|
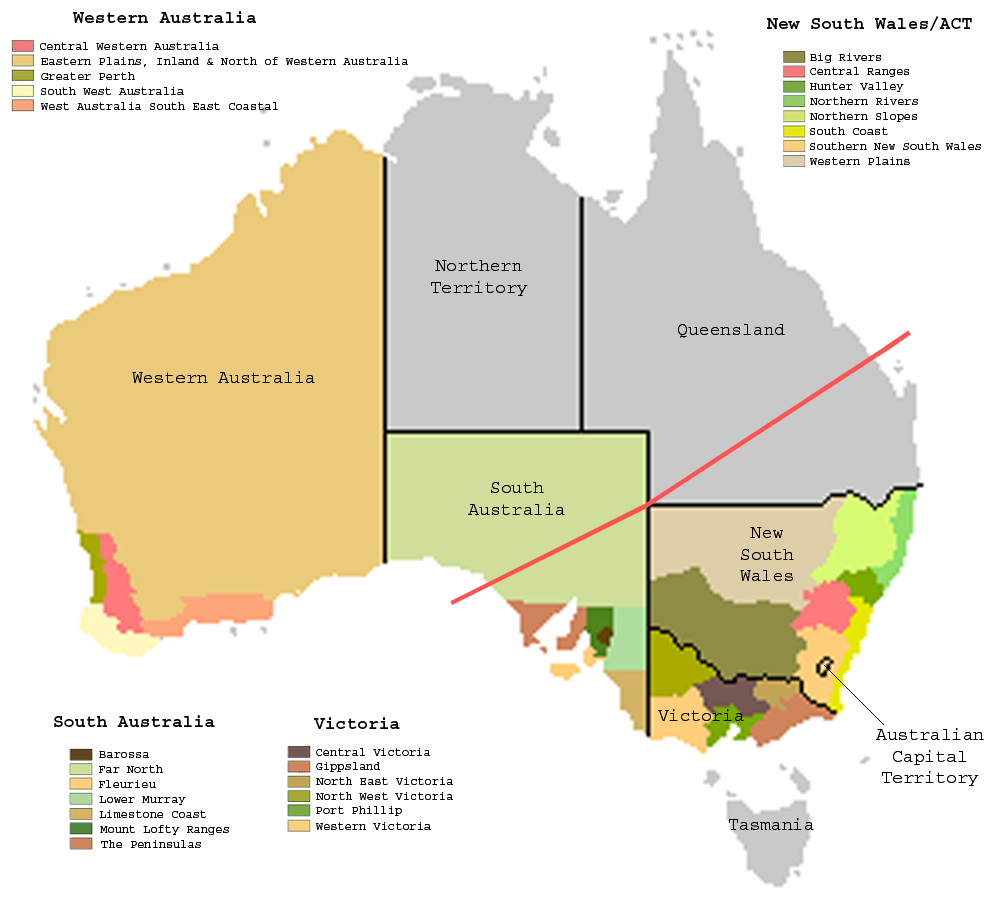
Riverina Wine Region
Riverina is an Australian Geographical Indication (AGI) registered in the Register of Protected GIs as a wine region. The Riverina AGI is centred on Griffith and is roughly circular with towns on the boundary including Mossgiel, Condobolin, Temora, Junee, Culcairn, Berrigan, Barooga, Finley, Deniliquin and Moulamein. It does not extend as far south as the Murray River. As such, the Riverina wine region is smaller than the generally known Riverina area. The Riverina region relies heavily on the Murrumbidgee Irrigation Scheme, initiated between 1906 and 1912 by Sir Samuel McCaughey Sir Samuel McCaughey (1 July 1835 – 25 July 1919) was an Irish-born pastoralist, politician and philanthropist in Australia. Early life McCaughey was born on 1 July 1835 at Tullynewey, near Ballymena, Ireland, the son of Francis McCaughey, .... The Riverina region produces 60% of the grapes in New South Wales from over of vines, 25% of Australian wine. References {{Wine regions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Rivers (wine)
Big Rivers is a grape growing zone in Australia. It covers the southwestern corner of the state of New South Wales. The zone currently includes four wine regions, which cover the main areas of grape growing in the zone, but not all of them. The four regions in the Big Rivers zone are Murray Darling, Perricoota, Riverina and Swan Hill. The Murray Darling and Swan Hill regions span the state border (the Murray River), and are partly in Big Rivers zone in New South Wales, and partly in the North West Victoria zone of Victoria. The area enclosed in the Big Rivers zone is bounded by the state boundaries with South Australia and Victoria. It extends as far north along the South Australia border to include the city of Broken Hill. It extends east along the Murray River past Albury. Parkes and Forbes ''Forbes'' () is an American business magazine owned by Integrated Whale Media Investments and the Forbes family. Published eight times a year, it features articles on finance, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berrigan, New South Wales
Berrigan is a town on the Riverina Highway in the Riverina region of New South Wales, Australia. Berrigan is in the Berrigan Shire Local government in Australia, local government area and contains the Berrigan Shire Council offices. At the , Berrigan had a population of 1,260. History The earliest association with settlement in the area comes in 1849 through the agency of Momalong Station, where Robert Rand had settled some 22.5 thousand acres. The location of the town was formerly swamp land. The unfavourable location was chosen as the mail run from Corowa to Finley, New South Wales, Murray Hut ran through Berrigan on much the same location as the present Riverina Highway, and the road from Jerilderie, New South Wales, Jerilderie lies on the same route now as it did back then. The Berrigan Post Office opened on 11 May 1884. In 1888, the first hotel - Berrigan Hotel - was built on the intersection of the two main roads through to town, with other stores rapidly following alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel McCaughey
Sir Samuel McCaughey (1 July 1835 – 25 July 1919) was an Irish-born pastoralist, politician and philanthropist in Australia. Early life McCaughey was born on 1 July 1835 at Tullynewey, near Ballymena, Ireland, the son of Francis McCaughey, farmer and merchant, and his wife Eliza, ''née'' Wilson. McCaughey came to Australia with an uncle, Charles Wilson, a brother of Sir Samuel Wilson and landed at Melbourne in April 1856. He immediately went to the country and began working as a jackaroo, in three months was appointed an overseer, and two years later became manager of Kewell station while his uncle was on a visit to England. Career In 1860, after his uncle's return, he acquired an interest in Coonong station near Urana with two partners. His brother John, who came out later, became a partner in other stations. During the early days of Coonong station McCaughey suffered greatly from drought conditions, but overcame these by sinking bores for artesian water and construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murrumbidgee Irrigation Area
The Murrumbidgee Irrigation Area (MIA) is geographically located within the Riverina area of New South Wales. It was created to control and divert the flow of local river and creek systems for the purpose of food production. The main river systems feeding and fed by the area are the Murrumbidgee River, Murrumbidgee and the Tumut River, Tumut. It is one of the most diverse and productive regions in Australia contributing over 5 billion annually to the Australian economy. As a result of the New South Wales Royal Commission into the Conservation of Water in the 1880s, the establishment of the MIA commenced in 1903 with the construction of canals west of Narrandera and the construction of Burrinjuck Dam. The MIA was formally established in 1912 after the commissioning of the Burrinjuck Dam on the Murrumbidgee River. Further expansion occurred in the 1970s with the completion of the Snowy Mountains Scheme and construction of Blowering Dam on the Tumut River, which meets the Murr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riverina
The Riverina is an agricultural region of south-western New South Wales, Australia. The Riverina is distinguished from other Australian regions by the combination of flat plains, warm to hot climate and an ample supply of water for irrigation. This combination has allowed the Riverina to develop into one of the most productive and agriculturally diverse areas of Australia. Bordered on the south by the state of Victoria and on the east by the Great Dividing Range, the Riverina covers those areas of New South Wales in the Murray and Murrumbidgee drainage zones to their confluence in the west. Home to Aboriginal groups including the Wiradjuri people for over 40,000 years, the Riverina was colonised by Europeans in the mid-19th century as a pastoral region providing beef and wool to markets in Australia and beyond. In the 20th century, the development of major irrigation areas in the Murray and Murrumbidgee valleys has led to the introduction of crops such as rice and wine grap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wine Australia
Wine Australia is an Australian Government statutory corporation that promotes and regulates the Australian wine industry. It was created as the Australian Wine and Brandy Corporation (AWBC) in 1981 to replace the Australian Wine Board by the ''Australian Wine and Brandy Corporation Act 1980'', and had its name changed by the amended ''Wine Corporation Act 1980'', passed in December 2010. Wine Australia is now governed by the superseding law, ''Wine Australia Act 2013''. Wine Australia determines the boundaries of Australia's wine regions and sometimes names them. Wine Australia also regulates wine exports, ensuring the quality and integrity of each shipment of wine exported. Wine Australia has three main departments; Compliance, Market Development and Knowledge Development. Wine Australia has its headquarters in Adelaide. History Wine Australia is a type of statutory authority known as a statutory corporation, established by the Australian Government. It was originally creat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moulamein, New South Wales
Moulamein is a small town in New South Wales, Australia, in the Murray River Council local government area. At the , Moulamein had a population of 484 . Moulamein is the oldest town in the Riverina. The town is located between Balranald, Hay, Deniliquin and Swan Hill, at the junction of the Edward River and Billabong Creek. The name Moulamein is derived from a local Aboriginal word meaning "the meeting of the waters". The climate of this area is semi-arid, and the area is rich in birdlife such as waterfowl, wedge-tailed eagles and emus. This area also has many kangaroos. History Some accounts of Moulamein’s history make unsourced statements such as: "settled as early as 1830". However it is highly unlikely the township was established as early as 1830 considering that this was about the time of Charles Sturt’s exploration along the Murrumbidgee River just to the north of this region. In about 1842 Augustus Morris came to the Riverina seeking grazing land in association w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deniliquin, New South Wales
Deniliquin () is a town in the Riverina region of New South Wales, Australia, close to the border with Victoria. It is the largest town in the Edward River Council local government area. Deniliquin is located at the intersection of the Riverina and Cobb Highway approximately south west of the state capital, Sydney and due north of Melbourne. The town is divided in two parts by the Edward River, an anabranch of the Murray River, with the main business district located on the south bank. The town services a productive agricultural district with prominent rice, wool and timber industries. At the , the urban population of Deniliquin was 6,833. History Prior to European settlement, the Aboriginal inhabitants of the Deniliquin area were the Barababaraba people. In 1843, the entrepreneur and speculator Benjamin Boyd acquired land in the vicinity of present-day Deniliquin (probably via his agent Augustus Morris). The location was known as The Sandhills, but Boyd (or Morris) named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finley, New South Wales
Finley '' Macquarie Dictionary, Fourth Edition'' (2005). Melbourne, The Macquarie Library Pty Ltd. is a town in the Riverina region of New South Wales, Australia. It is the largest town in the Berrigan Shire local government area. At the 2016 census, Finley had a population of 2,519 people. The town is located approximately west of Albury on the intersection of the Newell Highway and Riverina Highways. History The first permanent residence in the town was built in 1878. The post office opened on 1 January 1881 but was known as Murray Hut until 1893. Europeans first settled the area around Finley in the early 1840s, with wheat becoming the main crop. The Finley Agricultural & Pastoral Association was formed in 1912 and held its first show on 17 September 1913. The same agricultural show is still held annually on the first Sunday in September (Father's Day). Periods of severe drought, combined with the Great Depression of the early 1930s, forced many farmers to abandon thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barooga, New South Wales
Barooga is a border town in the Riverina region of New South Wales, Australia, located in the Berrigan Shire local government area. It is situated just north of the Murray River which forms the border with Victoria. Barooga's population at the 2016 census was 1,817. Barooga is a mainly residential area and most of its commercial and industrial needs are met in its twin town of Cobram on the south side of the Murray River. History Barooga Post Office opened on 1 May 1896. Heritage listings Barooga has a number of heritage-listed sites, including: * Vermont Street: Old Cobram-Barooga Bridge Attractions Being only two and a half hours drive from Melbourne, Barooga is a popular holiday destination because it offers two registered clubs, a 36-hole golf course and river attractions and also a large Botanical Garden. Other attractions include a twenty-metre swing bridge, Quicks Beach, walking tracks and the Barooga Markets. Barooga is also home to the Barooga PBR - On The Murray ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culcairn, New South Wales
Culcairn () is a town in the south-east Riverina region of New South Wales, Australia. Culcairn is located in the Greater Hume Shire local government area on the Olympic Highway between Albury and Wagga Wagga. The town is south-west of the state capital, Sydney and at the 2016 census had a population of 1,473. The town is an important supply centre for nearby towns and villages including, Morven, Gerogery, Henty, Walla Walla and Pleasant Hills. Billabong Creek runs along the southern edge of town, lending its name to the local high school. History European settlement of Culcairn began in 1834, following favorable reports on grazing potential and grass cover by the explorers Hume and Hovell when traveling overland to the Port Phillip district in 1824. A number of stations were gazetted and between 1862 and 1865 the district was terrorized by the bushranger, Dan "Mad Dog" Morgan. The reward for Morgan would reach £1,000. He was ambushed and killed in Victoria after hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botrytis Cinerea
''Botrytis cinerea'' is a necrotrophic fungus that affects many plant species, although its most notable hosts may be wine grapes. In viticulture, it is commonly known as "botrytis bunch rot"; in horticulture, it is usually called "grey mould" or "gray mold". The fungus gives rise to two different kinds of infections on grapes. The first, grey rot, is the result of consistently wet or humid conditions, and typically results in the loss of the affected bunches. The second, noble rot, occurs when drier conditions follow wetter, and can result in distinctive sweet dessert wines, such as Sauternes (wine), Sauternes or the Aszú of Tokaji/Grasă de Cotnari. The species name ''Botrytis cinerea'' is derived from the Latin for "grapes like ashes"; although poetic, the "grapes" refers to the bunching of the fungal spores on their Conidium, conidiophores, and "ashes" just refers to the greyish colour of the spores ''en masse''. The fungus is usually referred to by its anamorph (asexual form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)