|
Regions Of Belarus
At the top level of administration, Belarus is divided into six regions and one capital city. The six regions are oblasts (also known as ''voblastsi''), while the city of Minsk has a special status as the capital of Belarus. Minsk also serves as the administrative center of Minsk Region. At the second level, the regions are divided into districts (raions). The layout and extent of the regions were set in 1960 when Belarus (then the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic) was a constituent republic of the Soviet Union. History At the start of the 20th century, the boundaries of the Belarusian lands within the Russian Empire were still being defined. In 1900 it was contained within all of the Minsk and Mogilev governorates, most of Grodno Governorate, parts of Vitebsk Governorate, and parts of Vilna Governorate. World War I, the independence of Poland, as well as the 1920–1921 Polish–Soviet War affected the boundaries. In 1921, Belarus had what is now all of Minsk Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mogilev Governorate
Mogilev Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit ('' guberniya'') of the Northwestern Krai of the Russian Empire. The governorate bordered the Vitebsk Governorate to the north, the Smolensk Governorate to the east, the Chernigov Governorate to the south, and the Minsk Governorate to the west. Its capital was Mogilev, also referred to as Mogilev-on-the-Dnieper, or Mogilev Gubernskiy. The area of the Mogilev Governorate covered concomitant Belarus' Vitebsk, Mogilev and Gomel Regions. The area of the governorate was inhabited in the 10th century by the Slav tribes of the Krivichi and Radimichi. In the 14th century, the land became part of Lithuania, and later Poland. The governorate was formed in 1772, in the aftermath of the First partition of Poland, from parts of the voivodeships of Witebsk, Mścisław, Połock and Inflanty. Parts of these territories were also used to form the Pskov Governorate. In 1796, Mogilev and Polotsk Governorates were united and formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maladzyechna Voblast
Molodechno Region, also known as Maladzyechna Region or Molodechno Oblast (; ), was a region ( voblasts) of the Byelorussian SSR, the first-level administration division in the republic. Initially the region was formed on 4 December 1939, following the annexation of Western Belorussia into the Byelorussian SSR from the Second Polish Republic, as Vileyka Region. However, after the liberation of Byelorussia by the Red Army in July 1944, most of the pre-war civil administration was not possible for a number of reasons, one of which was that the city of Vileyka was heavily damaged during the war, and the transportation links between it and the rest of the region were too. However, the nearby city of Maladzyechna (Molodechno) located away from Vileyka escaped heavy destruction, and as a result, on 20 September 1944, Maladzyechna Region was established. Initially it contained 14 districts. These districts were Astravets, Ashmyany, Volozhin, Ilya, Iwye, Krivichi, Kurenets (I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
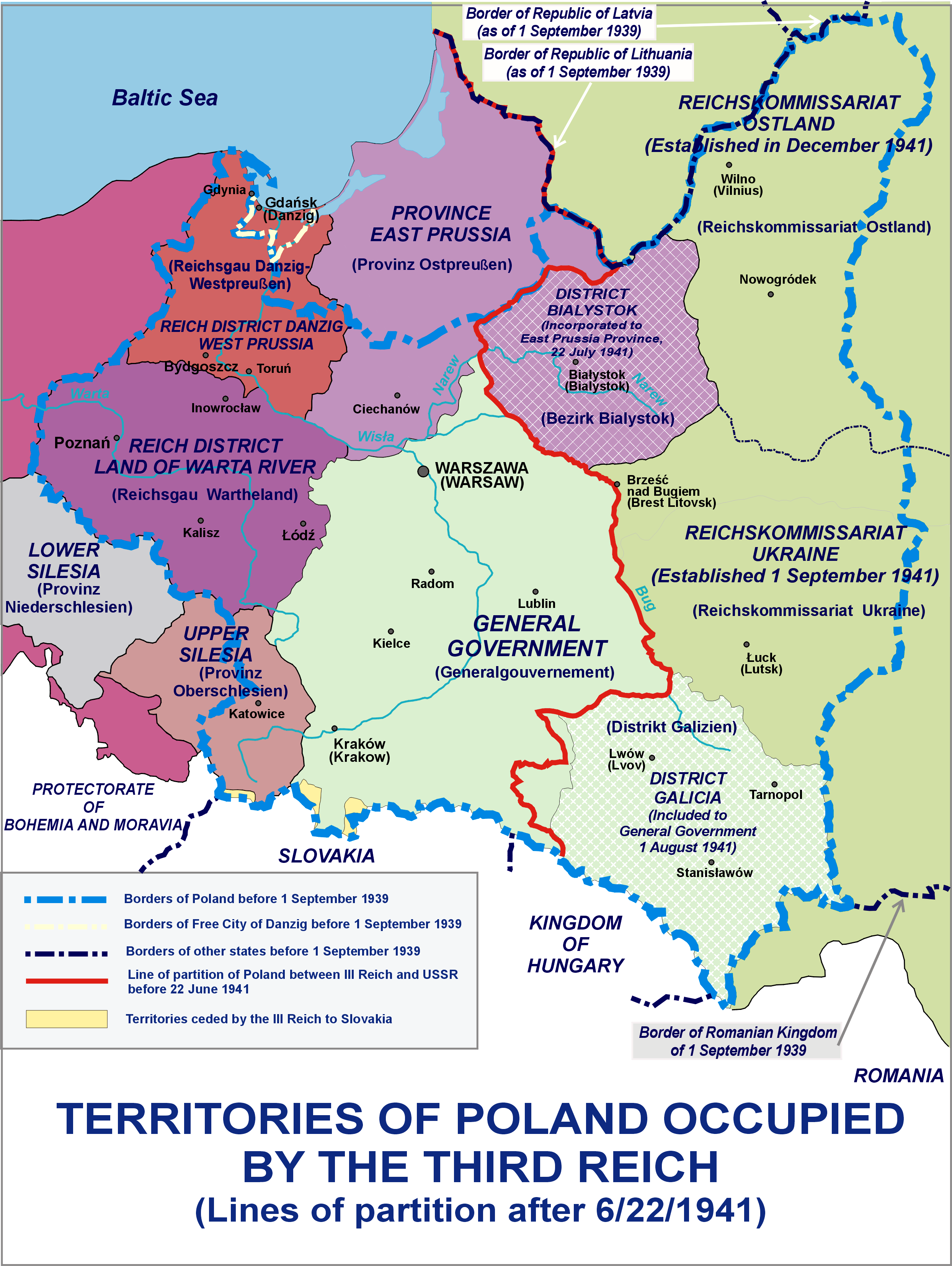
Belastok Region
Belastok Region, also known as Belastok Voblasts or Belostok Oblast, was a short-lived region (''oblast'') of the Byelorussian SSR during World War II, lasting from September 1939 until Operation Barbarossa in 1941, and again for a short period in 1944. The administrative center of the region was the city of Białystok (Belastok), which was annexed from Poland in 1939. History Integration into the Soviet Union From 23 September to October 1939, the secretary of the central committee of the Belarusian SSR lived in Bialystok due to the protracted procedures for the transfer of the territories west of Bialystok by German troops to Białystok. While the leaders of provincial boards and were immediately established at the level of the Central Committee and the Military Front Council, the lower structures (poviat, gmina) were established "in consultation with the military authorities", which most often boiled down to providing these authorities with the right to choose the right peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baranavichy Voblast
Baranavichy Region, Baranavichy Voblasts, or Baranovichi Oblast (; ) was a region ( voblasts) of the Byelorussian SSR created after the annexation of Western Belorussia into the Byelorussian SSR in November 1939. The administrative centre of the region was the city of Baranavichy. The region was originally known as Navahrudak Region but it was soon renamed after Baranavichy. The region was made up of 26 districts in 1944. These districts were Byten, Haradzishcha, Ivyanets, Iwye, Yuratsishki, Karelichy, Kletsk, Kazlowshchyna, Lyakhavichy, Lida, Lubcha, Mir, Masty, Navahrudak, Novaya Mysh, Nyasvizh, Radun, Slonim, Stowbtsy, Shchuchyn, Vasilishki, Valozhyn, Voranava, Dzyatlava, Zelva and Zhaludok. In 1944, the region was diminished after transferring the districts of Lida, Radun, Shchuchyn, Vasilishki, Voranava, Masty, Zelva and Zheludok to the newly founded Grodno Region (including remaining parts of Belastok Region) and those of Iwye, Yuratsishki and Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babruysk Voblast
Bobruysk Region or Babruysk Region (; ), created on 20 September 1944, was an administrative division of Belarus with its administrative centre at Babruysk Babruysk (, ) or Bobruysk (, ; , ) is a city in Mogilev Region, Belarus. It serves as the administrative center of Babruysk District, though it is administratively separated from the district. It is situated on the Berezina, Berezina River. Bab .... On 8 January 1954, the region was abolished and became part of Mogilev Region. External linksAdministrative divisions of Belarus: history(Russian) Former subdivisions of Belarus States and territories established in 1944 Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic {{Belarus-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prothesis (linguistics)
In linguistics, prothesis (; from post-classical Latin based on ' 'placing before'), or less commonly prosthesis (from Ancient Greek ' 'addition'), is the addition of a sound or syllable at the beginning of a word without changing the word's meaning or the rest of its morphology (linguistics), structure. A vowel or consonant added by prothesis is called prothetic or less commonly prosthetic. Prothesis is different from the adding of a prefix, which changes the meaning of a word. Prothesis is a metaplasm, a change in spelling or pronunciation. The opposite process, the loss of a sound from the beginning of a word, is called apheresis (linguistics), apheresis or aphesis. Word formation Prothesis may occur during word formation from loanword, borrowing from foreign languages or the derivation from protolanguages. Romance languages An example is that + stop consonant, stop consonant cluster, clusters (known as '), in Latin, gained a preceding in early Romance languages (Old Span ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Language
Russian is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language belonging to the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of the four extant East Slavic languages, and is the native language of the Russians. It was the ''de facto'' and ''de jure'' De facto#National languages, official language of the former Soviet Union.1977 Soviet Constitution, Constitution and Fundamental Law of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, 1977: Section II, Chapter 6, Article 36 Russian has remained an official language of the Russia, Russian Federation, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan, and is still commonly used as a lingua franca in Ukraine, Moldova, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to a lesser extent in the Baltic states and Russian language in Israel, Israel. Russian has over 253 million total speakers worldwide. It is the List of languages by number of speakers in Europe, most spoken native language in Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopædia Britannica
The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, which spans 32 volumes and 32,640 pages, was the last printed edition. Since 2016, it has been published exclusively as an online encyclopedia, online encyclopaedia. Printed for 244 years, the ''Britannica'' was the longest-running in-print encyclopaedia in the English language. It was first published between 1768 and 1771 in Edinburgh, Scotland, in three volumes. The encyclopaedia grew in size; the second edition was 10 volumes, and by its fourth edition (1801–1810), it had expanded to 20 volumes. Its rising stature as a scholarly work helped recruit eminent contributors, and the 9th (1875–1889) and Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition, 11th editions (1911) are landmark encyclopaedias for scholarship and literary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byelorussian SSR
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR, Byelorussian SSR or Byelorussia; ; ), also known as Soviet Belarus or simply Belarus, was a republic of the Soviet Union (USSR). It existed between 1920 and 1922 as an independent state, and afterwards as one of fifteen constituent republics of the USSR from 1922 to 1991, with its own legislation from 1990 to 1991. The republic was ruled by the Communist Party of Byelorussia. It was also known as the ''White Russian Soviet Socialist Republic''. Following the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk in March 1918, which ended Russia's involvement in World War I, the Belarusian Democratic Republic (BDR) was proclaimed under German occupation; however, as German troops left, the Socialist Soviet Republic of Byelorussia was established in its place by the Bolsheviks in December, and it was later merged with the Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic in 1919 to form the Socialist Soviet Republic of Lithuania and Belorussia, which ceased to ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Soviet War
The Polish–Soviet War (14 February 1919 – 18 March 1921) was fought primarily between the Second Polish Republic and the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, following World War I and the Russian Revolution. After the collapse of the Central Powers and the Armistice of 11 November 1918, Vladimir Lenin's Soviet Russia annulled the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk and moved forces westward to reclaim the ''Ober Ost'' regions abandoned by the Germans. Lenin viewed the newly independent Poland as a critical route for spreading communist revolutions into Europe. Meanwhile, Polish leaders, including Józef Piłsudski, aimed to restore Poland's First Partition of Poland, pre-1772 borders and secure the country's position in the region. Throughout 1919, Polish forces occupied much of present-day Lithuania and Belarus, emerging victorious in the Polish–Ukrainian War. However, Soviet forces regained strength after their victories in the Russian Civil War, and Symon Petliura, lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |