|
Roma Minority Of Hungary
Romani people in Hungary (also known as roma or Romani Hungarians; hu, magyarországi romák, magyar cigányok) are Hungarian citizens of Romani descent. According to the 2011 census, they comprise 3.18% of the total population, which alone makes them the largest minority in the country, although various estimations have put the number of Romani people as high as 8% of the total population. They are sometimes referred as Hungarian Gypsies, but that is considered to be a racial slur. History and language Origin The Romani people in Hungary originate from East India, from the northwestern Indian regions of Rajasthan and Punjab The linguistic evidence has indisputably shown that roots of Romani language lie in India: the language has grammatical characteristics of Indo-Aryan languages and shares with them a big part of the basic lexicon, for example, body parts or daily routines. More exactly, Romani shares the basic lexicon with Hindi and Punjabi. It shares many phonetic fea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Aryan Languages
The Indo-Aryan languages (or sometimes Indic languages) are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. As of the early 21st century, they have more than 800 million speakers, primarily concentrated in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Maldives. Moreover, apart from the Indian subcontinent, large immigrant and expatriate Indo-Aryan–speaking communities live in Northwestern Europe, Western Asia, North America, the Caribbean, Southeast Africa, Polynesia and Australia, along with several million speakers of Romani languages primarily concentrated in Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. There are over 200 known Indo-Aryan languages. Modern Indo-Aryan languages descend from Old Indo-Aryan languages such as early Vedic Sanskrit, through Middle Indo-Aryan languages (or Prakrits). The largest such languages in terms of First language, first-speakers are Hindustani language, Hindi–Urdu (),Standard Hindi firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen I at Esztergom around the year 1000;Kristó Gyula – Barta János – Gergely Jenő: Magyarország története előidőktől 2000-ig (History of Hungary from the prehistory to 2000), Pannonica Kiadó, Budapest, 2002, , p. 687, pp. 37, pp. 113 ("Magyarország a 12. század második felére jelentős európai tényezővé, középhatalommá vált."/"By the 12th century Hungary became an important European factor, became a middle power.", "A Nyugat részévé vált Magyarország.../Hungary became part of the West"), pp. 616–644 his family (the Árpád dynasty) led the monarchy for 300 years. By the 12th century, the kingdom became a European middle power within the Western world. Due to the Ottoman occupation of the central and south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Turkic Language
Old Turkic (also East Old Turkic, Orkhon Turkic language, Old Uyghur) is the earliest attested form of the Turkic languages, found in Göktürk and Uyghur Khaganate inscriptions dating from about the eighth to the 13th century. It is the oldest attested member of the Siberian Turkic branch of Turkic, which is extant in the modern Western Yugur language. It is not the ancestor of the Uyghur language; the contemporaneous ancestor of Uyghur is called Middle Turkic, later Chagatai or Turki. Old Turkic is attested in a number of scripts, including the Old Turkic script, the Old Uyghur alphabet (a form of the Sogdian alphabet), the Brahmi script, and the Manichaean script. Old Turkic often refers not to a single language, but collectively to the closely related and mutually intelligible stages of various Common Turkic languages spoken during the late first millennium. Sources The sources of Old Turkic are divided into two corpora: *the 8th to 10th century Orkhon inscription ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Diaspora
Overseas Indians (IAST: ), officially Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) and Overseas Citizens of India (OCIs) are Indians who live outside of the Republic of India. According to the Government of India, ''Non-Resident Indians'' are citizens of India who are not living in the country, while the term ''People of Indian Origin'' are people of Indian birth or ancestry who are not citizens of India, but are citizens of other nations and may additionally have Overseas Citizenship of India (OCI), with those having the OCI status known as ''Overseas Citizens of India''. According to a Ministry of External Affairs report, there are 32 million NRIs and OCIs residing outside India and overseas Indians comprise the world's largest overseas diaspora. Every year 2.5 million (25 lakhs) Indians migrate overseas, which is the highest annual number of migrants in the world. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of India
The Government of India (ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, consisting of 28 union states and eight union territories. Under the Constitution, there are three primary branches of government: the legislative, the executive and the judiciary, whose powers are vested in a bicameral Parliament, President, aided by the Council of Ministers, and the Supreme Court respectively. Through judicial evolution, the Parliament has lost its sovereignty as its amendments to the Constitution are subject to judicial intervention. Judicial appointments in India are unique in that the executive or legislature have negligible say. Etymology and history The Government of India Act 1833, passed by the British parliament, is the first such act of law with the epithet "Government of India". Basic structure The gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minister Of External Affairs (India)
The Minister of External Affairs (or simply, the Foreign Minister, in Hindi ''Videsh Mantri'' ) is the head of the Ministry of External Affairs of the Government of India. One of the senior-most offices in the Union Cabinet, the chief responsibility of the Foreign Minister is to represent India and its government in the international community. The Foreign Minister also plays an important role in determining Indian foreign policy. Occasionally, the Foreign Minister is assisted by a Minister of State for External Affairs or the lower-ranked Deputy Minister of External Affairs. India's first Prime Minister, Jawaharlal Nehru, also held the Foreign Minister post throughout his 17-year premiership of the country; he remains the country's longest-serving Foreign Minister. Several other Prime Ministers have since held the additional charge of foreign minister, but never has any other cabinet minister held additional charge of the office. There have been a number of Foreign Ministers wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ḍoma
The Dom (Sanskrit ''ḍoma'', dialectally also Domra, Domba, Domaka, Dombari and variants) are castes, or groups, scattered across India. Dom were a caste of drummer. According to Tantra scriptures, the Dom were engaged in the occupations of singing and playing music. Historically, they were considered an untouchable caste and their traditional occupation was the disposal and cremation of dead bodies. They are in the list of Scheduled caste for Reservation in India in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Odisha and West Bengal. Etymology According to Tantra scriptures, individuals who live by singing and music were mention as Dom. According to historian M.P Joshi, the word Duma is connected to the sound of a drum. Its presumed root, ''ḍom'', which is connected with drumming, is linked to ''damara'' and ''damaru'', Sanskrit terms for "drum" and the Sanskrit verbal root डम् ''ḍam-'' 'to sound (as a drum)', perhaps a loan from Dravidian, e.g. Kannada ''ḍamāra' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
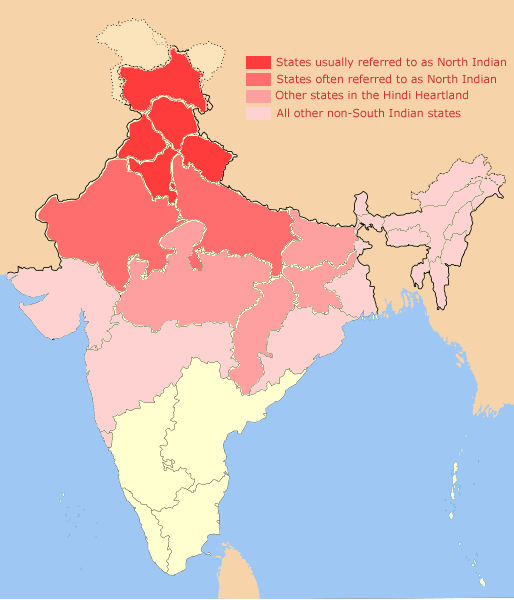
North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central Asia. The term North India has varying definitions. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Northern Zonal Council Administrative division included the states of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Rajasthan and Union Territories of Chandigarh, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. The Ministry of Culture in its ''North Culture Zone'' includes the state of Uttarakhand but excludes Delhi whereas the Geological Survey of India includes Uttar Pradesh and Delhi but excludes Rajasthan and Chandigarh. Other states sometimes included are Bihar, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal. North India has been the historical centre of the Mughal Empire, the Delhi Sultanate and the British Indian Empire. It has a diverse culture, and includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengali Language
Bengali ( ), generally known by its endonym Bangla (, ), is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language native to the Bengal region of South Asia. It is the official, national, and most widely spoken language of Bangladesh and the second most widely spoken of the 22 scheduled languages of India. With approximately 300 million native speakers and another 37 million as second language speakers, Bengali is the List of languages by number of native speakers, fifth most-spoken native language and the List of languages by total number of speakers, seventh most spoken language by total number of speakers in the world. Bengali is the fifth most spoken Indo-European language. Bengali is the official language, official and national language of Bangladesh, with 98% of Bangladeshis using Bengali as their first language. Within India, Bengali is the official language of the states of West Bengal, Tripura and the Barak Valley region of the state of Assam. It is also a second official lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |