|
Renewable Energy In The United Kingdom
Renewable energy in the United Kingdom contributes to production for electricity, heat, and transport. From the mid-1990s, renewable energy began to play a part in the UK's electricity generation, building on a small hydroelectric capacity. Wind power, which is abundant in the UK, has since become the main source of renewable energy. , renewable sources generated 40.2% of the electricity produced in the UK; around 6% of total UK energy usage. Interest has increased in recent years due to UK and EU targets for reductions in carbon emissions, and government incentives for renewable electricity such as the Renewable Obligation Certificate scheme (ROCs) and feed in tariffs (FITs), as well as for renewable heat such as the Renewable Heat Incentive. The 2009 EU Renewable Directive established a target of 15% reduction in total energy consumption in the UK by 2020. History Heat from wood fires goes back to the earliest human habitation of Britain. Waterwheel technology was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Farm - Geograph
Wind is the natural movement of atmosphere of Earth, air or other gases relative to a planetary surface, planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The two main causes of large-scale atmospheric circulation are the differential heating between the equator and the poles, and the rotation of the planet (Coriolis effect). Within the tropics and subtropics, thermal low circulations over terrain and high plateaus can drive monsoon circulations. In coastal areas the sea breeze/land breeze cycle can define local winds; in areas that have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes can prevail. Winds are commonly classified by their scale (spatial), spatial scale, their speed and direction, the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marykirk
Marykirk ( gd, Obar Luathnait) is a village in the Kincardine and Mearns area of Aberdeenshire, Scotland, next to the border with Angus at the River North Esk. The village is approximately 6 miles ENE of Montrose at the southern end of the Howe of the Mearns. The road bridge carrying the A937 over the River North Esk is a substantial structure with four arches. It was designed by Robert Stevenson and completed in 1815 at the cost of £1,000 replacing the previous route to the village, an ancient ford. There is a rail bridge across the same river some 600 m north of the road bridge and the village once had a rail station to the north east. The present parish church was rebuilt in 1806 replacing the previous church, the remains of which can be found in the adjacent kirkyard. The older church was dedicated to St Mary and consecrated in 1242 by the Bishop de Bernham. The settlement and parish were called Aberluthnot before being renamed after the church. The village was made a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orkney
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north of the coast of Caithness and has about 70 islands, of which 20 are inhabited. The largest island, the Mainland, Orkney, Mainland, has an area of , making it the List of islands of Scotland, sixth-largest Scottish island and the List of islands of the British Isles, tenth-largest island in the British Isles. Orkney’s largest settlement, and also its administrative centre, is Kirkwall. Orkney is one of the 32 Subdivisions of Scotland, council areas of Scotland, as well as a Orkney (Scottish Parliament constituency), constituency of the Scottish Parliament, a Lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area, and an counties of Scotland, historic county. The local council is Orkney Islands Council, one of only three councils in Scotland with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Thermal Collector
A solar thermal collector collects heat by absorbing sunlight. The term "solar collector" commonly refers to a device for solar hot water heating, but may refer to large power generating installations such as solar parabolic troughs and solar towers or non water heating devices such as solar air heaters. Solar thermal collectors are either non-concentrating or concentrating. In non-concentrating collectors, the aperture area (i.e., the area that receives the solar radiation) is roughly the same as the absorber area (i.e., the area absorbing the radiation). A common example of such a system is a metal plate that is painted a dark color to maximize the absorption of sunlight. The energy is then collected by cooling the plate with a working fluid, often water or glycol running in pipes attached to the plate. Concentrating collectors have a much larger aperture than the absorber area. The aperture is typically in the form of a mirror that is focussed on the absorber, which in mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UK Miners' Strike (1972)
The 1972 UK miners' strike was a major dispute over pay between the National Union of Mineworkers (NUM) and the Conservative Edward Heath government of the United Kingdom. Miners' wages had not kept pace with those of other industrial workers since 1960. The strike began on 9 January 1972 and ended on 28 February 1972, when the miners returned to work. The strike was called by the National Executive Committee of the NUM and ended when the miners accepted an improved pay offer in a ballot. It was the first time since 1926 that British miners had been on official strike, but there had been a widespread unofficial strike in 1969. Background Competition from cheap oil imports arrived in the late 1950s and the coal industry began to suffer from increasing losses. In 1960 Alf Robens became the chairman of the National Coal Board (NCB), and he introduced a policy concentrating on the most productive pits. During his ten-year tenure, productivity increased by 70%, but with far fewer pit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
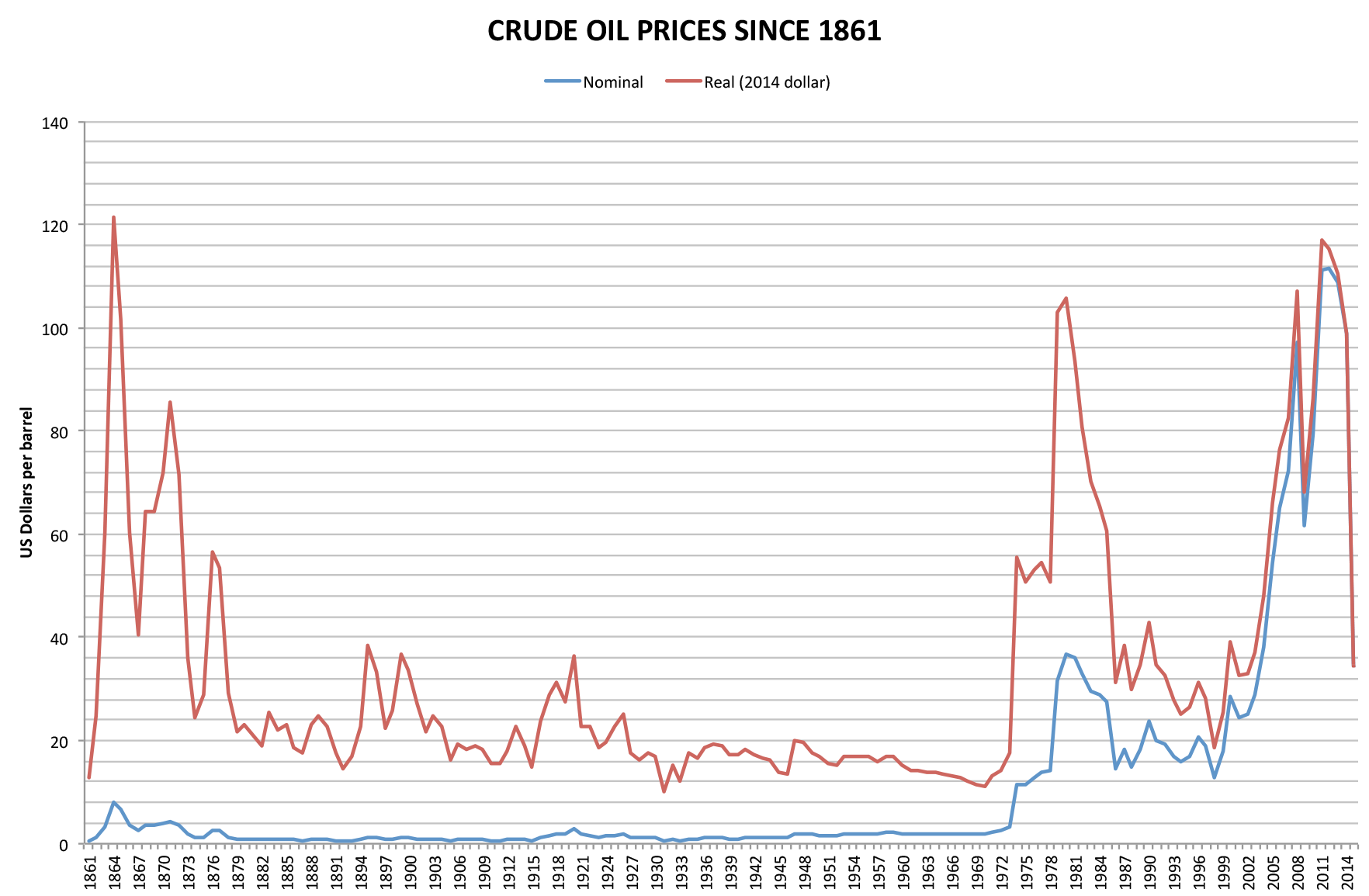
1973 Oil Crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supported Israel during the Yom Kippur War. The initial nations targeted were Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom and the United States, though the embargo also later extended to Portugal, Rhodesia and South Africa. By the end of the embargo in March 1974, the price of oil had risen nearly 300%, from US to nearly globally; US prices were significantly higher. The embargo caused an oil crisis, or "shock", with many short- and long-term effects on global politics and the global economy. It was later called the "first oil shock", followed by the 1979 oil crisis, termed the "second oil shock". Background Arab-Israeli conflict Ever since the recreation of the State of Israel in 1948 there has been Arab–Israeli conflict in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UK Electricity Generation By Type Of Fuel, 1998-2020
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 1707 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argyll And Bute
Argyll and Bute ( sco, Argyll an Buit; gd, Earra-Ghàidheal agus Bòd, ) is one of 32 unitary authority council areas in Scotland and a lieutenancy area. The current lord-lieutenant for Argyll and Bute is Jane Margaret MacLeod (14 July 2020). The administrative centre for the council area is in Lochgilphead at Kilmory Castle, a 19th-century Gothic Revival building and estate. The current council leader is Robin Currie, a councillor for Kintyre and the Islands. Description Argyll and Bute covers the second-largest administrative area of any Scottish council. The council area adjoins those of Highland, Perth and Kinross, Stirling and West Dunbartonshire. Its border runs through Loch Lomond. The present council area was created in 1996, when it was carved out of the Strathclyde region, which was a two-tier local government region of 19 districts, created in 1975. Argyll and Bute merged the existing Argyll and Bute district and one ward of the Dumbarton district. The Dumbart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruachan Power Station
The Cruachan Power Station (also known as the Cruachan Dam) is a pumped-storage hydroelectric power station in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. The scheme can provide 440 MW of power and produced 705 GWh in 2009. The turbine hall is located inside Ben Cruachan, and the scheme takes water between Cruachan Reservoir to Loch Awe, a height difference of . It is one of only four pumped storage power stations in the UK, and is capable of providing a black start capability to the National Grid. Construction began in 1959 to coincide with the Hunterston A nuclear power station in Ayrshire. Cruachan uses cheap off-peak electricity generated at night to pump water to the higher reservoir, which can then be released during the day to provide power as necessary. The power station is open to visitors, and around 50,000 tourists visit it each year. Location The power station is on the A85 road, about 8 km or 5 miles west of Dalmally, on a branch of Loch Awe leading to the River Awe, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other Renewable energy, renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of Low-carbon power, low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pumped-storage Hydroelectricity
Pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH), or pumped hydroelectric energy storage (PHES), is a type of hydroelectric energy storage used by electric power systems for load balancing. The method stores energy in the form of gravitational potential energy of water, pumped from a lower elevation reservoir to a higher elevation. Low-cost surplus off-peak electric power is typically used to run the pumps. During periods of high electrical demand, the stored water is released through turbines to produce electric power. Although the losses of the pumping process make the plant a net consumer of energy overall, the system increases revenue by selling more electricity during periods of peak demand, when electricity prices are highest. If the upper lake collects significant rainfall or is fed by a river then the plant may be a net energy producer in the manner of a traditional hydroelectric plant. Pumped-storage hydroelectricity allows energy from intermittent sources (such as solar, wind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arc Lamp
An arc lamp or arc light is a lamp that produces light by an electric arc (also called a voltaic arc). The carbon arc light, which consists of an arc between carbon electrodes in air, invented by Humphry Davy in the first decade of the 1800s, was the first practical electric light. It was widely used starting in the 1870s for street and large building lighting until it was superseded by the incandescent light in the early 20th century. It continued in use in more specialized applications where a high intensity point light source was needed, such as searchlights and movie projectors until after World War II. The carbon arc lamp is now obsolete for most of these purposes, but it is still used as a source of high intensity ultraviolet light. The term is now used for gas discharge lamps, which produce light by an arc between metal electrodes through a gas in a glass bulb. The common fluorescent lamp is a low-pressure mercury arc lamp. The xenon arc lamp, which produces a high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |