, Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic, Russian SFSR. His father's surname was originally Kalantaryan. His mother worked in the Soviet Ministry for Foreign Trade. Lavrov graduated from high school with a silver medal. Since his favorite class was physics, he planned to enter either the Moscow Engineering Physics Institute (National Research Nuclear University), National Research Nuclear University or the Moscow Institute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
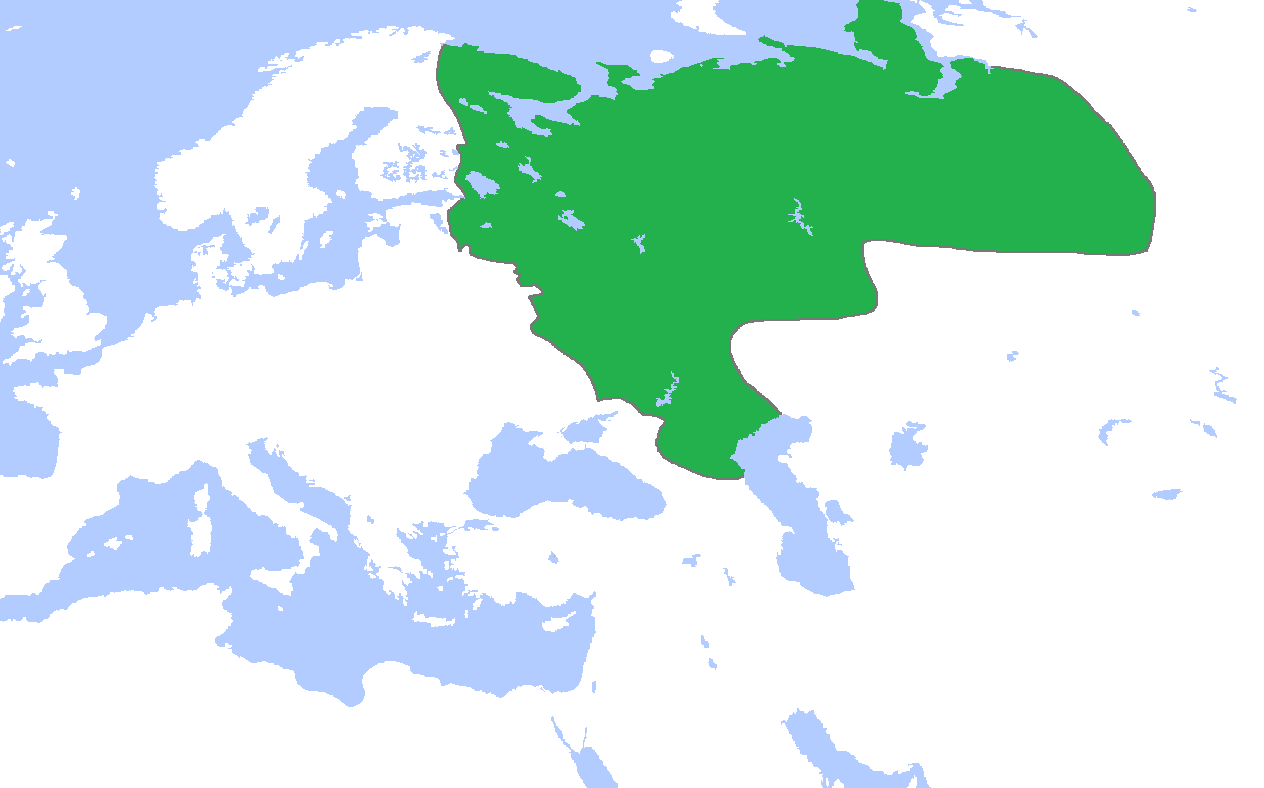
Prikaz
A prikaz (russian: прика́з, ''prikaz''; , plural: ) was an administrative, judicial, territorial, or executive office functioning on behalf of palace, civil, military, or church authorities in Muscovy and in Russia from the 15th to the 18th centuries. The term usually suggests the functionality of a modern "ministry", "office" or "department". In modern Russian, ''prikaz'' literally means an "order". Most of the prikazes were subordinated to the Boyar Duma. Some of them (palace prikazes (russian: links=no, дворцовые приказы, ) were subordinated to the ''taynyi prikaz'' or ''pervyi prikaz'', which answered directly to the tsar. The patriarch of Moscow and All Russia had his own prikazes. History Originally, prikazes were created by private orders (russian: приказ, prikaz) given by the tsar to a certain person. The functions of the prikazy would be led by boyars and professional administrators. From 1512, the term "Prikaz" started to be used to refer t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasili IV Of Russia
Vasili IV Shuisky (russian: Василий IV Иванович Шуйский, ''Vasiliy IV Ivanovich Shuyskiy'', c. 155212 September 1612) was Tsar of Russia between 1606 and 1610 after the murder of False Dmitri I. His rule coincided with the Time of Troubles. He was the only member of House of Shuisky to become Tsar and the last member of the Rurikid dynasty to rule as tsar. Life He was a son of Ivan Andreyevich Shuisky. Born Prince Vasili Ivanovich Shuisky, he descended from sovereign princes of Nizhny Novgorod and was a 20th-generation male-line descendant of the 9th-century Varangian prince Rurik. Vasili Ivanovich was one of the leading boyars of the Tsardom of Russia during the reigns of Feodor I () and Boris Godunov (). In the court intrigues of the Time of Troubles (1598–1613), Vasily and his younger brother Dmitry Shuisky usually acted together and fought as one. It was Shuisky who, in obedience to the secret orders of Tsar-to-be Boris, went to Uglich t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasily Telepnev
Vasili, Vasily, Vasilii or Vasiliy (Russian: Василий) is a Russian masculine given name of Greek origin and corresponds to ''Basil''. It may refer to: *Vasili I of Moscow Grand Prince from 1389–1425 * Vasili II of Moscow Grand Prince from 1425–1462 *Vasili III of Russia Tsar from 1505–1533 *Vasili IV of Russia Tsar from 1606–1610 *Basil Fool for Christ (1469–1557), also known as Saint Basil, or Vasily Blazhenny *Vasily Alekseyev (1942–2011), Soviet weightlifter *Vasily Arkhipov (1926–1998), Soviet Naval officer in the Cuban Missile Crisis *Vasily Boldyrev (1875–1933), Russian general *Vasily Chapayev (1887–1919), Russian Army commander *Vasily Chuikov (1900–1982), Soviet marschal *Vasily Degtyaryov (1880–1949), Russian weapons designer and Major General *Vasily Dzhugashvili (1921–1962), Stalin's son *Vasili Golovachov (born 1948), Russian science fiction author *Vasily Grossman (1905–1964), Soviet writer and journalist *Vasily Ignatenko (1961–198 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Dmitriy I
False Dmitry I ( rus, Лжедмитрий I, Lzhedmitriy I) (or Pseudo-Demetrius I) reigned as the Tsar of Russia from 10 June 1605 until his death on 17 May 1606 under the name of Dmitriy Ivanovich ( rus, Дмитрий Иванович). According to historian Chester S.L. Dunning, Dmitry was "the only Tsar ever raised to the throne by means of a military campaign and popular uprisings". He was the first, and most successful, of three "pretenders" (russian: самозванцы (sing.: самозванец), samozvanets) who claimed during the Time of Troubles to be the youngest son of Ivan the Terrible, tsarevich Dmitry Ivanovich, who supposedly escaped a 1591 assassination attempt when he was eight years old. It is generally believed that the real Dmitry of Uglich died in Uglich in 1591. False Dmitry claimed that his mother, Maria Nagaya, anticipated the assassination attempt ordered by Boris Godunov and helped him escape to a monastery in the Tsardom of Russia, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Gramotin
Ivan Tarasyevich Gramotin () (died 1638) was a Russian diplomat and head of the ''Posolsky Prikaz'' (foreign ministry). Ivan Gramotin was known to have been a very smart, well-read and eloquent person. He was one of the prominent figures during the Time of Troubles in Russia. Gramotin was appointed head of the ''Posolsky Prikaz'' in August 1605 during the reign of the False Dmitry I. In 1606, he conducted negotiations with the Polish envoys. Two years later, he betrayed the False Dmitry and tried to become close to Vasily IV of Russia, but eventually failed. In 1608, Ivan Gramotin joined the ranks of the False Dmitry II and became a close associate of Sigismund III Vasa in 1610. After Vasily IV had been admitted to monastic vows, the Polish king appointed Gramotin head of the ''Posolsky Prikaz'' in the rank of stamp bearer. He also held a position in the ''Pomestny Prikaz'' and the Boyar Duma. In 1612, Gramotin was sent to Poland by the boyars to negotiate the accession of Wladi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Иван Тарасович Грамотин
Ivan () is a Slavic male given name, connected with the variant of the Greek name (English: John) from Hebrew meaning 'God is gracious'. It is associated worldwide with Slavic countries. The earliest person known to bear the name was Bulgarian tsar Ivan Vladislav. It is very popular in Russia, Ukraine, Croatia, Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Slovenia, Bulgaria, Belarus, North Macedonia, and Montenegro and has also become more popular in Romance-speaking countries since the 20th century. Etymology Ivan is the common Slavic Latin spelling, while Cyrillic spelling is two-fold: in Bulgarian, Russian, Macedonian, Serbian and Montenegrin it is Иван, while in Belarusian and Ukrainian it is Іван. The Old Church Slavonic (or Old Cyrillic) spelling is . It is the Slavic relative of the Latin name , corresponding to English ''John''. This Slavic version of the name originates from New Testament Greek (''Iōánnēs'') rather than from the Latin . The Greek name is in tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afanasy Vlasyev
Afanasy (russian: Афана́сий) is the Russian form of Athanasios, a Greek name meaning "immortal". It may refer to: People: * Afanasy Bagration, Prince Adarnase of Kartli (1707–1784), Georgian prince royal and Russian Empire general * Afanasy Beloborodov (1903–1990), Russian general * Afanasy Fet (1820–1892), Russian poet * Afanasy Grigoriev (1782–1868), Russian architect * Afanasy Nikitin (died 1472), Russian merchant and traveler * Afanasy Ordin-Nashchokin (1605–1680), Russian statesman * Afanasy Razmaritsyn (1844–1917), Russian-Ukrainian painter * Afanasy Seredin-Sabatin (1860–1921), Russian architect and journalist, first Western architect to live and work in the Korean Empire * Afanasy Shchapov (1830–1876), Russian historian Fictional people: * Afanasy Ivanovich Tovstogub, the main character of Nikolai Gogol's short story ''The Old World Landowners'' The surname Afanasyev (russian: Афана́сьев) is derived from the name. The surname Afonin Afon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boris Godunov
Borís Fyodorovich Godunóv (; russian: Борис Фёдорович Годунов; 1552 ) ruled the Tsardom of Russia as ''de facto'' regent from c. 1585 to 1598 and then as the first non-Rurikid tsar from 1598 to 1605. After the end of his reign, Russia descended into the Time of Troubles. Early years Boris Godunov was the most noted member of an ancient, now extinct, Russian family of Tatar origin ( Chet), which came from the Horde to Kostroma in the early 14th century. This cites: * Platon Vasilievich Pavlov, ''On the Historical Significance of the Reign of Boris Godunov'' (Rus.) (Moscow, 1850) * Sergyei Mikhailivich Solovev, ''History of Russia'' (Rus.) (2nd ed., vols. vii–viii., St Petersburg, 1897). This legend is written in the annals dating from early 17th century. He was descended from the Tatar Prince Chet, who went from the Golden Horde to Russia and founded the Ipatiev Monastery in Kostroma. Boris was probably born before or after the Kazan campaign. Boris was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feodor I Of Russia
Fyodor I Ivanovich (russian: Фёдор I Иванович) or Feodor I Ioannovich (russian: Феодор I Иоаннович; 31 May 1557 – 17 January (NS) 1598), also known as Feodor the Bellringer (russian: Феодор Звонарь), reigned as Tsar of Russia from 1584 until his death in 1598. Feodor's mother died when he was three, and he grew up in the shadow of his father, Ivan the Terrible. A pious man of retiring disposition, Feodor took little interest in politics, and the country was effectively administered in his name by Boris Godunov, the brother of his beloved wife Irina. His childless death marked the end of the Rurik dynasty, and spurred Russia's descent into the catastrophic Time of Troubles. In Russian documents, Feodor is sometimes called ''blessed'' (russian: Блаженный). He is also listed in the "Great Synaxaristes" of the Orthodox Church, with his feast day on January 7 (OS). Background Feodor was born in Moscow, the son of Ivan IV (T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasily And Andrey Shchelkalov
Vasily Yakovlevich Shchelkalov (Василий Яковлевич Щелкалов in Russian) (? – 1610 or 1611) and Andrey Yakovlevich Shchelkalov (Андрей Яковлевич Щелкалов) (? - ) were two influential diplomats and heads of the '' Posolsky Prikaz'' during the reigns of Ivan the Terrible, Feodor I, and Boris Godunov in Russia. Andrey Yakovlevich Shchelkalov The name of Andrey Yakovlevich Shchelkalov first appeared in 1550, when he was entered in the so-called ''Book of a Thousand'' (Тысячная книга, or ''Tysyachnaya kniga''). The book contained genealogical information on noble Muscovite families (1070 people altogether, hence, the name of the book) and their land allotments around Moscow. In 1560, Andrey Shchelkalov was assigned to the Lithuanian ambassadors as a police officer. Two years later, he became a '' dyak'' (government official). In 1566, Andrey Shchelkalov was promoted to the rank of '' duma dyak'' (the lowest rank in the Boyar Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrey Vasilyev (diplomat)
Andrey Aleksandrovich Vasilyev (russian: Андрей Васильев; born 27 June 1962) is a Soviet rower. References * * 1962 births Living people Russian male rowers Soviet male rowers Rowers at the 1988 Summer Olympics Olympic silver medalists for the Soviet Union Olympic rowers of the Soviet Union Olympic medalists in rowing World Rowing Championships medalists for the Soviet Union Medalists at the 1988 Summer Olympics {{Russia-rowing-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |