|
Regional People's Representative Council
In Indonesia, a Regional House of Representatives ( id, Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat Daerah, DPRD; alternatively translatable as Regional People's Representative Council) is the unicameral legislative body of an Indonesian national subdivision, at either the provincial or at the regency/city level. They are based on the amended Constitution of Indonesia, which mandated the creation of such bodies for local governance. The legislatures are present in all Indonesian provinces, and all second-level subdivisions except for the constituent municipalities of Jakarta. Etymology In Aceh, the provincial legislature is named the Aceh House of Representatives ( id, Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat Aceh), while municipal legislatures are referred to as either City House of Representatives ( id, Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat Kota) or Regency House of Representatives (( id, Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat Kabupaten). The different names were set by Law 11 of 2006 on Acehnese government. Provinces in Western New Guinea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open List
Open list describes any variant of party-list proportional representation where voters have at least some influence on the order in which a party's candidates are elected. This is as opposed to closed list, which allows only active members, party officials, or consultants to determine the order of its candidates and gives the general voter no influence at all on the position of the candidates placed on the party list. Additionally, an open list system allows voters to select individuals rather than parties. Different systems give the voter different amounts of influence to change the default ranking. The voter's choice is usually called preference vote; the voters are usually allowed one or more preference votes to the open list candidates. Variants Relatively closed A "relatively closed" open list system is one where a candidate must get a ''full quota'' of votes on their own to be assured of winning a seat. (This quota, broadly speaking, is the total number of votes cast d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1971 Indonesian Legislative Election
Legislative elections were held in Indonesia on 3 July 1971, the first under the New Order regime. There were ten participants; nine political parties and the "functional group" Golkar, which came first with more than 60 percent of the vote, resulting in an absolute majority in the People's Representative Council. Background In March 1966, President Sukarno signed a document giving Army commander Suharto authority to restore order. Suharto used this document to ban the Communist Party of Indonesia (PKI), which was officially blamed for the coup attempt the previous September. In June, the Provisional People's Consultative Assembly (MPRS) passed a resolution calling for elections to be held by 5 June 1968. Two years later, the People's Consultative Assembly elected Suharto president.Ricklefs (2008) p. 451 The army-backed New Order regime subsequently announced that the Golkar organisation would be its political vehicle. The regime stressed that Golkar ("Functional Groups") was n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open List
Open list describes any variant of party-list proportional representation where voters have at least some influence on the order in which a party's candidates are elected. This is as opposed to closed list, which allows only active members, party officials, or consultants to determine the order of its candidates and gives the general voter no influence at all on the position of the candidates placed on the party list. Additionally, an open list system allows voters to select individuals rather than parties. Different systems give the voter different amounts of influence to change the default ranking. The voter's choice is usually called preference vote; the voters are usually allowed one or more preference votes to the open list candidates. Variants Relatively closed A "relatively closed" open list system is one where a candidate must get a ''full quota'' of votes on their own to be assured of winning a seat. (This quota, broadly speaking, is the total number of votes cast d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2004 Indonesian Legislative Election
Indonesia held legislative elections on 5 April 2004 for both houses of the People's Consultative Assembly, the country's national legislature. This included all 550 seats in the People's Representative Council and 128 seats of the new Regional Representative Council. Final results of the popular vote tally showed that Golkar, the former ruling party of the New Order (Indonesia), New Order era, received the most votes. It had lost to the Indonesian Democratic Party – Struggle in the 1999 Indonesian legislative election, 1999 legislative election. The Democratic Party (Indonesia), Democratic Party and the Prosperous Justice Party, two of the newest parties to participate in the elections, received a combined 14.8% of the popular vote. Based on the final allocation of seats in the People's Representative Council, Golkar, the Indonesian Democratic Party – Struggle, the National Awakening Party, the United Development Party, the Democratic Party, the Prosperous Justice Party, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Term Limits
A term limit is a legal restriction that limits the number of terms an officeholder may serve in a particular elected office. When term limits are found in presidential and semi-presidential systems they act as a method of curbing the potential for monopoly, where a leader effectively becomes " president for life". This is intended to protect a republic from becoming a ''de facto'' dictatorship. Term limits may be applied as a lifetime limit on the number of terms an officeholder may serve, or the restrictions may be applied as a limit on the number of consecutive terms they may serve. History Europe Term limits date back to Ancient Greece and the Roman Republic, as well as the Republic of Venice. In ancient Athenian democracy, many officeholders were limited to a single term. Council members were allowed a maximum of two terms. The position of Strategos could be held for an indefinite number of terms. In the Roman Republic, a law was passed imposing a limit of a single ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Court Of Indonesia
The Supreme Court of the Republic of Indonesia ( id, Mahkamah Agung Republik Indonesia) is the independent judicial arm of the state. It maintains a system of courts and sits above the other courts and is the final court of appeal. It can also re-examine cases if new evidence emerges. Jurisdiction The Supreme Court is independent as of the third amendment to the Constitution of Indonesia. The Supreme Court has oversight over the high courts (''Pengadilan Tinggi'') and district courts (''Pengadilan Negeri''). There are about 68 high courts: 31 General Courts, 29 Religious Courts, 4 Administrative Courts and 4 Military Courts. There are around 250 district courts with additional district courts being created from time to time.In late 2011, the former chief justice of the Supreme Court, Harifin A. Tumpa, said that the Indonesian government could only aim to establish district courts in 400 of the nation's 530 provinces, regencies (''kabupaten'') and municipalities (''kotamadya''). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutional Court Of Indonesia
The Constitutional Court of the Republic of Indonesia ( id, Mahkamah Konstitusi Republik Indonesia) is one of the apex courts in Indonesia along with the Indonesian Supreme Court. Its primary role is reviewing the constitutionality of statutes (''undang-undang''). It also has other functions, including resolving disputes over the powers of state institutions, settling disputes over the results of general elections, deciding on the dissolution of political parties, and supervising impeachment. The last two functions have never been exercised by the Court. The Indonesian Constitutional Court was established as a consequence of the third amendment to the Constitution of Indonesia, ratified by the People's Consultative Assembly on 9 November 2001. Between the adoption of the third Constitutional amendment and the establishment of the Constitutional Court, the duties of the Constitutional Court were carried out by the Indonesian Supreme Court.Denny Indrayana (2008), pp. 241, 266 T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Home Affairs (Indonesia)
The Ministry of Home Affairs ( id, Kementerian Dalam Negeri or ''Kemendagri'') is a ministry of the Government of Indonesia responsible for internal matters of the state. The ministry was formerly known as the Department of Home Affairs (Indonesian: ''Departemen Dalam Negeri Republik Indonesia'', abbreviated as ''Depdagri'') until 2010 when the nomenclature of the Department of Home Affairs was changed to the Ministry of Home Affairs in accordance with the Regulation of the Minister of Home Affairs Number 3 of 2010 concerning the Nomenclature of the Ministry of Home Affairs. It is headed by the Minister of Home Affairs. Starting 23 October 2019, Tito Karnavian held this office. History The Indonesian Department of Home of Affairs traces its origin to the ''Departement van Binnenlands Bestuur'' of the Dutch East Indies Government. Its main function was to oversee police force, transmigration, and agrarian matters. It existed until 1942, the year of the Japanese invasion. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-Suharto Era In Indonesia
The Post-Suharto era is the contemporary history in Indonesia, which began with the resignation of authoritarian president Suharto on 21 May 1998. Since his resignation, the country has been in a period of transition known as the Reform era ( id, Era Reformasi). This period has been characterised by a more open and liberal political-social environment. Issues over this period have included a push for a stronger democracy and civilian rule, elements of the military trying to retain their influence, a growing Islamism in politics and society, and demands for greater regional autonomy. The process of has resulted in a higher degree of freedom of speech, in contrast to the pervasive censorship under the New Order. This has led to a more open political debate in the news media and increased expression in the arts. Events that have shaped Indonesia in this period include a bombing campaign by Islamic terrorists (including the 2002 Bali bombings), with 2004 Indian Ocean earthqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
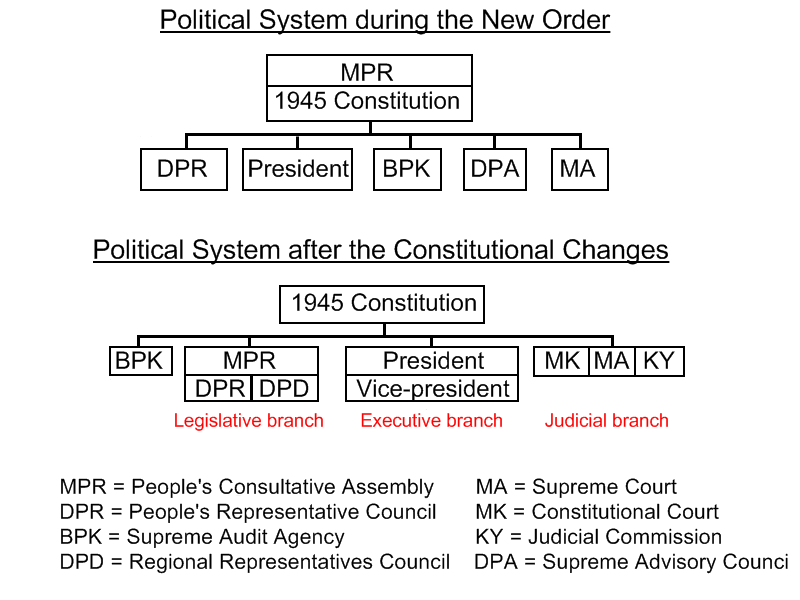
Amendments To The Constitution Of Indonesia
Four amendments to the Constitution of Indonesia was approved by the People's Consultative Assembly (MPR) on 1999 until 2002 period. Procedure to amend the constitution is dictated on Article 37 of the Constitution. The amendment is wholly processed by the legislature, on this case the MPR as a joint sitting of its two components, the People's Representative Council (DPR) and the Regional Representative Council (DPD). Amendment procedure Constitutional amendment procedure are dictated by the Article 37 of the Constitution. The current procedure were introduced by the Fourth amendment to the constitution in 2002. The article requires an amendment to be proposed by at least a third of the entire People's Consultative Assembly (MPR) members on a written form describing the proposed amendments and its justification. The quorum for a parliamentary special session to amend the constitution are set on two-thirds majority of the MPR members. An amendment proposal needs only a simple maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubber Stamp (politics)
A rubber stamp, as a political metaphor, is a person or institution with considerable ''de jure'' power but little ''de facto'' power — one that rarely or never disagrees with more powerful organizations. Historian Edward S. Ellis called this type of legislature a toy parliament. In situations where this superior official's signature may frequently be required for routine paperwork, a literal rubber stamp is used, with a likeness of their hand-written signature. In essence, the term is meant to convey an endorsement without careful thought or personal investment in the outcome, especially since it is usually expected as the stamper's duty to do so. In the situation where a dictator's legislature is a "rubber stamp", the orders they are meant to endorse are formalities they are expected to legitimize, and are usually done to create the superficial appearance of legislative and dictatorial harmony rather than because they have actual power. In a constitutional monarchy or parliame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


%2C_p168.jpg)