|
Ritchey–Chrétien Telescope
A Ritchey–Chrétien telescope (RCT or simply RC) is a specialized variant of the Cassegrain telescope that has a hyperbolic primary mirror and a hyperbolic secondary mirror designed to eliminate off-axis optical errors (coma). The RCT has a wider field of view free of optical errors compared to a more traditional reflecting telescope configuration. Since the mid 20th century, a majority of large professional research telescopes have been Ritchey–Chrétien configurations; some well-known examples are the Hubble Space Telescope, the Keck telescopes and the ESO Very Large Telescope. History The Ritchey–Chrétien telescope was invented in the early 1910s by American astronomer George Willis Ritchey and French astronomer Henri Chrétien. Ritchey constructed the first successful RCT, which had an aperture diameter of in 1927 (e.g. Ritchey 24-inch reflector). The second RCT was a instrument constructed by Ritchey for the United States Naval Observatory; that telescope is st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spherical Aberration
In optics, spherical aberration (SA) is a type of optical aberration, aberration found in optical systems that have elements with spherical surfaces. Lens (optics), Lenses and curved mirrors are prime examples, because this shape is easier to manufacture. Light rays that strike a spherical surface off-centre are refraction, refracted or reflection (physics), reflected more or less than those that strike close to the centre. This deviation reduces the quality of images produced by optical systems. Overview A spherical lens has an Optical aberration#Aberration of elements, i.e. smallest objects at right angles to the axis, aplanatic point (i.e., no spherical aberration) only at a radius that equals the radius of the sphere divided by the index of refraction of the lens material. A typical value of refractive index for crown glass is 1.5 (see List of refractive indices, list), which indicates that only about 43% of the area (67% of diameter) of a spherical lens is useful. It is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McGraw-Hill Professional
McGraw Hill is an American educational publishing company and one of the "big three" educational publishers that publishes educational content, software, and services for pre-K through postgraduate education. The company also publishes reference and trade publications for the medical, business, and engineering professions. McGraw Hill operates in 28 countries, has about 4,000 employees globally, and offers products and services to about 140 countries in about 60 languages. Formerly a division of The McGraw Hill Companies (later renamed McGraw Hill Financial, now S&P Global), McGraw Hill Education was divested and acquired by Apollo Global Management in March 2013 for $2.4 billion in cash. McGraw Hill was sold in 2021 to Platinum Equity for $4.5 billion. Corporate History McGraw Hill was founded in 1888 when James H. McGraw, co-founder of the company, purchased the ''American Journal of Railway Appliances''. He continued to add further publications, eventually establishing The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radius Of Curvature (optics)
Radius of curvature (ROC) has specific meaning and sign convention in optical design. A spherical lens or mirror surface has a center of curvature located either along or decentered from the system local optical axis. The vertex of the lens surface is located on the local optical axis. The distance from the vertex to the center of curvature is the radius of curvature of the surface. The sign convention for the optical radius of curvature is as follows: * If the vertex lies to the left of the center of curvature, the radius of curvature is positive. * If the vertex lies to the right of the center of curvature, the radius of curvature is negative. Thus when viewing a biconvex lens from the side, the left surface radius of curvature is positive, and the right radius of curvature is negative. Note however that ''in areas of optics other than design'', other sign conventions are sometimes used. In particular, many undergraduate physics textbooks use the Gaussian sign conventi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagram Reflector RitcheyChretien
A diagram is a symbolic representation of information using visualization techniques. Diagrams have been used since prehistoric times on walls of caves, but became more prevalent during the Enlightenment. Sometimes, the technique uses a three-dimensional visualization which is then projected onto a two-dimensional surface. The word ''graph'' is sometimes used as a synonym for diagram. Overview The term "diagram" in its commonly used sense can have a general or specific meaning: * ''visual information device'' : Like the term "illustration", "diagram" is used as a collective term standing for the whole class of technical genres, including graphs, technical drawings and tables. * ''specific kind of visual display'' : This is the genre that shows qualitative data with shapes that are connected by lines, arrows, or other visual links. In science the term is used in both ways. For example, Anderson (1997) stated more generally: "diagrams are pictorial, yet abstract, representatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modulation Transfer Function
The optical transfer function (OTF) of an optical system such as a camera, microscope, human eye, or image projector, projector specifies how different spatial frequencies are captured or transmitted. It is used by optical engineers to describe how the optics project light from the object or scene onto a photographic film, Image sensor, detector array, retina, screen, or simply the next item in the optical transmission chain. A variant, the modulation transfer function (MTF), neglects phase effects, but is equivalent to the OTF in many situations. Either transfer function specifies the response to a periodic sine-wave pattern passing through the lens system, as a function of its spatial frequency or period, and its orientation. Formally, the OTF is defined as the Fourier transform of the point spread function (PSF, that is, the impulse response of the optics, the image of a point source). As a Fourier transform, the OTF is complex-valued; but it will be real-valued in the common c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lurie–Houghton Telescope
The Houghton telescope or Lurie–Houghton telescope is a catadioptric telescope. Houghton's original design was patented in 1944. Instead of the fairly hard to make Schmidt corrector plate, Schmidt and heavy meniscus corrector, meniscus (Maksutov) corrector lens (optics), lenses, the corrector for the Houghton is relatively easy to make. It consists of two lenses: a positive and a negative, set at the front of the telescope which fixes the telescope's aperture. All lens and mirror surfaces are spherical mirror, spheroidal, which eases construction. These lenses are relatively thin, though not as thin as the Schmidt corrector plate, Schmidt corrector. With a good anti-reflective coating, light loss and "ghost" reflections are minimal. Lurie slightly modified Houghton's original design by adding a diagonal mirror to direct the focused light outside the telescope tube in the same way as a Newtonian telescope. The corrector Each surface of the lenses in the correctorThe total power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schmidt Camera
A Schmidt camera, also referred to as the Schmidt telescope, is a catadioptric astrophotographic telescope designed to provide wide fields of view with limited aberrations. The design was invented by Bernhard Schmidt in 1930. Some notable examples are the Samuel Oschin telescope (formerly Palomar Schmidt), the UK Schmidt Telescope and the ESO Schmidt; these provided the major source of all-sky photographic imaging from 1950 until 2000, when electronic detectors took over. A recent example is the Kepler space telescope exoplanet finder. Other related designs are the Wright camera and Lurie–Houghton telescope. Invention and design The Schmidt camera was invented by German–Estonian optician Bernhard Schmidt in 1930. Its optical components are an easy-to-make spherical primary mirror, and an aspherical correcting lens, known as a Schmidt corrector plate, located at the center of curvature of the primary mirror. The film or other detector is placed inside the camera, at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VISTA (telescope)
The VISTA (Visible and Infrared Survey Telescope for Astronomy) is a wide-field reflecting telescope with a 4.1 metre mirror, located at the Paranal Observatory in Chile. It is operated by the European Southern Observatory and started science operations in December 2009. VISTA was conceived and developed by a consortium of universities in the United Kingdom led by Queen Mary University of London and became an in-kind contribution to ESO as part of the UK's accession agreement, with the subscription paid by the UK Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC). VISTA is a survey telescope working at infrared wavelengths, and is by far the largest telescope in the world dedicated to surveying the sky at near-infrared wavelengths. The telescope has only one instrument: VIRCAM, the Vista InfraRed CAMera. This is a 3-tonne camera containing 16 special detectors sensitive to infrared light, with a combined total of 67 million pixels. A second-generation instrument called 4MOST, a 240 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloan Digital Sky Survey
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey or SDSS is a major multi-spectral imaging and spectroscopic redshift survey using a dedicated 2.5-m wide-angle optical telescope at Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico, United States. The project began in 2000 and was named after the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, which contributed significant funding. A consortium of the University of Washington and Princeton University was established to conduct a redshift survey. The Astrophysical Research Consortium (ARC) was established in 1984 with the additional participation of New Mexico State University and Washington State University to manage activities at Apache Point. In 1991 the Sloan Foundation granted the ARC funding for survey efforts and the construction of equipment to carry out the work.. Background At the time of its design, the SDSS was a pioneering combination of novel instrumentation as well as data reduction and storage techniques that drove major advances in astronomical observations, di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-mirror Anastigmat
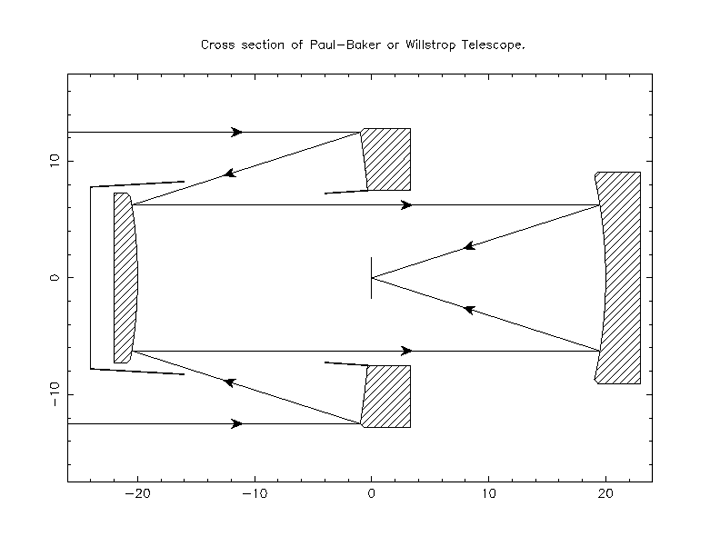
A three-mirror anastigmat is an anastigmat telescope built with three curved mirrors, enabling it to minimize all three main optical aberrations – spherical aberration, coma, and astigmatism. This is primarily used to enable wide fields of view, much larger than possible with telescopes with just one or two curved surfaces. A telescope with only one curved mirror, such as a Newtonian telescope, will always have aberrations. If the mirror is spherical, it will suffer from spherical aberration. If the mirror is made parabolic, to correct the spherical aberration, then it must necessarily suffer from coma and off-axis astigmatism. With two curved mirrors, such as the Ritchey–Chrétien telescope, coma can be minimized as well. This allows a larger useful field of view, and the remaining astigmatism is symmetrical around the distorted objects, allowing astrometry across the wide field of view. However, the astigmatism can be reduced by including a third curved optical element. Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monthly Notices Of The Royal Astronomical Society
''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in astronomy and astrophysics. It has been in continuous existence since 1827 and publishes letters and papers reporting original research in relevant fields. Despite the name, the journal is no longer monthly, nor does it carry the notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. History The first issue of MNRAS was published on 9 February 1827 as ''Monthly Notices of the Astronomical Society of London'' and it has been in continuous publication ever since. It took its current name from the second volume, after the Astronomical Society of London became the Royal Astronomical Society (RAS). Until 1960 it carried the monthly notices of the RAS, at which time these were transferred to the newly established ''Quarterly Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (1960–1996) and then to its successor journal ''Astronomy & Geophysics'' (since 1997). Until 1965, MNRAS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |