|
Right To Explanation
In the regulation of algorithms, particularly artificial intelligence and its subfield of machine learning, a right to explanation (or right to ''an'' explanation) is a right to be given an explanation for an output of the algorithm. Such rights primarily refer to individual rights to be given an explanation for decisions that significantly affect an individual, particularly legally or financially. For example, a person who applies for a loan and is denied may ask for an explanation, which could be "Credit bureau X reports that you declared bankruptcy last year; this is the main factor in considering you too likely to default, and thus we will not give you the loan you applied for." Some such legal rights already exist, while the scope of a general "right to explanation" is a matter of ongoing debate. There have been arguments made that a "social right to explanation" is a crucial foundation for an information society, particularly as the institutions of that society will need to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulation
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. For example: * in government, typically regulation (or its plural) refers to the delegated legislation which is adopted to enforce primary legislation; including Land-use planning, land-use regulation * in economy: regulatory economics * in finance: financial regulation * in business, industry self-regulation occurs through self-regulatory organizations and trade associations which allow industries to set and enforce rules with less government involvement; and, * in biology, gene regulation and metabolic regulation allow living organisms to adapt to their environment and maintain homeostasis; * in psychology, self-regulation theory is the study of how individuals regulate their thoughts and behaviors to reach goals. Forms Regulation in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Protection Directive
The Data Protection Directive, officially Directive 95/46/EC, enacted in October 1995, was a European Union directive which regulated the processing of personal data within the European Union (EU) and the free movement of such data. The Data Protection Directive was an important component of EU privacy and human rights law. The principles set out in the Data Protection Directive were aimed at the protection of fundamental rights and freedoms in the processing of personal data. The General Data Protection Regulation, adopted in April 2016, superseded the Data Protection Directive and became enforceable on 25 May 2018. Context The right to privacy is a highly developed area of law in Europe. All the member states of the Council of Europe (CoE) are also signatories of the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR). Article 8 of the ECHR provides a right to respect for one's "private and family life, his home and his correspondence", subject to certain restrictions. The European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulation Of Algorithms
Regulation of algorithms, or algorithmic regulation, is the creation of laws, rules and public sector policies for promotion and regulation of algorithms, particularly in artificial intelligence and machine learning. For the subset of AI algorithms, the term regulation of artificial intelligence is used. The regulatory and policy landscape for artificial intelligence (AI) is an emerging issue in jurisdictions globally, including in the European Union. Regulation of AI is considered necessary to both encourage AI and manage associated risks, but challenging. Another emerging topic is the regulation of blockchain algorithms (Use of the smart contracts must be regulated) and is mentioned along with regulation of AI algorithms. Many countries have enacted High-frequency trading#Regulation and enforcement, regulations of high frequency trades, which is shifting due to technological progress into the realm of AI algorithms. The motivation for regulation of algorithms is the apprehensio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithmic Transparency
Algorithmic transparency is the principle that the factors that influence the decisions made by algorithms should be visible, or transparent, to the people who use, regulate, and are affected by systems that employ those algorithms. Although the phrase was coined in 2016 by Nicholas Diakopoulos and Michael Koliska about the role of algorithms in deciding the content of digital journalism services, the underlying principle dates back to the 1970s and the rise of automated systems for scoring consumer credit. The phrases "algorithmic transparency" and "algorithmic accountability" are sometimes used interchangeably – especially since they were coined by the same people – but they have subtly different meanings. Specifically, "algorithmic transparency" states that the inputs to the algorithm and the algorithm's use itself must be known, but they need not be fair. " Algorithmic accountability" implies that the organizations that use algorithms must be accountable for the decisions ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
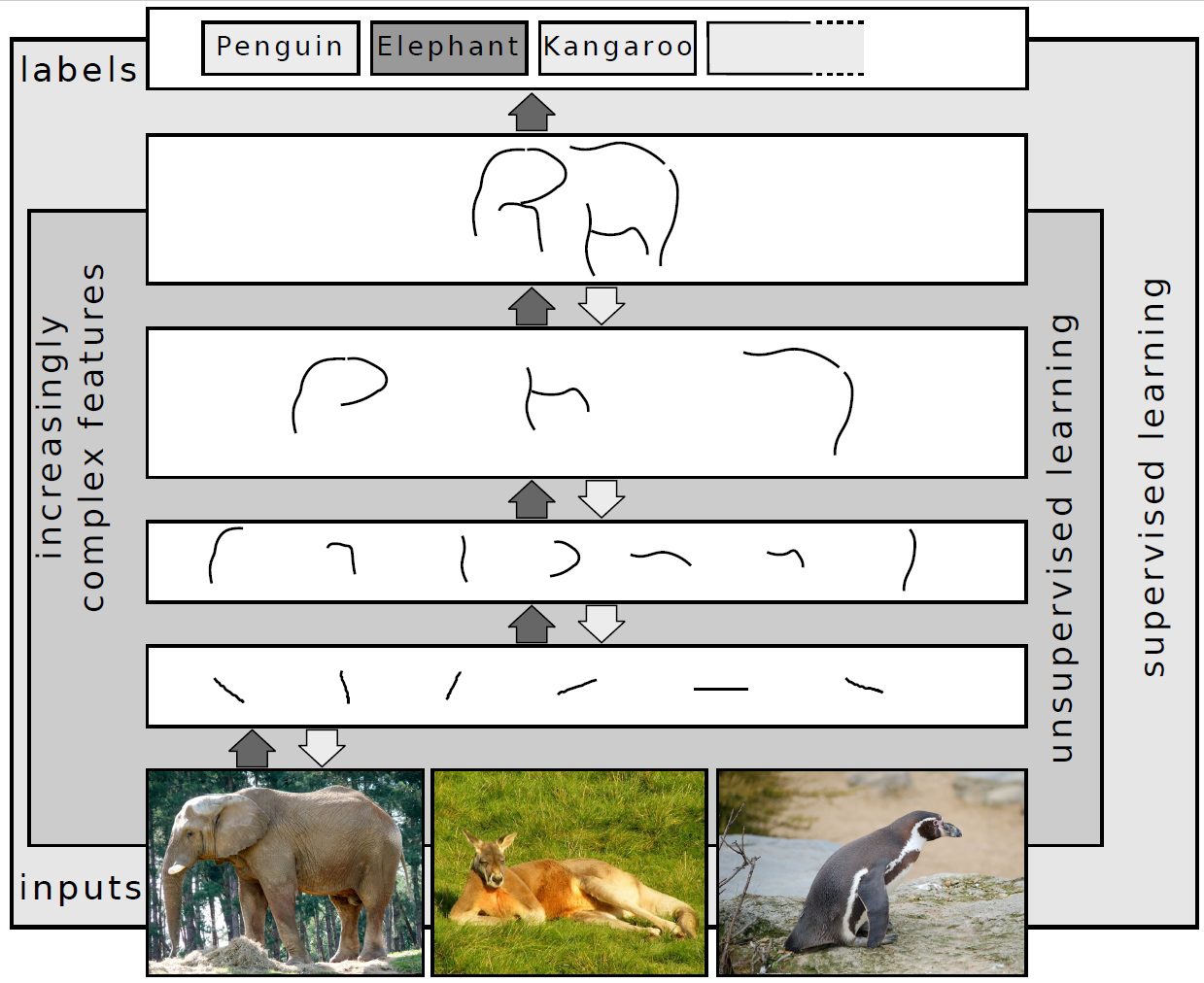
Explainable AI
Explainable AI (XAI), often overlapping with interpretable AI, or explainable machine learning (XML), is a field of research within artificial intelligence (AI) that explores methods that provide humans with the ability of ''intellectual oversight'' over AI algorithms. The main focus is on the reasoning behind the decisions or predictions made by the AI algorithms, to make them more understandable and transparent. This addresses users' requirement to assess safety and scrutinize the automated decision making in applications. XAI counters the "black box" tendency of machine learning, where even the AI's designers cannot explain why it arrived at a specific decision. XAI hopes to help users of AI-powered systems perform more effectively by improving their understanding of how those systems reason. XAI may be an implementation of the social right to explanation. Even if there is no such legal right or regulatory requirement, XAI can improve the user experience of a product or servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Neural Network
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on utilizing multilayered neural network (machine learning), neural networks to perform tasks such as Statistical classification, classification, Regression analysis, regression, and representation learning. The field takes inspiration from Neuroscience, biological neuroscience and is centered around stacking Artificial neuron, artificial neurons into layers and "training" them to process data. The adjective "deep" refers to the use of multiple layers (ranging from three to several hundred or thousands) in the network. Methods used can be either Supervised learning, supervised, Semi-supervised learning, semi-supervised or Unsupervised learning, unsupervised. Some common deep learning network architectures include Fully connected network, fully connected networks, deep belief networks, recurrent neural networks, convolutional neural networks, Generative adversarial network, generative adversarial networks, Transformer (ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithmic Accountability
Algorithmic accountability refers to the allocation of responsibility for the consequences of real-world actions influenced by algorithms used in decision-making processes. Ideally, algorithms should be designed to eliminate bias from their decision-making outcomes. This means they ought to evaluate only relevant characteristics of the input data, avoiding distinctions based on attributes that are generally inappropriate in social contexts, such as an individual's ethnicity in legal judgments. However, adherence to this principle is not always guaranteed, and there are instances where individuals may be adversely affected by algorithmic decisions. Responsibility for any harm resulting from a machine's decision may lie with the algorithm itself or with the individuals who designed it, particularly if the decision resulted from bias or flawed data analysis inherent in the algorithm's design. Algorithm usage Algorithms are widely utilized across various sectors of society that inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regions—five of which are overseas—span a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Privacy
Information privacy is the relationship between the collection and dissemination of data, technology, the public expectation of privacy, contextual information norms, and the legal and political issues surrounding them. It is also known as data privacy or data protection. Information types Various types of personal information often come under privacy concerns. Cable television This describes the ability to control what information one reveals about oneself over cable television, and who can access that information. For example, third parties can track IP TV programs someone has watched at any given time. "The addition of any information in a broadcasting stream is not required for an audience rating survey, additional devices are not requested to be installed in the houses of viewers or listeners, and without the necessity of their cooperations, audience ratings can be automatically performed in real-time." Educational In the United Kingdom in 2012, the Education Secretary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gig Economy
The gig economy is the economic system by which a workforce of people (known as gig workers) engage in freelance and/or side-employment. Description The gig economy is composed of corporate entities, workers and consumers. The Internal Revenue Service defines the gig economy as "activity where people earn income providing on-demand work, services or goods", noting that the activity is often facilitated through a digital platform such as a mobile app or website and earnings may be in the form of "cash, property, goods, or virtual currency". According to the Fair Work Ombudsman, the digital platforms or marketplaces connect individual service providers directly to customers for a fee. The BBC presented the following definition for the term: "a labour market characterised by the prevalence of short-term contracts or freelance work, as opposed to permanent jobs". The term "gig" comes from the slang term for individual appearances by performing artists like musicians and comedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platform Work Directive
The Platform Work Directive (EU2024/2831is a proposed European Union Directive on the regulation of platform work in EU law. Contents Article 1 sets out the Directive's purpose to improve work, ensure "correct determination of latform workers'employment status" and promote fairness, transparency and accountability in algorithmic management in platform work, and support sustainable growth in digital labour platforms. Under (2) the Directive applies to everyone with an employment contract or relationship, and article 10 also applies to those who do not, and (3) it applies wherever the platform is established. Article 2 sets out definitions of (1) 'digital labour platform' as a commercial service at a distance by electronic means at the request of a recipient, with an essential component of organising work, but does not include share asset platforms (2) platform work means work organised by contract (3) person performing platform work is irrespective of the contract (4) platform wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recommender System
A recommender system (RecSys), or a recommendation system (sometimes replacing ''system'' with terms such as ''platform'', ''engine'', or ''algorithm'') and sometimes only called "the algorithm" or "algorithm", is a subclass of information filtering system that provides suggestions for items that are most pertinent to a particular user. Recommender systems are particularly useful when an individual needs to choose an item from a potentially overwhelming number of items that a service may offer. Modern recommendation systems such as those used on large social media sites make extensive use of AI, machine learning and related techniques to learn the behavior and preferences of each user and categorize content to tailor their feed individually. Typically, the suggestions refer to various decision-making processes, such as what product to purchase, what music to listen to, or what online news to read. Recommender systems are used in a variety of areas, with commonly recognised ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |