|
Rotorua Caldera
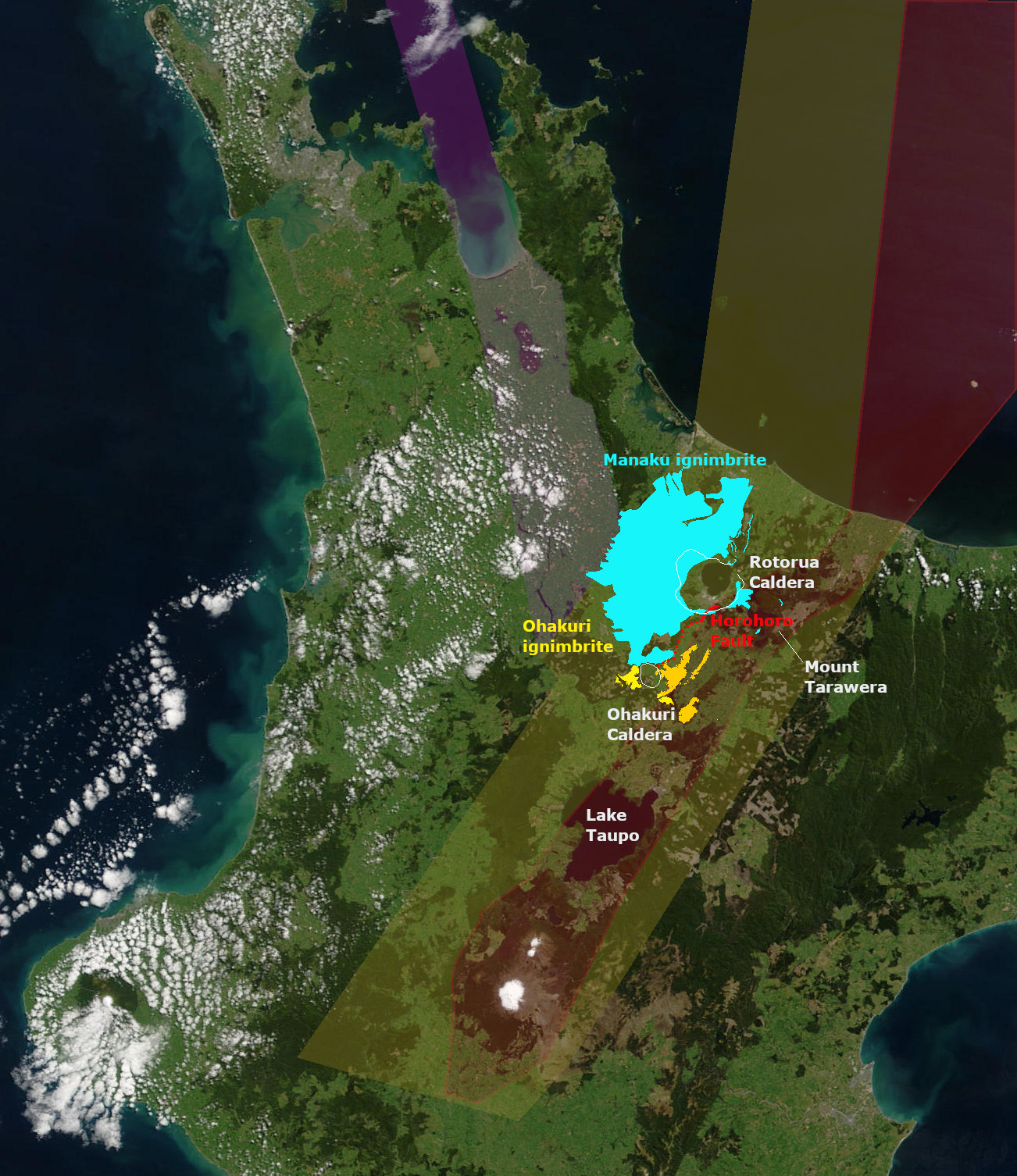
The Rotorua Caldera, now in filled with Lake Rotorua, is a large rhyolitic caldera. It is one of several large volcanoes located in the Taupō Volcanic Zone on the North Island of New Zealand. Geography The major regional settlement of Rotorua is located in the caldera. There is geothermal activity in the city of Rotorua and the geothermal areas of Tikitere and Whakarewarewa are associated with the caldera. These areas are still associated with small hydrothermal eruptions. Geology Eruption history The caldera was formed in a single event paired List of large volcanic eruptions, major eruption, that lasted only weeks, is now dated about 240,000 years ago, and which ejected more than of rhyolitic Mamaku ignimbrite giving it a Volcanic Explosivity Index of 7. The eruption has been reinterpreted as a paired eruption with a very slightly later, slightly smaller southerly eruption from the same mush body feeding the Ohakuri Caldera. Ignimbrite, up to thick covering about , was depo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotorua
Rotorua () is a city in the Bay of Plenty region of New Zealand's North Island. The city lies on the southern shores of Lake Rotorua, from which it takes its name. It is the seat of the Rotorua Lakes District, a territorial authority encompassing Rotorua and several other nearby towns. Rotorua has an estimated resident population of , making it the country's 12th largest urban area, and the Bay of Plenty's second largest urban area behind Tauranga. Rotorua is a major destination for both domestic and international tourists; the tourism industry is by far the largest industry in the district. It is known for its geothermal activity, and features geysers – notably the Pōhutu Geyser at Whakarewarewa – and hot mud pools. This thermal activity is sourced to the Rotorua Caldera, in which the town lies. Rotorua is home to the Toi Ohomai Institute of Technology. History The name Rotorua comes from the Māori language, where the full name for the city and lake is . ''Roto'' m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Large Volcanic Eruptions
This is a sortable summary of the pages Timeline of volcanism on Earth, List of Quaternary volcanic eruptions, and Large volume volcanic eruptions in the Basin and Range Province. Uncertainties as to dates and tephra volumes are not restated, and references are not repeated. Volcanic explosivity index (VEI) values for events in the Miocene epoch sometimes lack references. They are given as VEI-equivalent, as an estimate of the erupted tephra volume. This is not a comprehensive list. List References Bibliography * ** Supplementary Table I: ** Supplementary Table II: * Further reading * *Volcano Global Risk Identification and Analysis Project Website * {{List of volcanoes Volcanic eruptions Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra (ash, lapilli, volcanic bombs and volcanic blocks), and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often ... Lists of volcanic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohakuri
Ohakuri is a rural community in the Taupō District and Waikato region of New Zealand's North Island. It features the Orakei Korako Geothermal Area, the artificial Lake Ohakuri and the Ohakuri Dam. The area also includes Maroanui Marae, a meeting place of the local Ngāti Tūwharetoa hapū of Ngāti Hinerau. It features a meeting house of the same name. The marae was renovated between 2008 and 2010, with a grant from the nearby Wairakei Power Station. The renovations included wheelchair ramps and accessible toilets for disabled members of the hapū. Demographics Ohakuri statistical area, which also includes Ātiamuri and Oruanui, covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. Ohakuri statistical area had a population of 1,842 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 171 people (10.2%) since the 2013 census, and an increase of 408 people (28.5%) since the 2006 census. There were 654 households, comprising 963 males an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andesite
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predominantly of sodium-rich plagioclase plus pyroxene or hornblende. Andesite is the extrusive equivalent of plutonic diorite. Characteristic of subduction zones, andesite represents the dominant rock type in island arcs. The average composition of the continental crust is andesitic. Along with basalts, andesites are a component of the Martian crust. The name ''andesite'' is derived from the Andes mountain range, where this rock type is found in abundance. It was first applied by Christian Leopold von Buch in 1826. Description Andesite is an aphanitic (fine-grained) igneous rock that is intermediate in its content of silica and low in alkali metals. It has less than 20% quartz and 10% feldspathoid by volume, with at least 65% of the fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial planet, rocky planet or natural satellite, moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt is chemically equivalent to slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro. The eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20 volcanoes per year. Basalt is also an important rock type on other planetary bodies in the Solar System. For example, the bulk of the plains of volcanism on Venus, Venus, which cover ~80% of the surface, are basaltic; the lunar mare, lunar maria are plains of flood-basaltic lava flows; and basalt is a common rock on the surface of Mars. Molten basalt lava has a low viscosity due to its relatively low silica content (between 45% and 52%), resulting in rapidly moving lava flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eruption
Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra (ash, lapilli, volcanic bombs and volcanic blocks), and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often named after famous volcanoes where that type of behavior has been observed. Some volcanoes may exhibit only one characteristic type of eruption during a period of activity, while others may display an entire sequence of types all in one eruptive series. There are three different types of eruptions: * Magmatic eruptions are the most well-observed type of eruption. They involve the decompression of gas within magma that propels it forward. * Phreatic eruptions are driven by the superheating of steam due to the close proximity of magma. This type exhibits no magmatic release, instead causing the granulation of existing rock. * Phreatomagmatic eruptions are driven by the direct interaction of magma and water, as opposed to phreatic erupti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The mineral assemblage is predominantly quartz, sanidine, and plagioclase. It is the extrusive equivalent to granite. Rhyolitic magma is extremely viscous, due to its high silica content. This favors explosive eruptions over effusive eruptions, so this type of magma is more often erupted as pyroclastic rock than as lava flows. Rhyolitic ash-flow tuffs are among the most voluminous of continental igneous rock formations. Rhyolitic tuff has been extensively used for construction. Obsidian, which is rhyolitic volcanic glass, has been used for tools from prehistoric times to the present day because it can be shaped to an extremely sharp edge. Rhyolitic pumice finds use as an abrasive, in concrete, and as a soil amendment. Description Rhyolite i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mokoia Island
__NOTOC__ Mokoia Island is located in Lake Rotorua in New Zealand. It has an area of 1.35 square kilometres. The uninhabited island is a rhyolite lava dome, rising to 180 metres above the lake surface. It was formed after the Rotorua caldera collapsed and rhyolitic magma was pushed through the cracks. One of the cracks was below where Mokoia island is today. The foreshores of the island have geothermal springs with hot spring water forming the Hinemoa pool, known to locals as Waikimihia. It also has very rich volcanic soil, which was why the local Māori grew kūmara on it. The stone statue of Matuatonga on the island protected the island's kūmara crop, and tohunga would bring seed kūmara to touch the statue. It was also a very good strategic location, which was why it was often fought over. Mokoia Island is privately owned by local Māori iwi, who run it in conjunction with the New Zealand Department of Conservation. It is a bird sanctuary and access is limited to tour part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magma Chamber
A magma chamber is a large pool of liquid rock beneath the surface of the Earth. The molten rock, or magma, in such a chamber is less dense than the surrounding country rock, which produces buoyant forces on the magma that tend to drive it upwards. If the magma finds a path to the surface, then the result will be a volcanic eruption; consequently, many volcanoes are situated over magma chambers. These chambers are hard to detect deep within the Earth, and therefore most of those known are close to the surface, commonly between 1 km and 10 km down. Dynamics of magma chambers Magma rises through cracks from beneath and across the crust because it is less dense than the surrounding rock. When the magma cannot find a path upwards it pools into a magma chamber. These chambers are commonly built up over time, by successive horizontal or vertical magma injections. Influx of new magma causes reaction of pre-existing crystals and the pressure in the chamber to increase. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dense-rock Equivalent
Dense-rock equivalent (DRE) is a volcanologic calculation used to estimate volcanic eruption volume. One of the widely accepted measures of the size of a historic or prehistoric eruption is the volume of magma ejected as pumice and volcanic ash, known as tephra during an explosive phase of the eruption, or the volume of lava extruded during an effusive phase of a volcanic eruption. Eruption volumes are commonly expressed in cubic kilometers (km3). Historical and geological estimates of tephra volumes are usually obtained by mapping the distribution and thickness of tephra deposits on the ground after the eruption is over. For historical volcanic explosions, further estimates must be made of tephra deposits that might have changed significantly over time by other geological processes including erosion. Tephra volumes measured in this way must then be corrected for void spaces ( vesicles – bubbles within the pumice, empty spaces between individual pieces of pumice or ash) to get ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyroclastic Flow
A pyroclastic flow (also known as a pyroclastic density current or a pyroclastic cloud) is a fast-moving current of hot gas and volcanic matter (collectively known as tephra) that flows along the ground away from a volcano at average speeds of but is capable of reaching speeds up to . The gases and tephra can reach temperatures of about . Pyroclastic flows are the most deadly of all volcanic hazards and are produced as a result of certain explosive eruptions; they normally touch the ground and hurtle downhill, or spread laterally under gravity. Their speed depends upon the density of the current, the volcanic output rate, and the gradient of the slope. Origin of term The word ''pyroclast'' is derived from the Greek (''pýr''), meaning "fire", and (''klastós''), meaning "broken in pieces". A name for pyroclastic flows which glow red in the dark is (French, "burning cloud"); this was notably used to describe the disastrous 1902 eruption of Mount Pelée on Martinique, a French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |