|
Religion In Slovenia
The dominant religion in Slovenia is Christianity, primarily the Catholic Church, the largest Christian denomination in the country. Other Christian groups having significant followings in the country include Eastern Orthodoxy and Protestantism (Lutheranism). Islam, Judaism and Hinduism are small minorities in Slovenia. About 18% of the population are either agnostic or atheist.Slovenia Statistical OfficePopulation by religion, statistical regions Census 2002. Religion played a significant role in the development of the Slovenian nation and of the country of Slovenia. After a centuries-long tradition of a state church, interrupted by the periods of Protestant Reformation (in the 16th century) and post–World War II socialism (which ousted religion from the public life), a degree of separation of the state and the church has been reached in independent Slovenia. In February 2007 Slovenia passed a new Religious Freedom Act with a bias towards the Catholic Church (particularl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church In Slovenia
, native_name_lang = , image = File:StNicholas-Ljubljana.JPG , imagewidth = 200px , alt = , caption = Saint Nicholas Cathedral, Ljubljana , abbreviation = , type = National polity , main_classification = Catholic Church, Catholic , orientation = Christianity , scripture = Bible , theology = Catholic theology , polity = Episcopal Polity, Episcopal , governance = Episcopal Conference of Slovenia, ŠKS , structure = , leader_title = Pope , leader_name = Pope Francis, Francis , leader_title1 = , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = , leader_title3 = , leader_name3 = , fellowships_type = , fellowships = , fellowships_type1 = , fellowships1 = , division_type = , division = , division_type1 = , division1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socialism
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the economic, political and social theories and movements associated with the implementation of such systems. Social ownership can be state/public, community, collective, cooperative, or employee. While no single definition encapsulates the many types of socialism, social ownership is the one common element. Different types of socialism vary based on the role of markets and planning in resource allocation, on the structure of management in organizations, and from below or from above approaches, with some socialists favouring a party, state, or technocratic-driven approach. Socialists disagree on whether government, particularly existing government, is the correct vehicle for change. Socialist systems are divided into non-market and market f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovenian Language
Slovene ( or ), or alternatively Slovenian (; or ), is a South Slavic language, a sub-branch that is part of the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is spoken by about 2.5 million speakers worldwide (excluding speakers of Kajkavian), mainly ethnic Slovenes, the majority of whom live in Slovenia, where it is the sole official language. As Slovenia is part of the European Union, Slovene is also one of its 24 official and working languages. Standard Slovene Standard Slovene is the national standard language that was formed in the 18th and 19th century, based on Upper and Lower Carniolan dialect groups, more specifically on language of Ljubljana and its adjacent areas. The Lower Carniolan dialect group was the dialect used in the 16th century by Primož Trubar for his writings, while he also used Slovene as spoken in Ljubljana, since he lived in the city for more than 20 years. It was the speech of Ljubljana that Trubar took as a foundation of what lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primož Trubar
Primož Trubar or Primus Truber () (1508 – 28 June 1586) was a Slovene Protestant Reformer of the Lutheran tradition, mostly known as the author of the first Slovene language printed book, the founder and the first superintendent of the Protestant Church of the Duchy of Carniola, and for consolidating the Slovenian language. Trubar introduced The Reformation in Slovenia, leading the Austrian Habsburgs to wage the Counter-Reformation, which a small Protestant community survived. Trubar is a key figure of Slovenian history and in many aspects a major historical personality. Life and work Trubar was born in the village of Rašica (now in the Municipality of Velike Lašče) in the Duchy of Carniola, then under the Habsburgs. In the years 1520–1521 he attended school in Rijeka, in 1522–1524 he continued his education in Salzburg. From there he went to Trieste under the tutorship of the Roman Catholic bishop Pietro Bonomo, where he got in touch with the Humanist writers, in pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in particular to papal authority, arising from what were perceived to be errors, abuses, and discrepancies by the Catholic Church. The Reformation was the start of Protestantism and the split of the Western Church into Protestantism and what is now the Roman Catholic Church. It is also considered to be one of the events that signified the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the early modern period in Europe.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 291–293 Prior to Martin Luther, there were many earlier reform movements. Although the Reformation is usually considered to have started with the publication of the '' Ninety-five Theses'' by Martin Luther in 1517, he was not excommunicated by Pope Leo X until January 1521. The Diet of Worms of May 152 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murska Sobota
Murska Sobota (, Slovenian abbreviation: ''MS'' ; german: Olsnitz;''Radkersburg und Luttenberg'' (map, 1:75,000). 1894. Vienna: K.u.k. Militärgeographisches Institut. hu, Muraszombat) is a town in northeastern Slovenia. It is the centre of the Municipality of Murska Sobota near the Mura River in the region of Prekmurje and is the regional capital. Name Officially, the town is known as Murska Sobota, although informally it is usually simply referred to as ''Sobota'' by its inhabitants and ''Murska'' by people from other parts of Slovenia. The settlement was first attested in written documents in 1297 as ''Belmura'' (and as ''Murazombatha'' in 1348 and ''Murazumbota'' in 1366). The traditional German name of the town is ''Olsnitz'', which is derived from the old Slovene name ''Olšnica''. The modern Slovene name is a translation of the Hungarian name ''Muraszombat,'' which was the official name of the town until 1919. In Hungarian, ''szombat'' means 'Saturday', referring to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celje
) , pushpin_map = Slovenia , pushpin_label_position = left , pushpin_map_caption = Location of the city of Celje in Slovenia , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = Traditional region , subdivision_name1 = Styria , subdivision_type2 = Statistical region , subdivision_name2 = Savinja , subdivision_type3 = Municipality , subdivision_name3 = Celje , established_title = Town rights , established_date = 11 April 1451 , founder = , named_for = , parts_type = Districts & local communities , parts_style = list , p1 = , p2 = , government_type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novo Mesto
Novo Mesto (; sl, Novo mesto; also known by other alternative names) is a city on a bend of the Krka River in the City Municipality of Novo Mesto in southeastern Slovenia, close to the border with Croatia. The town is traditionally considered the economic and cultural centre of the historical Lower Carniola region. Name Novo Mesto was attested in historical sources in 1365 as ''Růdolfswerde'' (and as ''Rudolfswerd'' in 1392 and ''Noua Mesta'' in 1419). The German name (spelled ''Rudolfswerth'' in the modern era) is a compound of the personal name ''Rudolf'' and ''wert'' 'island, peninsula, land above the water', and refers to Rudolf IV, Duke of Austria, who conferred town rights upon the settlement in 1365. The parallel German name ''Neustadtl'' was also in use (attested as ''Newestat'' in 1365, and probably a translation of the Slovene name). The name used for the settlement before 1365 is unknown. The Slovene name ''Novo mesto'' literally means 'new town'; names like this ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benedict XVI
Pope Benedict XVI ( la, Benedictus XVI; it, Benedetto XVI; german: link=no, Benedikt XVI.; born Joseph Aloisius Ratzinger, , on 16 April 1927) is a retired prelate of the Catholic church who served as the head of the Church and the sovereign of the Vatican City State from 19 April 2005 until his resignation on 28 February 2013. Benedict's election as pope occurred in the 2005 papal conclave that followed the death of Pope John Paul II. Benedict has chosen to be known by the title "pope emeritus" upon his resignation. Ordained as a priest in 1951 in his native Bavaria, Ratzinger embarked on an academic career and established himself as a highly regarded theologian by the late 1950s. He was appointed a full professor in 1958 at the age of 31. After a long career as a professor of theology at several German universities, he was appointed Archbishop of Munich and Freising and created a cardinal by Pope Paul VI in 1977, an unusual promotion for someone with little pastoral expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maribor
Maribor ( , , , ; also known by other #Name, historical names) is the second-largest city in Slovenia and the largest city of the traditional region of Styria (Slovenia), Lower Styria. It is also the seat of the City Municipality of Maribor, the seat of the Drava Statistical Region, Drava statistical region and the Eastern Slovenia region. Maribor is also the economic, administrative, educational, and cultural centre of eastern Slovenia. Maribor was first mentioned as a castle in 1164, as a settlement in 1209, and as a city in 1254. Like most Slovene Lands, Slovene ethnic territory, Maribor was under Habsburg monarchy, Habsburg rule until 1918, when Rudolf Maister and his men secured the city for the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs, which then joined the Kingdom of Serbia to form the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. In 1991 Maribor became part of independent Slovenia. Maribor, along with the Portuguese city of Guimarães, was selected the European Capital of Culture for 2012. Name M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
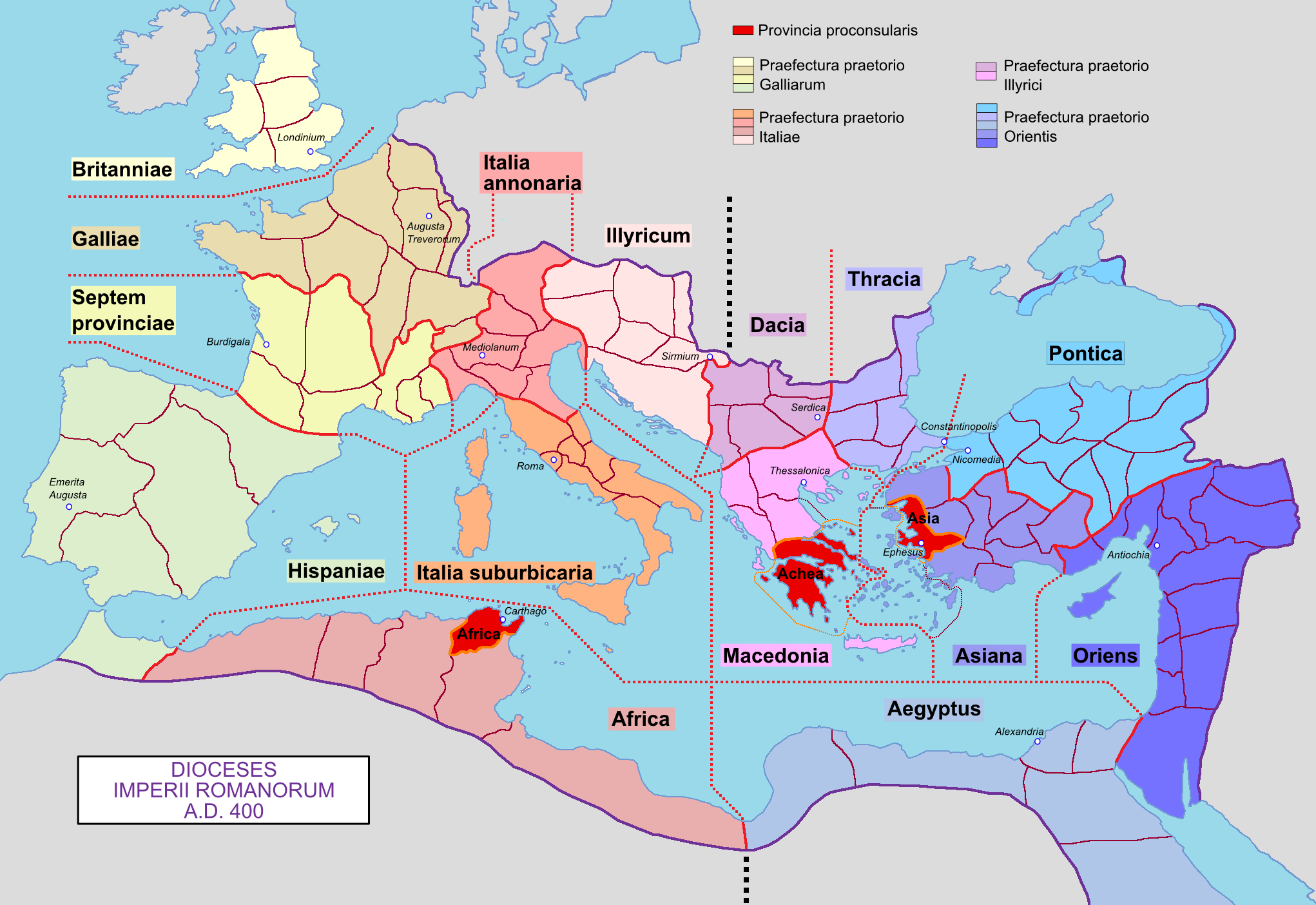
Archdiocese
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into dioceses based on the civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situation must have hardly survived Julian, 361–363. Episcopal courts are not heard of again in the East until 398 and in the West in 408. The quality of these courts was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese
In Ecclesiastical polity, church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided Roman province, provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the Roman diocese, diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek language, Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into Roman diocese, dioceses based on the Roman diocese, civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the Roman province, provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's State church of the Roman Empire, official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine the Great, Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)