|
Rite Of Strict Observance
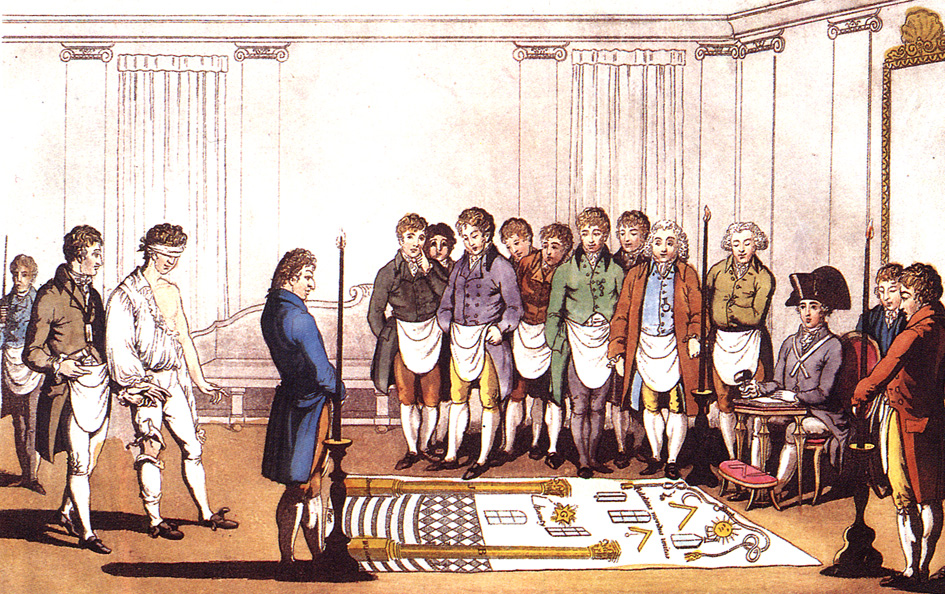
The Rite of Strict Observance was a Rite of Freemasonry, a series of progressive degrees that were conferred by the Order of Strict Observance, a Masonic body of the 18th century. History Baron Karl Gotthelf von Hund (1722–1776) introduced a new "Scottish" Rite to Germany, which he renamed "Rectified Masonry" and, after 1764, the "Strict Observance", while referring to the English system of Freemasonry as the "Late Observance." The Rite appealed to German national pride, attracted the non-nobility, and was allegedly directed by "Unknown Superiors". The Strict Observance was particularly devoted to the reform of Masonry, with special reference to the elimination of the occult sciences which at the time were widely practiced in many lodges, and the establishment of cohesion and homogeneity in Masonry through the enforcement of strict discipline, the regulation of functions, etc. By 1768 the Rite of Strict Observance counted some forty lodges. Despite its initial popularity, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rite Of Freemasonry
Masonic ritual is the scripted words and actions that are spoken or performed during the degree work in a Masonic lodge. Masonic symbolism is that which is used to illustrate the principles which Freemasonry espouses. Masonic ritual has appeared in a number of contexts within literature including in "The Man Who Would Be King", by Rudyard Kipling, and ''War and Peace'', by Leo Tolstoy. Purpose Freemasonry is described in its own ritual as a "Beautiful and profound system of morality, veiled in allegories and illustrated by symbols". The symbolism of Freemasonry is found throughout the Masonic lodge, and contains many of the working tools of a medieval or renaissance stonemason. The whole system is transmitted to initiates through the medium of Masonic ritual, which consists of lectures and allegorical plays. Common to all of Freemasonry is the three grade system of ''Craft'' or ''Blue Lodge'' freemasonry, whose allegory is centred on the building of the Temple of Solomon, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freemasonry
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities and clients. Modern Freemasonry broadly consists of two main recognition groups: * Regular Freemasonry insists that a volume of scripture be open in a working lodge, that every member profess belief in a Supreme Being, that no women be admitted, and that the discussion of religion and politics be banned. * Continental Freemasonry consists of the jurisdictions that have removed some, or all, of these restrictions. The basic, local organisational unit of Freemasonry is the Lodge. These private Lodges are usually supervised at the regional level (usually coterminous with a state, province, or national border) by a Grand Lodge or Grand Orient. There is no international, worldwide Grand Lodge that supervises all of Freemasonry; each Grand Lod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
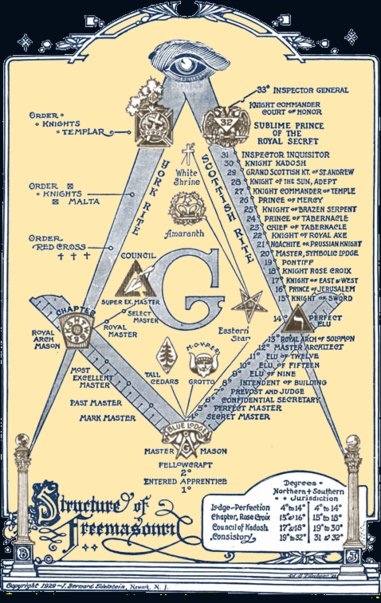
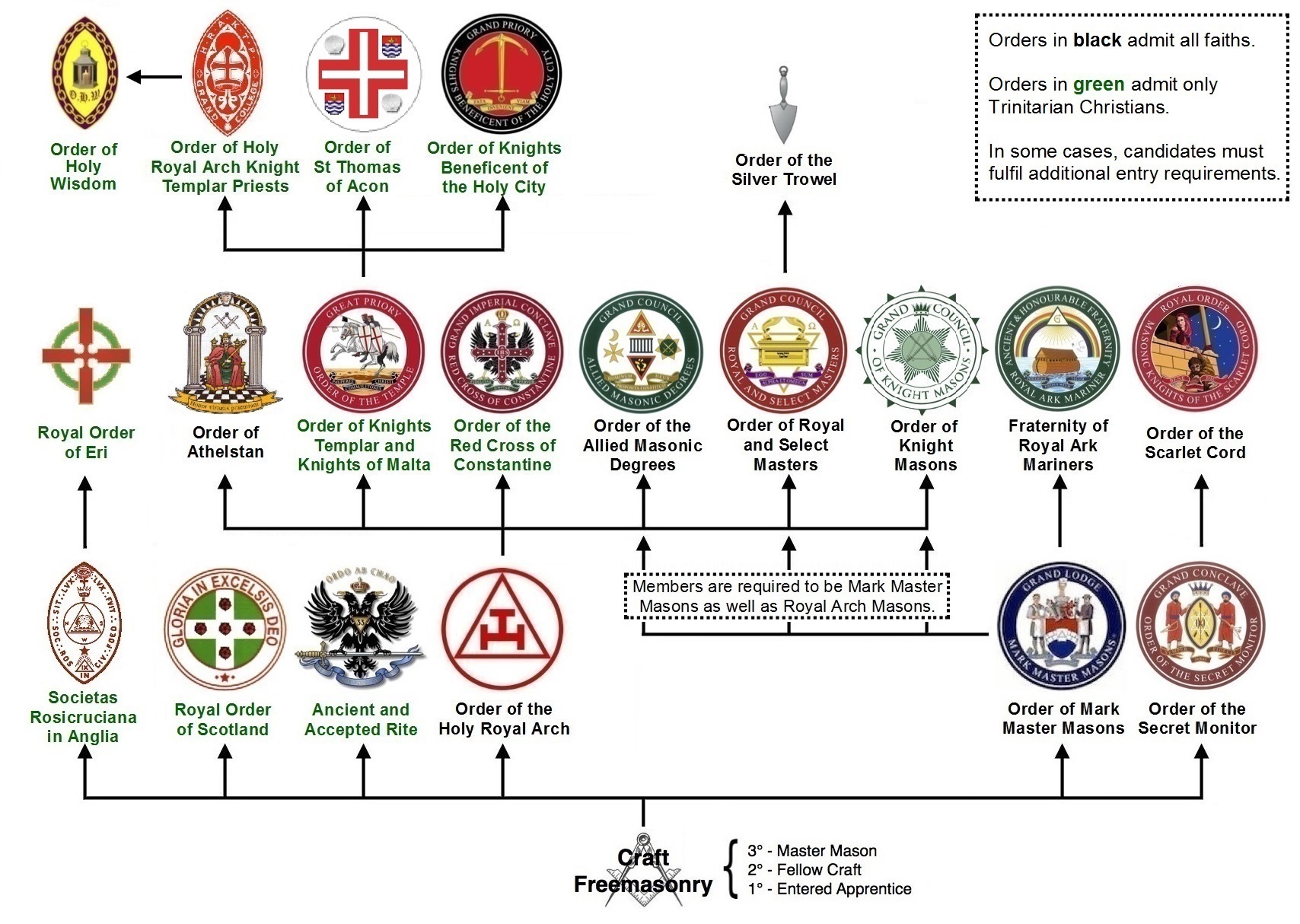
Masonic Body
There are many organisations and orders which form part of the widespread fraternity of Freemasonry, each having its own structure and terminology. Collectively these may be referred to as Masonic bodies, Masonic orders or appendant bodies (or orders) of Freemasonry. Overview of relationships between masonic organizations The basic unit of Freemasonry is the Masonic Lodge, which alone can "make" (initiate) a Freemason. Such lodges are controlled by a Grand Lodge with national or regional authority for all lodges within its territory. A masonic lodge confers the three masonic degree (freemasonry), degrees of Entered Apprentice, Fellowcraft (or Fellow Craft), and Master Mason. Whilst there is no degree in Freemasonry higher than that of Master Mason, there are additional degrees that are offered only to those who are Master Masons. Most of these are supervised by their own "Grand" bodies (independent from the Grand Lodge). The United Grand Lodge of England (which has no direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Gotthelf Von Hund
Karl Gotthelf, Baron von Hund und Altengrotkau (11 September 1722, Unwürde - 8 November 1776, Meiningen) was a German freemason. In 1751, he founded the Rite of Strict Observance. Childhood and youth Karl Gotthelf von Hund came from Silesia, descended from Henry von Hund und Altengrotkau (ca 1480). Henry's son was Commander of the Order of Malta in Glatz, where in 1518 and 1523 he held the Office of the Governor. Documents from around 1300 show John and Christopher von Hund, but it is not proven that they belong to the line that later became Altengrotkau. Karl Gotthelf's father, Joachim Hildebrand von Hund was chamberlain and Electoral Saxon landowner. The family of von Hund and Altengrotkau owned their estate from 1607 and from 1704 the estate of Upper Kittlitz in Upper Lusatia. Karl's father died very early, so that his still minor son inherited the estate. The guardianship of the son and his mother fell to Caspar Heinrich von Rodewitz. Karl Gotthelf was the youngest of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premier Grand Lodge Of England
The organisation now known as the Premier Grand Lodge of England was founded on 24 June 1717 as the Grand Lodge of London and Westminster. Originally concerned with the practice of Freemasonry in London and Westminster, it soon became known as the Grand Lodge of England. Because it was the first Masonic Grand Lodge to be created, modern convention now calls it the Premier Grand Lodge of England in order to distinguish it from the ''Most Ancient and Honourable Society of Free and Accepted Masons according to the Old Constitutions'', usually referred to as the Ancient Grand Lodge of England, and the Grand Lodge of All England Meeting at York. It existed until 1813, when it united with the Ancient Grand Lodge of England to create the United Grand Lodge of England.Douglas Knoop, ''The Genesis of Freemasonry'', Manchester University Press, 1947 The basic principles of the Grand Lodge of England were inspired by the ideal of tolerance and universal understanding of the Enlightenmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy (class), aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below Royal family, royalty. Nobility has often been an Estates of the realm, estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristics associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles or simply formal functions (e.g., Order of precedence, precedence), and vary by country and by era. Membership in the nobility, including rights and responsibilities, is typically Hereditary title, hereditary and Patrilinearity, patrilineal. Membership in the nobility has historically been granted by a monarch or government, and acquisition of sufficient power, wealth, ownerships, or royal favour has occasionally enabled commoners to ascend into the nobility. There are often a variety of ranks within the noble class. Legal recognition of nobility has been much more common in monarchies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacred Mysteries
Sacred mysteries are the areas of supernatural phenomena associated with a divinity or a religious belief and praxis. Sacred mysteries may be either: # Religious beliefs, rituals or practices which are kept secret from the uninitiated. # Beliefs of the religion which are public knowledge but cannot be easily explained by normal rational or scientific means. Although the term "mystery" is not often used in anthropology, access by initiation or rite of passage to otherwise secret beliefs is an extremely common feature of indigenous religions all over the world. A mystagogue or hierophant is a holder and teacher of secret knowledge in the former sense above, while mysticism may be defined as an area of philosophical or religious thought focusing on mysteries in the latter sense. Greece and Rome The mystery religions of antiquity were religious cults which required initiation of an "initiate" or new member before they were accepted, and sometimes had different levels of initiation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand College Of Rites
The Grand College of Rites (officially, the Grand College of Rites of the United States of America) is a Masonic organization. The Grand College of Rites was established by nine Master Masons in Washington, D.C. on May 12, 1932 for the purpose of controlling and preventing the resurrection of abandoned and unauthorized rituals in the United States. It collects these rituals from extinct organizations and prints them in an annual volume titled ''Collectanea'', which is privately distributed to its own members. Among the rituals over which the Grand College claims jurisdiction are those of the Egyptian Masonic Rite of Memphis, Ancient, Free, and Accepted Architects, Ancient and Primitive Rite, and others. See also *Masonic Appendant Bodies *List of Masonic Rites References External links The Grand College of Rites, U.S.A. Masonic organizations {{freemasonry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectified Scottish Rite
The Rectified Scottish Rite, also known as Order of Knights Beneficent of the Holy City or Knights Benefactor of the Holy City (french: Chevalier bienfaisant de la Cité sainte) is a Christian Masonic rite founded in Lyon (France) in 1778. Origins of this Rite The Rite was mainly elaborated by Jean-Baptiste Willermoz. This famous Mason reformed the French branch of the Rite of Strict Observance at the Congress of Gauls in 1778, including some items coming from the Elect Cohen Order and denying the Templar legacy. This date may be considered as the birth of the Rectified Scottish Rite. It came from several initiatory systems of the 18th century: * The Order of Knight Masons of the Elect Cohens of the Universe, of Martines de Pasqually, * The Templar Strict Observance, Knight Masonry born in Germany in the middle of the 18th century then spread in the rest of Europe, * Scottish Masonry (all the existing higher degrees, when it was not yet structured), * Craft Masonry in 3 deg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Rite
The Swedish Rite is a variation or Rite of Freemasonry that is common in Scandinavian countries and to a limited extent in Germany. It is different from other branches of Freemasonry in that, rather than having the three self-contained foundation degrees and seemingly-endless side degrees and appendant bodies, it has an integrated system with ten degrees. It is also different in that, rather than moving through the offices or 'chairs', progress in the Swedish Rite is based on moving through the ten degrees. A fundamental difference is the Swedish Rite's position on religious affiliation: Anglo/American 'Regular' Masonry requires a belief in any theistic religion and Continental 'Liberal' Masonry does not require belief in any religion, whereas Swedish Masonry is specifically Christian, and requires a Christian trinitarian belief in all its members. Nonetheless, the main Swedish Rite constitutions are all recognised as regular by the United Grand Lodge of England, and stand in f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Masonic Rites
In Freemasonry, a Rite is a series of progressive degrees that are conferred by various Masonic organizations or bodies, each of which operates under the control of its own central authority. In many cases, such as the York Rite, it can be a collection of separate Masonic organizations that would otherwise operate independently. Masonic degree systems frequently belong to the appendant bodies of Freemasonry that a Master Mason may join after the degrees of the Blue Lodge. Masonic degree systems Over time, a number of different Masonic degree systems have been developed, some of which are still in use, and others which have now ceased to exist. Known Masonic degree systems include: * Adonhiramite Rite * Ancient and Accepted Scottish Rite * Ancient and Primitive Rite * Brazillian Rite * French Rite * National Mexican Rite * Primitive Scottish Rite * Rectified Scottish Rite * Rite Français Moderne Rétabli * Rite of Adoption * Rite of Baldwyn * Rite of Memphis * Rite of M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |