|
Rentakios Helladikos
Rendakis ( el, Ρενδάκις), also Rendakios (Ρενδάκιος) or Rentakios (Ρεντάκιος) was the surname of a powerful Byzantine noble family in the 8th to 10th centuries. History The Rendakis family was first mentioned during the reign of Leo III the Isaurian (r. 717–741). Although the family were native Greek speakers, the etymology of the family name is believed by some scholars to have been of Slavs, Slavic origin. In the beginning of the 8th century, the number of officials of clearly provincial origin had increased, and the Rendakioi was one of these families. In the 9th century, the family numbered among the most powerful families in the Byzantine Empire, alongside those of Bryennios, Choirosphaktes, Monomachos family, Monomachos, and Tessarakontapechys. Members *Sisinnios Rendakis (Σισίννιος, ), ''patrikios'' and ''strategos'' of the Anatolic Theme under Emperor Leo III, according to the ''Miracles of Saint Demetrius'', he commanded the imperial fle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parakoimomenos
The ''parakoimōmenos'' ( el, παρακοιμώμενος, literally "the one who sleeps beside he emperor's chamber) was a Byzantine court position, usually reserved for eunuchs. The position's proximity to the emperors guaranteed its holders influence and power, and many of them, especially in the 9th and 10th centuries, functioned as the Byzantine Empire's chief ministers. History and functions The title was used anachronistically by various Byzantine writers for prominent eunuch court officials of the distant past, including Euphratas under Constantine the Great (reigned 306–337), the notorious Chrysaphius under Theodosius II (), or an unnamed holder of the office under Emperor Maurice (). The position was probably created no later than the reign of Leo IV the Khazar (), when the chronicler Theophanes the Confessor mentions a "''koubikoularios'' and ''parakoimomenos”'' serving Leo. In the beginning, it was a modest office, given to those ''koubikoularioi'' (from Lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th Century In Greece
9 (nine) is the natural number following and preceding . Evolution of the Arabic digit In the beginning, various Indians wrote a digit 9 similar in shape to the modern closing question mark without the bottom dot. The Kshatrapa, Andhra and Gupta started curving the bottom vertical line coming up with a -look-alike. The Nagari continued the bottom stroke to make a circle and enclose the 3-look-alike, in much the same way that the sign @ encircles a lowercase ''a''. As time went on, the enclosing circle became bigger and its line continued beyond the circle downwards, as the 3-look-alike became smaller. Soon, all that was left of the 3-look-alike was a squiggle. The Arabs simply connected that squiggle to the downward stroke at the middle and subsequent European change was purely cosmetic. While the shape of the glyph for the digit 9 has an ascender in most modern typefaces, in typefaces with text figures the character usually has a descender, as, for example, in . T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8th Century In Greece
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9. In mathematics 8 is: * a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2. * a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the first number of the form , being an integer greater than 1. * the first number which is neither prime nor semiprime. * the base of the octal number system, which is mostly used with computers. In octal, one digit represents three bits. In modern computers, a byte is a grouping of eight bits, also called an wikt:octet, octet. * a Fibonacci number, being plus . The next Fibonacci number is . 8 is the only positive Fibonacci number, aside from 1, that is a perfect cube. * the only nonzero perfect power that is one less than another perfect power, by Catalan conjecture, Mihăilescu's Theorem. * the order of the smallest non-abelian group all of whose subgroups are normal. * the dimension of the octonions and is the highest possible dimension of a normed divisio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Families
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergios Betelakes
Sergius was the name of a Roman Patrician Gens, Sergia (or Sergii), originally from Alba Longa ( Latium in central Italy). It is also found as Sergios. It may refer to: Name * Sergius (name) or Serge, a masculine given name Roman Catholic Popes *Pope Sergius I (died 701), Italian-born pope *Pope Sergius II (reigned died 847), Italian-born pope *Pope Sergius III (reigned 904–911), Italian-born pope *Pope Sergius IV (reigned died 1012), Italian-born pope Eastern Orthodox Patriarchs *Sergius of Bulgaria, Patriarch of Bulgaria c. 931 – c. 940 *Patriarch Sergius I of Constantinople, Patriarch 610–638 *Patriarch Sergius II of Constantinople, Patriarch 1001–1019 * Patriarch Sergius I of Moscow, Patriarch 1943–1944 Other Patriarchs * Sergius of Tella (died 546), Syriac Orthodox Patriarch of Antioch in 544–546 Other Christian Saints * Saint Sergius (martyr), Roman soldier companion of Saint Bacchus, martyred c. 303. * Sergius of Cappadocia (died 304), Martyred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rendakios The Athenian
Rendakis ( el, Ρενδάκις), also Rendakios (Ρενδάκιος) or Rentakios (Ρεντάκιος) was the surname of a powerful Byzantine noble family in the 8th to 10th centuries. History The Rendakis family was first mentioned during the reign of Leo III the Isaurian (r. 717–741). Although the family were native Greek speakers, the etymology of the family name is believed by some scholars to have been of Slavic origin. In the beginning of the 8th century, the number of officials of clearly provincial origin had increased, and the Rendakioi was one of these families. In the 9th century, the family numbered among the most powerful families in the Byzantine Empire, alongside those of Bryennios, Choirosphaktes, Monomachos, and Tessarakontapechys. Members * Sisinnios Rendakis (Σισίννιος, ), '' patrikios'' and ''strategos'' of the Anatolic Theme under Emperor Leo III, according to the '' Miracles of Saint Demetrius'', he commanded the imperial fleet that saved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demetrios Phalakros
Demetrius is the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning “Demetris” - "devoted to goddess Demeter". Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, Dimitri, Dimitrie, Dimitar, Dumitru, Demitri, Dhimitër, and Dimitrije, in addition to other forms (such as Russian Dmitry) descended from it. Demetrius and its variations may refer to the following: *Demetrius of Alopece (4th century BC), Greek sculptor noted for his realism *Demetrius of Phalerum ( – BC) * Demetrius, somatophylax of Alexander the Great (d. 330 BC) *Demetrius - brother of Antigonus I Monophthalmus, king of Macedonia 306-301 BC *Demetrius I of Macedon (337–283 BC), called ''Poliorcetes'', son of Antigonus I Monophthalmus, King of Macedonia 294–288 BC *Demetrius the Fair (Demetrius the Handsome, Demetrius of Cyrene) (285 BC-249/250 BC) - Hellenistic king of Cyrene * Demetrius II Aetolicus, son of Antigonus II, King of Macedonia 239–229 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine Rendakis
Constantine most often refers to: * Constantine the Great, Roman emperor from 306 to 337, also known as Constantine I *Constantine, Algeria, a city in Algeria Constantine may also refer to: People * Constantine (name), a masculine given name and surname Roman/Byzantine emperors * Constantine II (emperor) * Constantine III (Western Roman emperor) * Constantine III (Byzantine emperor) * Constantine IV * Constantine V * Constantine VI * Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus * Constantine VIII * Constantine IX Monomachos * Constantine X Doukas * Constantine XI Palaiologos Emperors not enumerated * Tiberius II, reigned officially as "Constantine" *Constans II, reigned officially as "Constantine" *Constantine (son of Leo V) * Constantine (son of Theophilos) * Constantine (son of Basil I) * Constantine Doukas (co-emperor) * Constantine Lekapenos * Constantine Laskaris (?) Other rulers * Constantine I, Prince of Armenia * Constantine II, Prince of Armenia * Constantine I, K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Lekapenos
Christopher Lekapenos or Lecapenus ( gr, Χριστόφορος Λακαπηνός, Christóphoros Lakapenōs) was the eldest son of Emperor Romanos I Lekapenos () and co-emperor of the Eastern Roman Empire from 921 until his death in 931. Christopher was given the position of ''megas hetaireiarches'' (commander of the palace guard) in spring 919, after Romanos assumed the position of ''basileopator''. Romanos, in order to give his family precedence over the Macedonian line, raised Christopher to co-emperor on 21 May 921. In 928 Christopher's father-in-law, Niketas, unsuccessfully attempted to incite Christopher to usurp his father, resulting in Niketas being banished. Christopher died in August 931, succeeded by his father and two brothers, Stephen Lekapenos and Constantine Lekapenos, and Constantine VII. In December 944 his brothers overthrew and exiled his father, but they themselves were exiled after attempting to oust Constantine VII. Life Christopher was the eldest so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niketas Rentakios
Nicetas or Niketas () is a Greek given name, meaning "victorious one" (from Nike " victory"). The veneration of martyr saint Nicetas the Goth in the medieval period gave rise to the Slavic forms: '' Nikita, Mykyta and Mikita'' People with the name Nicetas * Nicetas of Syracuse, ( 400 – 335 BC), Greek philosopher * Nicetas of Smyrna, late 1st-century Greek sophist and rhetorician, see Second Sophistic * Nicetas of Remesiana, 4th-century bishop of the Dacians, now the patron saint of Romania * Nicetas the Goth, 4th-century martyr * Nicetas (Bishop of Aquileia), mid-5th-century archbishop of Aquileia * Nicetas (cousin of Heraclius), early 7th-century Byzantine general * Niketas the Persian, 7th-century Byzantine officer * Niketas (son of Artabasdos), mid-8th-century Byzantine general * Nicetas of Medikion (Nicetas the Confessor, 783 – 824), Byzantine monk and hegumenos * Nicetas the Patrician (Nicetas Monomachos, 761 – 836), Byzantine eunuch official and monk, opponent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
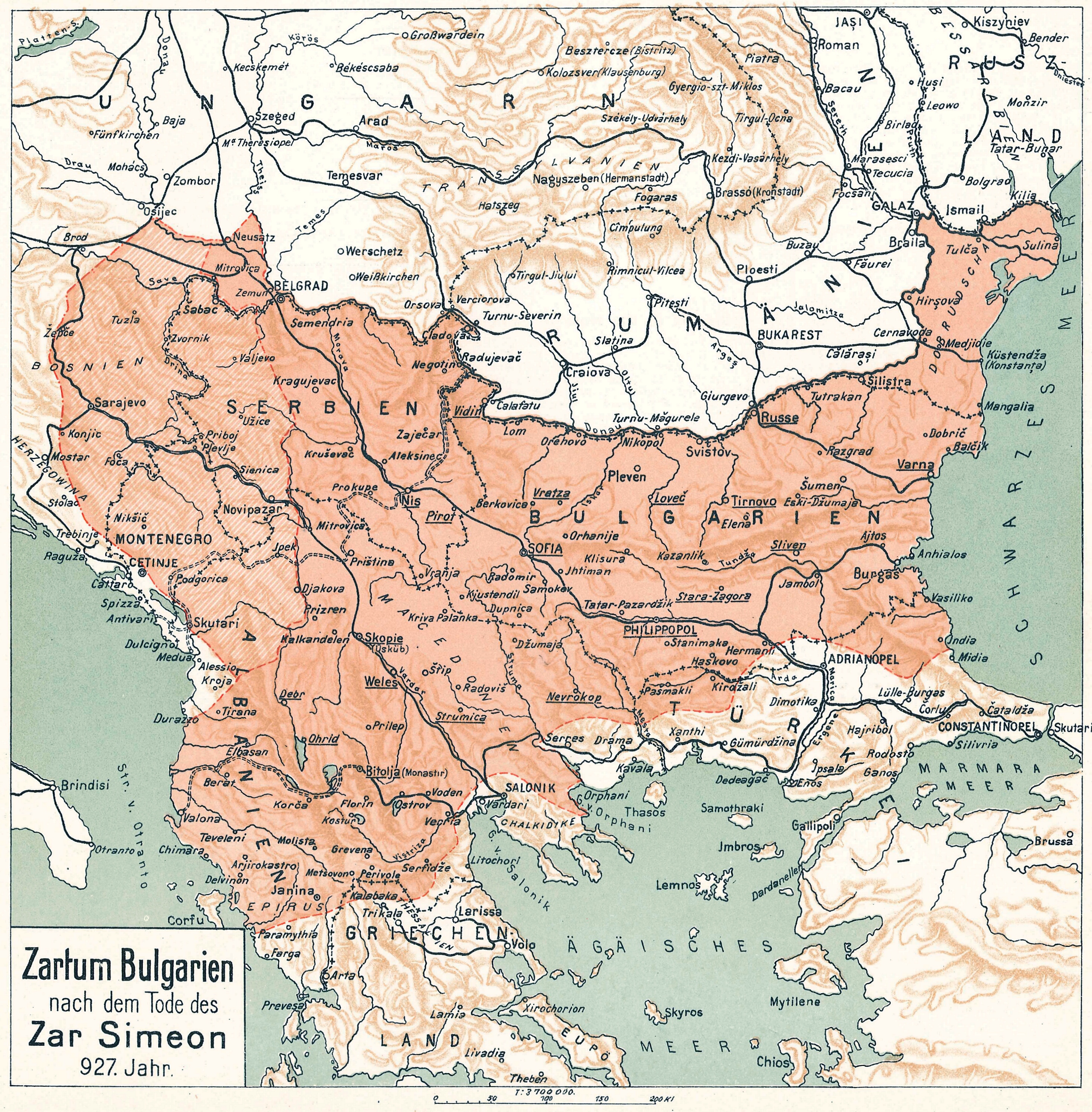
Simeon I Of Bulgaria
Tsar Simeon (also Symeon) I the Great ( cu, цѣсар҄ь Сѷмеѡ́нъ А҃ Вели́къ, cěsarĭ Sỳmeonŭ prĭvŭ Velikŭ bg, цар Симеон I Велики, Simeon I Veliki el, Συμεών Αʹ ὁ Μέγας, Sumeṓn prôtos ho Mégas) ruled over Bulgaria from 893 to 927,Lalkov, ''Rulers of Bulgaria'', pp. 23–25. during the First Bulgarian Empire. Simeon's successful campaigns against the Byzantines, Magyars and Serbs led Bulgaria to its greatest territorial expansion ever, making it the most powerful state in contemporary Eastern and Southeast Europe. His reign was also a period of unmatched cultural prosperity and enlightenment later deemed the Golden Age of Bulgarian culture. During Simeon's rule, Bulgaria spread over a territory between the Aegean, the Adriatic and the Black Sea.Bakalov, ''Istorija na Bǎlgarija'', "Simeon I Veliki". The newly independent Bulgarian Orthodox Church became the first new patriarchate besides the Pentarchy, and Bulgarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)