|
Roll Hardness Tester
A roll hardness tester is a device to measure the roll hardness, hardness profile and hardness variation of paper rolls. Method In the preparation phase, the plunger, guide bar and guide disk are pushed forward by the compression spring. At the end of the movement the hammer mass is hooked by the pawl. During the loading phase the hammer is pushed towards the surface in a controlled movement. The hammer mass remains locked in place by the pawl. This has the effect of stretching the impact spring to put it under tension. Impact Rebound: At the very end of the movement, the pawl spring releases the hammer mass. The impact spring contracts causing the hammer mass to strike against the plunger. This is the impact. The hammer mass then rebounds back to the body of the hammer and distance travelled is recorded on the scale. The rebound distance depends directly on the hardness of the roll under test: A softer roll will absorb more of the impact energy and the rebound distance will be l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TAPPI
TAPPI is a registered not-for-profit, international Non-Governmental Organization of about 14,000 member engineers, scientists, managers, academics and others involved in the areas of pulp, and paper. In addition to pulp and paper, the TAPPI membership includes some allied areas of packaging (such as corrugated fiberboard, flexible packaging, lamination, adhesives, coatings and extrusion). It was founded in 1915 as the Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry. TAPPI provides a forum for the professionals involved in the industry. It publishes articles, standards, and books, conducts events for peer-reviewed information relevant to the industry and offers scholarships. Peer-reviewed journals published by TAPPI include: * Journal of Pulp and Paper Science * TAPPI Journal * The Journal of Engineered Fibers and Fabrics The TAPPI website serves as a focal point for the members' access to knowledge and networks. TAPPI also serves as a major contributor to world standa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paper Mill
A paper mill is a factory devoted to making paper from vegetable fibres such as wood pulp, old rags, and other ingredients. Prior to the invention and adoption of the Fourdrinier machine and other types of paper machine that use an endless belt, all paper in a paper mill was made by hand, one sheet at a time, by specialized laborers. History Historical investigations into the origin of the paper mill are complicated by differing definitions and loose terminology from modern authors: Many modern scholars use the term to refer indiscriminately to all kinds of Mill (grinding), mills, whether powered by humans, Horse mill, by animals or Watermill, by water. Their propensity to refer to any ancient paper manufacturing center as a "mill", without further specifying its exact power source, has increased the difficulty of identifying the particularly efficient and historically important water-powered type. Human and animal-powered mills The use of human and animal powered mills w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
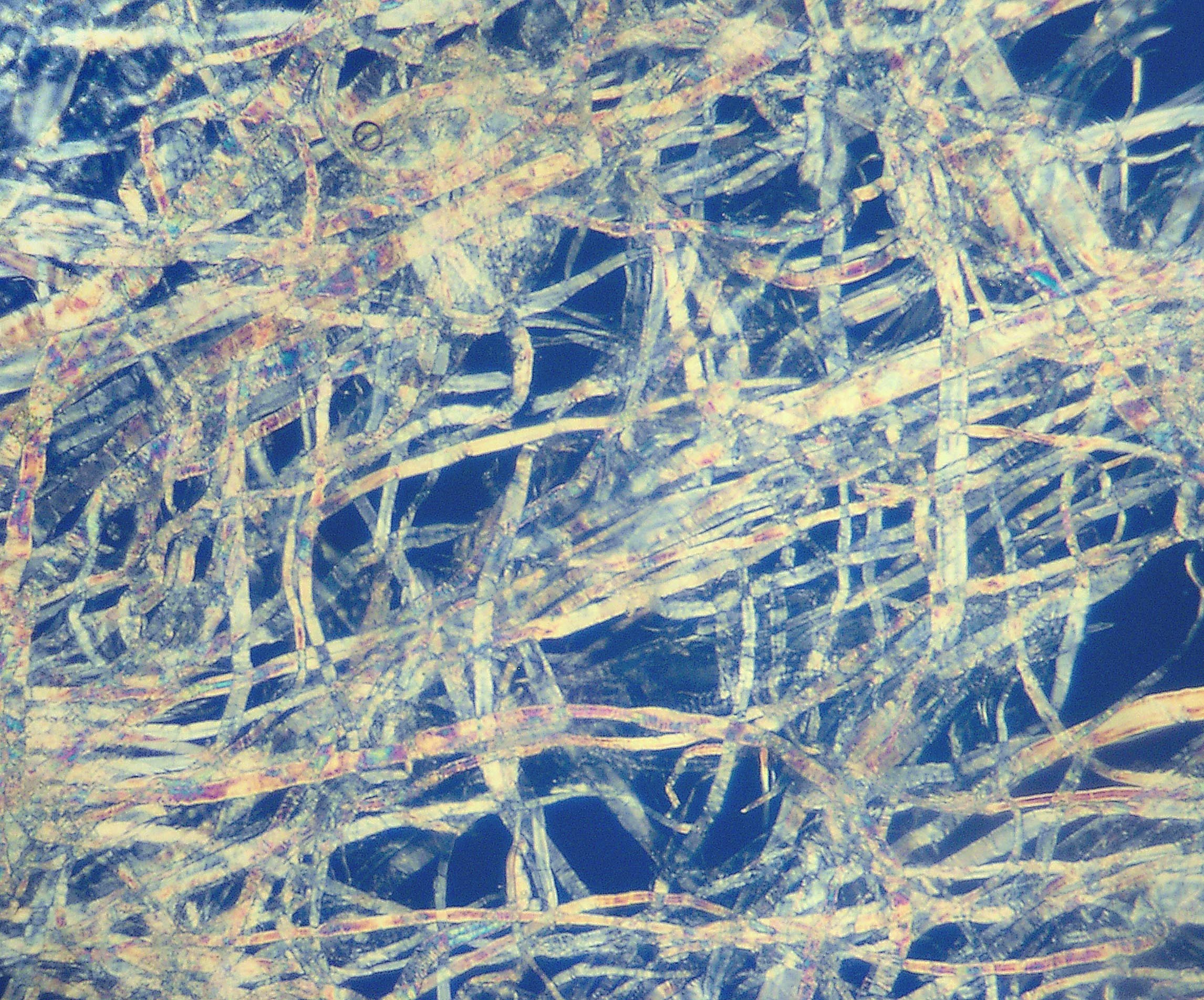
Pulp (paper)
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemical or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw material used in papermaking and the industrial production of other paper products. History Before the widely acknowledged invention of papermaking by Cai Lun in China around 105 AD, paper-like writing materials such as papyrus and amate were produced by ancient civilizations using plant materials which were largely unprocessed. Strips of bark or bast material were woven together, beaten into rough sheets, dried, and polished by hand. Pulp used in modern and traditional papermaking is distinguished by the process which produces a finer, more regular slurry of cellulose fibers which are pulled out of solution by a screen and dried to form sheets or rolls. The earliest paper produced in China consisted of bast fibers from the paper m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tablet Hardness Testing
Tablet hardness testing is a laboratory technique used by the pharmaceutical industry to determine the breaking point and structural integrity of a tablet and find out how it changes "under conditions of storage, transportation, packaging and handling before usage" The breaking point of a tablet is based on its shape. It is similar to friability testing, but they are not the same thing. Tablet hardness testers first appeared in the 1930s. In the 1950s, the Strong-Cobb tester was introduced. It was patented by Robert Albrecht on July 21, 1953. and used an air pump. The tablet breaking force was based on arbitrary units referred to as Strong-Cobbs. The new one gave readings that were inconsistent to those given by the older testers. Later, electro-mechanical testing machines were introduced. They often include mechanisms like motor drives, and the ability to send measurements to a computer or printer. There are 2 main processes to test tablet hardness: compression testing and 3 poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |