|
Ruslan And Ludmila (poem)
''Ruslan and Ludmila'' ( pre-reform Russian: ; post-reform rus, Русла́н и Людми́ла, Ruslán i Lyudmíla) is a poem by Alexander Pushkin, published in 1820. It is written as an epic fairy tale consisting of a dedication (посвящение), six "cantos" ( песни), and an epilogue ( эпилог). It tells the story of the abduction of Ludmila, the daughter of Prince Vladimir of the Kievan Rus' (reigned 980–1015), by an evil wizard and the attempt by the brave knight Ruslan to find and rescue her. Origin Pushkin began writing the poem in 1817, while attending the Imperial Lyceum at Tsarskoye Selo. He based it on Russian folktales he had heard as a child. Before it was published in 1820, Pushkin was exiled to the south of Russia for political ideas he had expressed in other works such as his ode to " Freedom" (вольность). A slightly revised edition was published in 1828. Synopsis Dedication Pushkin dedicates the poem to unnamed young ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reforms Of Russian Orthography
The Russian orthography has been reformed officially and unofficially by changing the Russian alphabet over the course of the history of the Russian language. Several important reforms happened in the 18th–20th centuries. Early changes Old East Slavic adopted the Cyrillic script, approximately during the 10th century and at about the same time as the introduction of Eastern Christianity into the territories inhabited by the Eastern Slavs. No distinction was drawn between the vernacular language and the liturgical, though the latter was based on South Slavic languages, South Slavic rather than East Slavic languages, Eastern Slavic norms. As the language evolved, several letters, notably the ''yuses'' (Ѫ, Ѭ, Ѧ, Ѩ) were gradually and unsystematically discarded from both secular and church usage over the next centuries. The emergence of the centralized Russian state in the 15th and 16th centuries, the consequent rise of the state bureaucracy along with the development of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prologue
A prologue or prolog (from Greek πρόλογος ''prólogos'', from πρό ''pró'', "before" and λόγος ''lógos'', "word") is an opening to a story that establishes the context and gives background details, often some earlier story that ties into the main one, and other miscellaneous information. The Ancient Greek ''prólogos'' included the modern meaning of ''prologue'', but was of wider significance, more like the meaning of preface. The importance, therefore, of the prologue in Greek drama was very great; it sometimes almost took the place of a romance, to which, or to an episode in which, the play itself succeeded. Latin On the Latin stage the prologue was often more elaborate than it was in Athens, and in the careful composition of the poems which Plautus prefixes to his plays we see what importance he gave to this portion of the entertainment; sometimes, as in the preface to the ''Rudens'', Plautus rises to the height of his genius in his adroit and romantic prolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annulment
Annulment is a legal procedure within Law, secular and Religious law, religious legal systems for declaring a marriage Void (law), null and void. Unlike divorce, it is usually ex post facto law, retroactive, meaning that an annulled marriage is considered to be invalid from the beginning almost as if it had never taken place (though some jurisdictions provide that the marriage is only void from the date of the annulment; for example, this is the case in section 12 of the Matrimonial Causes Act 1973 in England and Wales). In legal terminology, an annulment makes a void marriage or a voidable marriage null.John L. Esposito (2002), Women in Muslim Family Law, Syracuse University Press, , pp. 33–34 Void vs voidable marriage A difference exists between a ''void marriage'' and a ''voidable marriage''. A void marriage is a marriage that was not legally valid under the laws of the jurisdiction where the marriage occurred, and is void (law), void ''ab initio''. Although the marriage i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
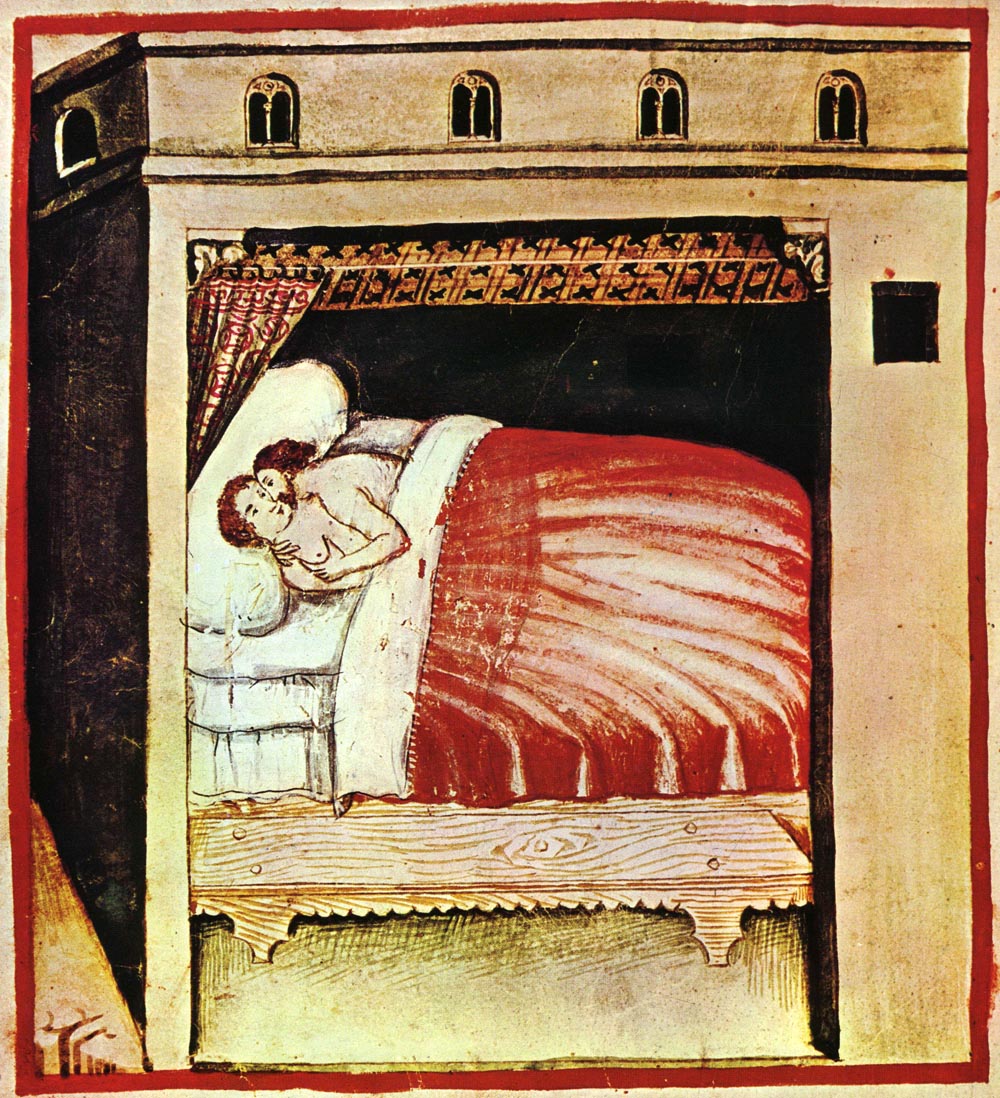
Consummate
In many traditions and statutes of civil or religious law, the consummation of a marriage, often called simply ''consummation'', is the first (or first officially credited) act of sexual intercourse between two people, following their marriage to each other. The definition of consummation usually refers to penile-vaginal sexual penetration, but some religious doctrines hold that there is an additional requirement that no contraception must be used. The religious, cultural, or legal significance of consummation may arise from theories of marriage as having the purpose of producing legally recognized descendants of the partners, or of providing sanction to their sexual acts together, or both, and its absence may amount to treating a marriage ''ceremony'' as falling short of ''completing'' the state of being married, or as creating a marriage which may later be repudiated. Thus in some legal systems a marriage may be annulled if it has not been consummated. Consummation is also relev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khan (title)
Khan ''khan/qan''; tr, han; Azerbaijani: ''xan''; Ottoman: ''han''; Old Turkic: ''kan''; Chinese: 汗 ''hán''; Goguryeo: 皆 ''key''; Buyeo: 加 ''ka''; Silla: 干 ''kan''; Gaya: 旱 ''kan''; Baekje: 瑕 ''ke''; Manchu: ; Persian: خان; Punjabi: ਖ਼ਾਨ; Hindustani: ख़ान or ख़ां (Devanagari), or (Nastaleeq); Balochi: خان; Bulgarian: хан, ''khan''; Chuvash: хун, ''hun''; Arabic: خان; bn, খান or ) () is a historic Turko-Mongol title originating among nomadic tribes in the Central and Eastern Eurasian Steppe to refer to a chief or ruler. It first appears among the Rouran and then the Göktürks as a variant of khagan (sovereign, emperor) and implied a subordinate ruler. In the Seljuk Empire, it was the highest noble title, ranking above malik (king) and emir (prince). In the Mongol Empire it signified the ruler of a horde (''ulus''), while the ruler of all the Mongols was the khagan or great khan. The title subsequently de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khazar
The Khazars ; he, כּוּזָרִים, Kūzārīm; la, Gazari, or ; zh, 突厥曷薩 ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a semi-nomadic Turkic people that in the late 6th-century CE established a major commercial empire covering the southeastern section of modern European Russia, southern Ukraine, Crimea, and Kazakhstan. They created what for its duration was the most powerful polity to emerge from the break-up of the Western Turkic Khaganate. Astride a major artery of commerce between Eastern Europe and Western Asia, Southwestern Asia, Khazaria became one of the foremost trading empires of the Early Middle Ages, early medieval world, commanding the western March (territory), marches of the Silk Road and playing a key commercial role as a crossroad between China, the Middle East and Kievan Rus'. For some three centuries (c. 650–965) the Khazars dominated the vast area extending from the Volga-Don steppes to the eastern Crimea and the northern Caucasus. Khazari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warrior
A warrior is a person specializing in combat or warfare, especially within the context of a tribal or clan-based warrior culture society that recognizes a separate warrior aristocracies, class, or caste. History Warriors seem to have been present in the earliest pre-state societies. Scholars have argued that horse-riding Yamnaya warriors from the Pontic–Caspian steppe played a key role during the Indo-European migrations and the diffusion of Indo-European languages across Eurasia. Most of the basic weapons used by warriors appeared before the rise of most hierarchical systems. Bows and arrows, clubs, spears, swords, and other edged weapons were in widespread use. However, with the new findings of metallurgy, the aforementioned weapons had grown in effectiveness. When the first hierarchical systems evolved 5000 years ago, the gap between the rulers and the ruled had increased. Making war to extend the outreach of their territories, rulers often forced men from lower orders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Tale Of Tsar Saltan
The Tale of Tsar Saltan, of His Son the Renowned and Mighty Bogatyr Prince Gvidon Saltanovich, and of the Beautiful Princess-Swan ( rus, «Сказка о царе Салтане, о сыне его славном и могучем богатыре князе Гвидоне Салтановиче и о прекрасной царевне Лебеди», Skazka o tsare Saltane, o syne yevo slavnom i moguchem bogatyre knyaze Gvidone Saltanoviche i o prekrasnoy tsarevne Lebedi ) is an 1831 fairy tale in verse by Alexander Pushkin. As a folk tale it is classified as Aarne–Thompson type 707, " The Three Golden Children", for it being a variation of The Dancing Water, the Singing Apple, and the Speaking Bird. Synopsis The story is about three sisters. The youngest is chosen by Tsar Saltan (Saltán) to be his wife. He orders the other two sisters to be his royal cook and weaver. They become jealous of their younger sister. When the tsar goes off to war, the tsaritsa gives birth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koschei
Koschei ( rus, Коще́й, r=Koshchey, p=kɐˈɕːej), often given the epithet "the Immortal", or "the Deathless" (russian: Коще́й Бессме́ртный), is an archetypal male antagonist in Russian folklore. The most common feature of tales involving Koschei is a spell which prevents him from being killed. He hides his soul inside nested objects to protect it. For example, the soul (or in the tales, it is usually called "death") may be hidden in a needle that is hidden inside an egg, the egg is in a duck, the duck is in a hare, the hare is in a chest, the chest is buried or chained up on a far island. Usually he takes the role of a malevolent rival father figure, who competes for (or entraps) a male hero's love interest. The origin of the tales is unknown. The archetype may contain elements derived from the 12th-century pagan Cuman-Kipchak (Polovtsian) leader Khan Konchak, who is recorded in ''The Tale of Igor's Campaign''; over time a balanced view of the non-Christi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

%2C_page_5.gif)