|
Runways
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt, concrete, or a mixture of both) or a natural surface (grass, dirt, gravel, ice, sand or salt). Runways, as well as taxiways and ramps, are sometimes referred to as "tarmac", though very few runways are built using tarmac. Takeoff and landing areas defined on the surface of water for seaplanes are generally referred to as waterways. Runway lengths are now commonly given in meters worldwide, except in North America where feet are commonly used. History In 1916, in a World War I war effort context, the first concrete-paved runway was built in Clermont-Ferrand in France, allowing local company Michelin to manufacture Bréguet Aviation military aircraft. In January 1919, aviation pioneer Orville Wright underlined the need for "distinctly marked and car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runway 34, Nagoya Airfield (3937428018)
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt, concrete, or a mixture of both) or a natural surface (grass, dirt, gravel, ice, sand or salt). Runways, as well as taxiways and ramps, are sometimes referred to as "tarmac", though very few runways are built using tarmac. Takeoff and landing areas defined on the surface of water for seaplanes are generally referred to as waterways. Runway lengths are now commonly given in meters worldwide, except in North America where feet are commonly used. History In 1916, in a World War I war effort context, the first concrete-paved runway was built in Clermont-Ferrand in France, allowing local company Michelin to manufacture Bréguet Aviation military aircraft. In January 1919, aviation pioneer Orville Wright underlined the need for "distinctly marked and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
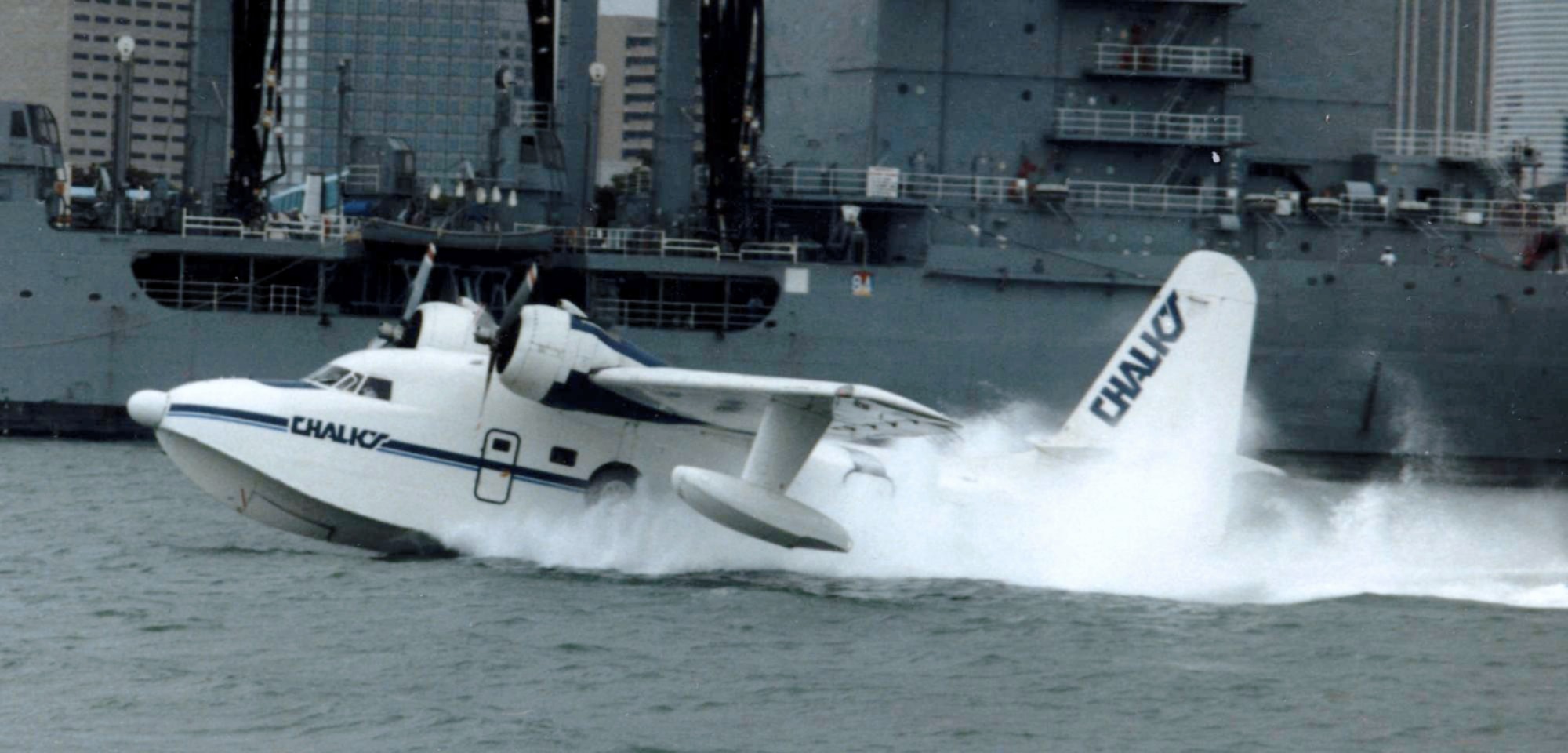
Seaplane
A seaplane is a powered fixed-wing aircraft capable of takeoff, taking off and water landing, landing (alighting) on water.Gunston, "The Cambridge Aerospace Dictionary", 2009. Seaplanes are usually divided into two categories based on their technological characteristics: floatplanes and flying boats; the latter are generally far larger and can carry far more. Seaplanes that can also take off and land on airfields are in a subclass called amphibious aircraft, or amphibians. Seaplanes were sometimes called ''hydroplanes'', but currently this term applies instead to Hydroplane (boat), motor-powered watercraft that use the technique of Planing (boat), hydrodynamic lift to skim the surface of water when running at speed. The use of seaplanes gradually tapered off after World War II, partially because of the investments in airports during the war but mainly because landplanes were less constrained by weather conditions that could result in sea states being too high to operate seaplan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerodrome
An aerodrome (Commonwealth English) or airdrome (American English) is a location from which aircraft flight operations take place, regardless of whether they involve air cargo, passengers, or neither, and regardless of whether it is for public or private use. Aerodromes include small general aviation airfields, large commercial airports, and military air bases. The term ''airport'' may imply a certain stature (having satisfied certain certification criteria or regulatory requirements) that not all aerodromes may have achieved. That means that all airports are aerodromes, but not all aerodromes are airports. Usage of the term "aerodrome" remains more common in Ireland and Commonwealth nations, and is conversely almost unknown in American English, where the term "airport" is applied almost exclusively. A water aerodrome is an area of open water used regularly by seaplanes, floatplanes or amphibious aircraft for landing and taking off. In formal terminology, as defined by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxiway
A taxiway is a path for aircraft at an airport connecting runways with aprons, hangars, terminals and other facilities. They mostly have a hard surface such as asphalt or concrete, although smaller general aviation airports sometimes use gravel or grass. Most airports do not have a specific speed limit for taxiing (though some do). There is a general rule on safe speed based on obstacles. Operators and aircraft manufacturers might have limits. Typical taxi speeds are 20–30 knots (37–56 km/h; 23–35 mph). High-speed exit Busy airports typically construct high-speed or rapid-exit taxiways to allow aircraft to leave the runway at higher speeds. This allows the aircraft to vacate the runway quicker, permitting another to land or take off in a shorter interval of time. This is accomplished by reducing the angle the exiting taxiway intercepts the runway at to 30 degrees, instead of 90 degrees, thus increasing the speed at which the aircraft can exit the runway onto the taxiway. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Lulsgate Bottom
Bristol Airport , at Lulsgate Plateau, Lulsgate Bottom, on the northern slopes of the Mendip Hills, in North Somerset, is the commercial airport serving the city of Bristol, England, and the surrounding area. It is southwest of Bristol city centre. Built on the site of a former RAF airfield, it opened in 1957 as Bristol (Lulsgate) Airport, replacing Bristol (Whitchurch) Airport as Bristol's municipal airport. From 1997 to 2010, it was known as Bristol International Airport. In 1997, a majority shareholding in the airport was sold to FirstGroup, and then in 2001 the airport was sold to a joint venture of Macquarie Group, Macquarie Bank and others. In September 2014, Ontario Teachers' Pension Plan bought out Macquarie to become the sole owner. In 2019, it was ranked the eighth List of busiest airports in the United Kingdom, busiest airport (overtaking Glasgow Airport from the previous year) in the United Kingdom, handling over 8.9 million passengers, a 3% increase compared with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
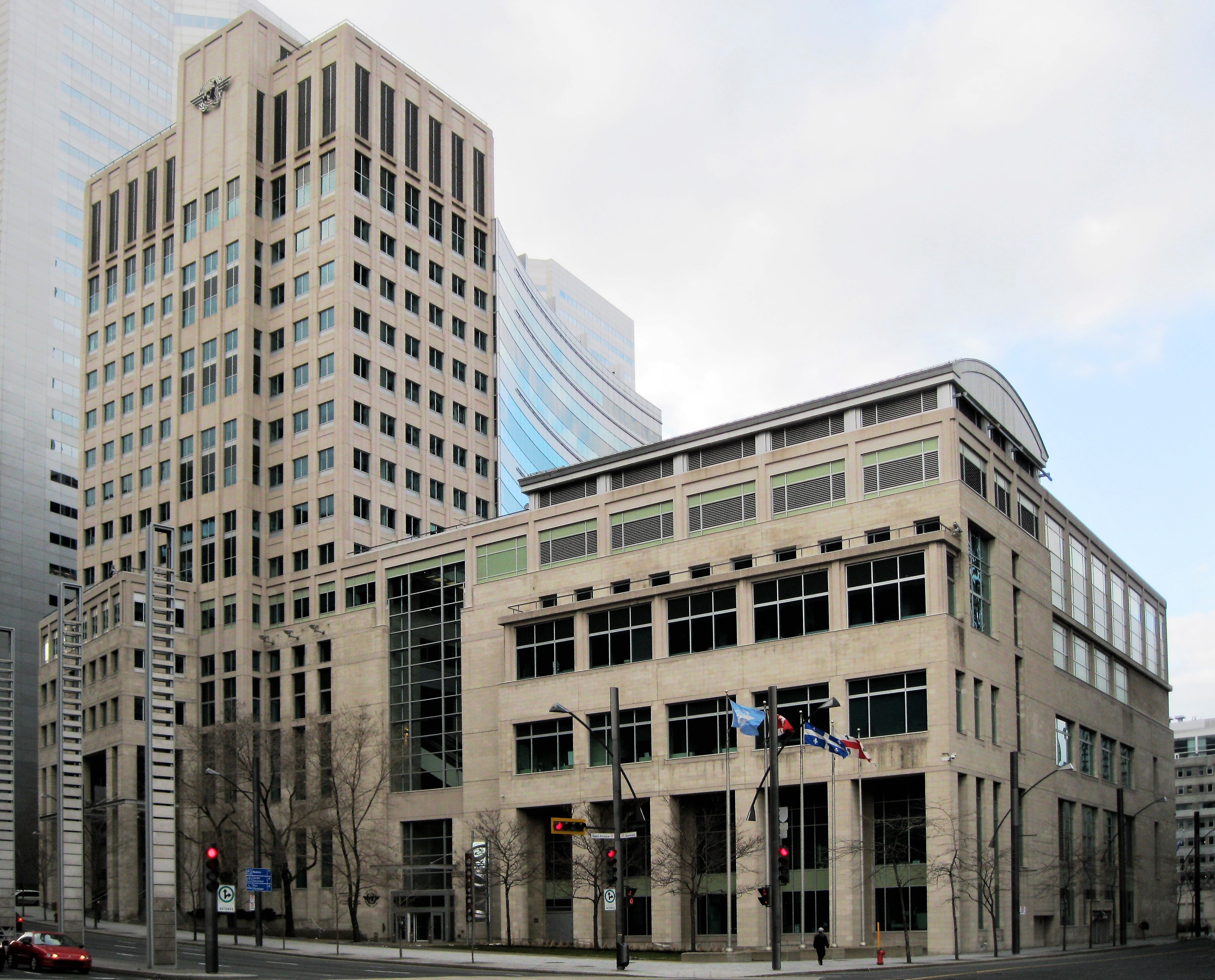
International Civil Aviation Organization
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO, ) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that coordinates the principles and techniques of international air navigation, and fosters the planning and development of international scheduled air transport, air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth. ICAO headquarters are located in the ''Quartier international de Montréal, Quartier International'' of Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The ICAO Council adopts standards and recommended practices concerning air navigation, its infrastructure, flight inspection, prevention of unlawful interference, and facilitation of border-crossing procedures for international civil aviation. ICAO defines the protocols for Aviation accidents and incidents, air accident investigation that are followed by :Organizations investigating aviation accidents and incidents, transport safety authorities in countries signatory to the Chicago Convention on International Civil Aviation. The Air Navigat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Airport
Bristol Airport , at Lulsgate Bottom, on the northern slopes of the Mendip Hills, in North Somerset, is the commercial airport serving the city of Bristol, England, and the surrounding area. It is southwest of Bristol city centre. Built on the site of a former RAF airfield, it opened in 1957 as Bristol (Lulsgate) Airport, replacing Bristol (Whitchurch) Airport as Bristol's municipal airport. From 1997 to 2010, it was known as Bristol International Airport. In 1997, a majority shareholding in the airport was sold to FirstGroup, and then in 2001 the airport was sold to a joint venture of Macquarie Bank and others. In September 2014, Ontario Teachers' Pension Plan bought out Macquarie to become the sole owner. In 2019, it was ranked the eighth busiest airport (overtaking Glasgow Airport from the previous year) in the United Kingdom, handling over 8.9 million passengers, a 3% increase compared with 2018. A passenger survey carried out in 2015 found that 32.5% of journeys using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airspeed
In aviation, airspeed is the speed of an aircraft relative to the air. Among the common conventions for qualifying airspeed are: * Indicated airspeed ("IAS"), what is read on an airspeed gauge connected to a Pitot-static system; * Calibrated airspeed ("CAS"), indicated airspeed adjusted for pitot system position and installation error; * Equivalent airspeed ("EAS"), calibrated airspeed adjusted for compressibility effects; * True airspeed ("TAS"), equivalent airspeed adjusted for air density, and is also the speed of the aircraft through the air in which it is flying. Calibrated airspeed is typically within a few knots of indicated airspeed, while equivalent airspeed decreases slightly from CAS as aircraft altitude increases or at high speeds. With EAS constant, true airspeed increases as aircraft altitude increases. This is because air density decreases with higher altitude. The measurement and indication of airspeed is ordinarily accomplished on board an aircraft by an air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Lake , a 1990 film
{{Disambiguation ...
Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake is a United States military facility in California. China Lake may also refer to: Places in the United States *China Lake, Kern County, California, an unincorporated community named for a nearby dry lake *China Lake Acres, California, a census-designated place (CDP) * China Lake (Maine), a pond in Kennebec County Other uses * ''China Lake'' (film), a 1983 thriller film * China Lake Grenade Launcher, developed at the military facility *''China Lake'', a 1992 novel by Anthony Hyde * The China Lake Murders ''The China Lake Murders'' is a 1990 television film starring Tom Skerritt. It is about a small desert town that experiences a series of murders. The film was rated PG-13 and first aired on the USA Network and for many years held the record for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Direction
Wind direction is generally reported by the direction from which it originates. For example, a ''north'' or ''northerly'' wind blows from the north to the south. The exceptions are onshore winds (blowing onto the shore from the water) and offshore winds (blowing off the shore to the water). Wind direction is usually reported in cardinal (or compass) direction, or in degrees. Consequently, a wind blowing from the north has a wind direction referred to as 0° (360°); a wind blowing from the east has a wind direction referred to as 90°, etc. Weather forecasts typically give the direction of the wind along with its speed, for example a "northerly wind at 15 km/h" is a wind blowing ''from'' the north at a speed of 15 km/h. Measurement techniques A variety of instruments can be used to measure wind direction, such as the windsock and wind vane. Both of these instruments work by moving to minimize air resistance. The way a weather vane is pointed by prevailing winds indicates the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
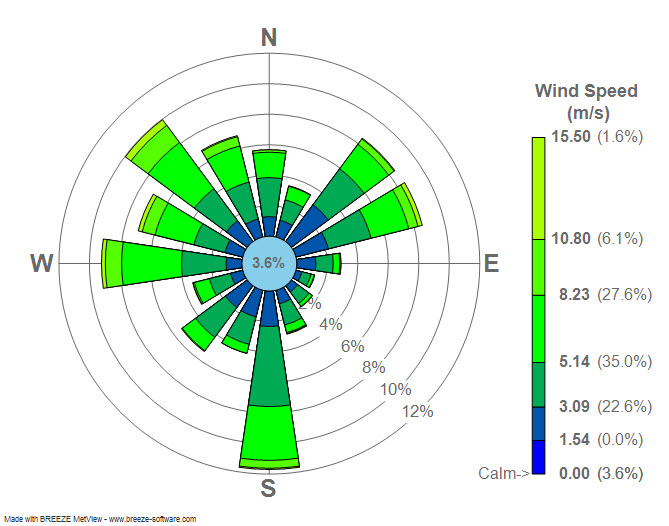
Wind Rose
A wind rose is a graphic tool used by meteorologists to give a succinct view of how wind speed and direction are typically distributed at a particular location. Historically, wind roses were predecessors of the compass rose (found on charts), as there was no differentiation between a cardinal direction and the wind which blew from such a direction. Using a polar coordinate system of gridding, the frequency of winds over a time period is plotted by wind direction, with colour bands showing wind speed ranges. The direction of the longest spoke shows the wind direction with the greatest frequency. History Before the development of the compass rose, a wind rose was included on maps in order to let the reader know which directions the 8 major winds (and sometimes 8 half-winds and 16 quarter-winds) blew within the plan view. No differentiation was made between cardinal directions and the winds which blew from those directions. North was depicted with a fleur de lis, while east w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prevailing Winds
In meteorology, prevailing wind in a region of the Earth's surface is a surface wind that blows predominantly from a particular direction. The dominant winds are the trends in direction of wind with the highest speed over a particular point on the Earth's surface at any given time. A region's prevailing and dominant winds are the result of global patterns of movement in the Earth's atmosphere. In general, winds are predominantly easterly at low latitudes globally. In the mid-latitudes, westerly winds are dominant, and their strength is largely determined by the polar cyclone. In areas where winds tend to be light, the sea breeze/land breeze cycle is the most important cause of the prevailing wind; in areas which have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes dominate the wind pattern. Highly elevated surfaces can induce a thermal low, which then augments the environmental wind flow. Wind roses are tools used to display the direction of the prevailing wind. Knowledge of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)