|
Rivers Of Ethiopia
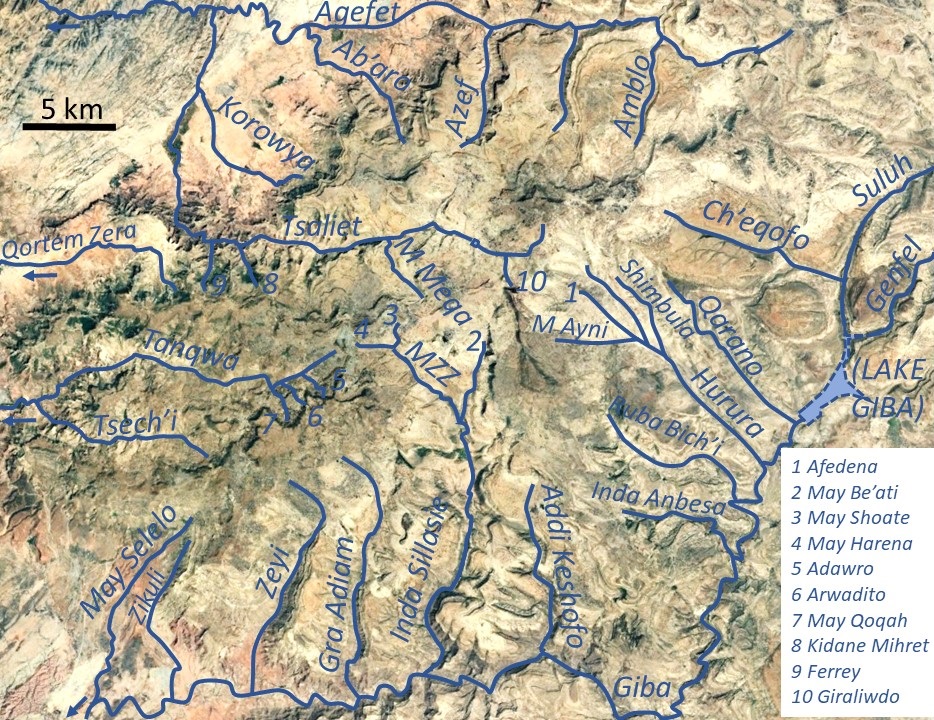
This is a list of streams and rivers in Ethiopia, arranged geographically by drainage basin. There is an alphabetic list at the end of this article. Flowing into the Mediterranean *''Nile (Egypt, Sudan)'' Atbarah River *Mareb River (or Gash River) (only reaches the Atbarah in times of flood) **Obel River *Tekezé River (or Takkaze or Setit) ** Zarima River **Ataba River **Wari River *** Qortem Zer'a *** Tsaliet **** Agefet ***** Ab'aro ***** Azef River ***** Amblo **** Korowya **** Ferrey River **** Kidane Mihret River **** May Meqa **** Graliwdo ** Giba River *** Tanqwa **** Tsech'i River **** May Qoqah **** Arwadito **** Adawro River *** May Selelo *** Zikuli River *** Gra Adiam River, also called Bitchoqo River *** Zeyi River *** Inda Sillasie River **** May Zegzeg ***** May Harena ***** May Sho'ate **** May Be'ati River *** Addi Keshofo River *** May Gabat *** Inda Anbesa *** Ruba Bich'i River *** Hurura **** Afedena River ***** May Ayni **** Shimbula *** Ila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopia Physiography
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east and northeast, Kenya to the south, South Sudan to the west, and Sudan to the northwest. Ethiopia has a total area of . As of 2022, it is home to around 113.5 million inhabitants, making it the 13th-most populous country in the world and the 2nd-most populous in Africa after Nigeria. The national capital and largest city, Addis Ababa, lies several kilometres west of the East African Rift that splits the country into the African and Somali tectonic plates. Anatomically modern humans emerged from modern-day Ethiopia and set out to the Near East and elsewhere in the Middle Paleolithic period. Southwestern Ethiopia has been proposed as a possible homeland of the Afroasiatic language famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amblo
Amblo is a river of the Nile basin. Rising in the mountains of Dogu’a Tembien in northern Ethiopia, it flows northward to empty finally in Weri’i and Tekezé River. Characteristics It is a confined ephemeral bedrock river, with an average slope gradient of 63 metres per kilometre. With its tributaries, the river has cut a deep gorge. Flash floods and flood buffering Runoff mostly happens in the form of high runoff discharge events that occur in a very short period (called flash floods). These are related to the steep topography, often little vegetation cover and intense convective rainfall. The peaks of such flash floods have often a 50 to 100 times larger discharge than the preceding baseflow. The magnitude of floods in this river has however been decreased due to interventions in the catchment. On steep slopes, exclosures have been established; the dense vegetation largely contributes to enhanced infiltration, less flooding and better baseflow. Physical conservation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zikuli River
Zikuli, also called Gereb Awhi or Mennewe River, is a river of the Nile basin. Rising in the mountains of Dogu’a Tembien in northern Ethiopia, it flows southward to empty finally in Giba and Tekezé River. Characteristics It is a confined ephemeral river, locally meandering in its narrow alluvial plain, with an average slope gradient of 37 metres per kilometre. With its tributaries, the river has cut a gorge. Flash floods and flood buffering Runoff mostly happens in the form of high runoff discharge events that occur in a very short period (called flash floods). These are related to the steep topography, often little vegetation cover and intense convective rainfall. The peaks of such flash floods have often a 50 to 100 times larger discharge than the preceding baseflow. The magnitude of floods in this river has however been decreased due to interventions in the catchment. On steep slopes, exclosures have been established; the dense vegetation largely contributes to enhanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
May Selelo
May Selelo is a river of the Nile basin. Rising in the mountains of Dogu’a Tembien in northern Ethiopia, it flows southward to empty in Giba and Tekezé River. Characteristics It is a confined ephemeral river, locally meandering in its narrow alluvial plain, with an average slope gradient of 43 metres per kilometre. With its tributaries, the river has cut a deep gorge. Flash floods and flood buffering Runoff mostly happens in the form of high runoff discharge events that occur in a very short period (called flash floods). These are related to the steep topography, often little vegetation cover and intense convective rainfall. The peaks of such flash floods have often a 50 to 100 times larger discharge than the preceding baseflow. The magnitude of floods in this river has however been decreased due to interventions in the catchment. On some steep slopes, exclosures have been established; the dense vegetation largely contributes to enhanced infiltration, less flooding and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adawro River
Adawro is a torrent of the Nile basin. Rising on the Ts’ats’en plateau of Dogu’a Tembien in northern Ethiopia, it flows northward to empty finally in Giba and Tekezé River. Characteristics It is a confined bedrock river, with an average slope gradient of 117 metres per kilometre. The river has cut a gorge in the surrounding basalt. Flash floods and flood buffering Runoff mostly happens in the form of high runoff discharge events that occur in a very short period (called flash floods). These are related to the steep topography, often little vegetation cover and intense convective rainfall. The peaks of such flash floods have often a 50 to 100 times larger discharge than the preceding baseflow. The magnitude of floods in this river has however been decreased due to interventions in the catchment, including the establishment of the Adawro exclosure on the upper slopes of the catchment. Physical conservation structures such as stone bunds and check dams also intercept r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arwadito
Arwadito is a torrent of the Nile basin. Rising on the Ts’ats’en plateau of Dogu’a Tembien in northern Ethiopia, it flows northward to empty finally in Giba and Tekezé River. Characteristics It is a confined bedrock river, with an average slope gradient of 149 metres per kilometre. The river has cut a gorge in the surrounding basalt. Flash floods and flood buffering Runoff mostly happens in the form of high runoff discharge events that occur in a very short period (called flash floods). These are related to the steep topography, often little vegetation cover and intense convective rainfall. The peaks of such flash floods have often a 50 to 100 times larger discharge than the preceding baseflow. The magnitude of floods in this river has however been decreased due to interventions in the catchment. Physical conservation structures such as stone bunds and check dams also intercept runoff. Observing that, in rivers with coarse bedload, gabion check dams were destroyed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
May Qoqah
May Qoqah is a river of the Nile basin. Rising on the Ts’ats’en plateau of Dogu’a Tembien in northern Ethiopia, it flows northward to empty finally in Giba and Tekezé River. Characteristics It is a confined bedrock river, with an average slope gradient of 90 metres per kilometre. The river has cut a gorge in the surrounding basalt. Flash floods and flood buffering Runoff mostly happens in the form of high runoff discharge events that occur in a very short period (called flash floods). These are related to the steep topography, often little vegetation cover and intense convective rainfall. The peaks of such flash floods have often a 50 to 100 times larger discharge than the preceding baseflow. The magnitude of floods in this river has however been decreased due to interventions in the catchment. Physical conservation structures such as stone bunds and check dams also intercept runoff. Observing that, in rivers with coarse bedload, gabion check dams were destroyed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsech'i River
Tsech'i is a river of the Nile basin. Rising in the mountains of Dogu’a Tembien in northern Ethiopia, it flows westward to empty finally in Giba and Tekezé River. Characteristics It is a confined ephemeral river, locally meandering in its narrow alluvial plain, with an average slope gradient of 46 metres per kilometre. With its tributaries, the river has cut a deep gorge. Flash floods and flood buffering Runoff mostly happens in the form of high runoff discharge events that occur in a very short period (called flash floods). These are related to the steep topography, often little vegetation cover and intense convective rainfall. The peaks of such flash floods have often a 50 to 100 times larger discharge than the preceding baseflow. The magnitude of floods in this river has however been decreased due to interventions in the catchment. On steep slopes, exclosures have been established; the dense vegetation largely contributes to enhanced infiltration, less flooding and be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanqwa
Tanqwa is a river of northern Ethiopia. Rising in the mountains of Dogu’a Tembien (2510 metres above sea level), it flows westward to Giba River which empties finally in the Tekezé River. Hydrography It is a confined river, locally meandering in its narrow alluvial plain, with a slope gradient of 25 metres per kilometre. With its tributaries, the river has cut a deep gorge. Tributaries Tributaries, upstream from Abiy Addi, include * Tsech'i River * May Qoqah * Arwadito * Adawro River Hydrology Hydrological characteristics The runoff footprint or annual total runoff volume is 41 million m³ at the bridge in Abiy Addi and 79 million m³ at the confluence with Giba River at Barashuwa. Peak discharges up to 543 m³ per second occur in the second part of the rainy season (month of August) when there are strong rains and the soils are saturated with water in many places. The percentage of total rainfall that directly leaves the catchment as storm runoff (also called ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giba River
Giba is a river of northern Ethiopia. It starts at the confluence of Genfel and Sulluh (which rises in the mountains of Mugulat) (3298 metres above sea level) and flows westward to the Tekezé River. Future Lake Giba will occupy the plain where Sulluh, Genfel and Agula'i Rivers meet, and hence be the future source of Giba River. Hydrography It is a confined river, locally meandering in its narrow alluvial plain, with a slope gradient of 7 metres per kilometre. With its tributaries, the river has cut a deep gorge. Tributaries Main tributaries, from downstream to upstream, are * Tanqwa ** Tsech'i River ** May Qoqah ** Arwadito ** Adawro River * May Selelo * Zikuli River * Gra Adiam River, also called Bitchoqo River * Zeyi River * Inda Sillasie River ** May Zegzeg *** May Harena *** May Sho'ate ** May Be'ati River * Addi Keshofo River * May Gabat * Inda Anbesa * Ruba Bich'i River * Hurura ** Afedena River *** May Ayni ** Shimbula * Ilala River * Qarano River * Agula'i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graliwdo
Graliwdo is a river of the Nile basin. Rising in the mountains of Degua Tembien, Dogu’a Tembien in northern Ethiopia, it flows northward to empty finally in Wari River, Weri’i and Tekezé River. Characteristics It is a confined ephemeral river, locally meandering in its narrow alluvial plain, with an average slope gradient of 78 metres per kilometre. Hydrology The effects of check dams on hydrograph, runoff response have been studied in this river. An increase of hydraulic roughness by check dams and water transmission losses in deposited sediments are responsible for the delay of runoff to reach the lower part of the river channels. The reduction of peak runoff discharge was larger in the river segment with check dams and vegetation (minus 12%) than in segment without treatment (minus 5.5%). Reduction of total runoff volume was also larger in the river with check dams than in the untreated river. The implementation of check dams combined with vegetation reduced peak flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
May Meqa
May Meqa is a river of the Nile basin. Rising in the mountains of Dogu’a Tembien in northern Ethiopia, it flows northward to empty finally in Weri’i and Tekezé River. Characteristics It is a confined ephemeral river, locally meandering in its narrow alluvial plain, with an average slope gradient of 40 metres per kilometre. The river changes names along is course: the upper part, in Miheno is called May Tsahli, the middle part in Addi Werho May Meqa, and the lower part, near the mouth May Mugda. The mouth is just 50 metres upstream from Tinsehe waterfall Flash floods and flood buffering Runoff mostly happens in the form of high runoff discharge events that occur in a very short period (called flash floods). These are related to the steep topography, often little vegetation cover and intense convective rainfall. The peaks of such flash floods have often a 50 to 100 times larger discharge than the preceding baseflow. The magnitude of floods in this river has however bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |