|
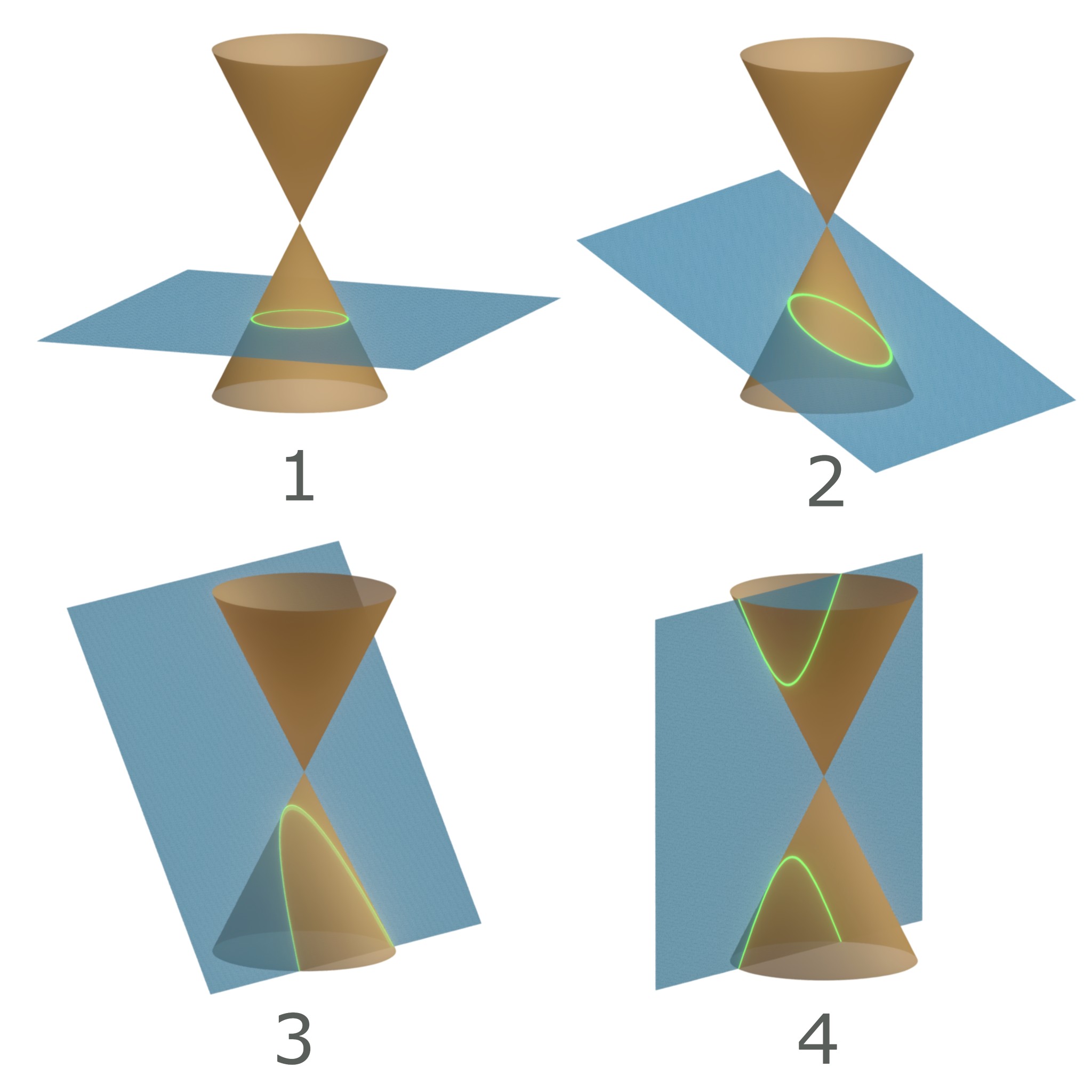
Rectangular Hyperbola
In mathematics, a hyperbola (; pl. hyperbolas or hyperbolae ; adj. hyperbolic ) is a type of smooth curve lying in a plane, defined by its geometric properties or by equations for which it is the solution set. A hyperbola has two pieces, called connected components or branches, that are mirror images of each other and resemble two infinite bows. The hyperbola is one of the three kinds of conic section, formed by the intersection of a plane and a double cone. (The other conic sections are the parabola and the ellipse. A circle is a special case of an ellipse.) If the plane intersects both halves of the double cone but does not pass through the apex of the cones, then the conic is a hyperbola. Hyperbolas arise in many ways: * as the curve representing the reciprocal function y(x) = 1/x in the Cartesian plane, * as the path followed by the shadow of the tip of a sundial, * as the shape of an open orbit (as distinct from a closed elliptical orbit), such as the orbit of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbola (PSF)
In mathematics, a hyperbola (; pl. hyperbolas or hyperbolae ; adj. hyperbolic ) is a type of smooth curve lying in a plane, defined by its geometric properties or by equations for which it is the solution set. A hyperbola has two pieces, called connected components or branches, that are mirror images of each other and resemble two infinite bows. The hyperbola is one of the three kinds of conic section, formed by the intersection of a plane and a double cone. (The other conic sections are the parabola and the ellipse. A circle is a special case of an ellipse.) If the plane intersects both halves of the double cone but does not pass through the apex of the cones, then the conic is a hyperbola. Hyperbolas arise in many ways: * as the curve representing the reciprocal function y(x) = 1/x in the Cartesian plane, * as the path followed by the shadow of the tip of a sundial, * as the shape of an open orbit (as distinct from a closed elliptical orbit), such as the orbit o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as a planet, moon, asteroid, or Lagrange point. Normally, orbit refers to a regularly repeating trajectory, although it may also refer to a non-repeating trajectory. To a close approximation, planets and satellites follow elliptic orbits, with the center of mass being orbited at a focal point of the ellipse, as described by Kepler's laws of planetary motion. For most situations, orbital motion is adequately approximated by Newtonian mechanics, which explains gravity as a force obeying an inverse-square law. However, Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, which accounts for gravity as due to curvature of spacetime, with orbits following geodesics, provides a more accurate calculation and understanding of the exact mechanics of or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directrix (conic Section)
In mathematics, a conic section, quadratic curve or conic is a curve obtained as the intersection of the Conical surface, surface of a cone (geometry), cone with a plane (mathematics), plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a special case of the ellipse, though historically it was sometimes called a fourth type. The Greek mathematics, ancient Greek mathematicians studied conic sections, culminating around 200 BC with Apollonius of Perga's systematic work on their properties. The conic sections in the Euclidean plane have various distinguishing properties, many of which can be used as alternative definitions. One such property defines a non-circular conic to be the set (mathematics), set of those points whose distances to some particular point, called a ''Focus (geometry), focus'', and some particular line, called a ''directrix'', are in a fixed ratio, called the ''Eccentricity (mathematics), eccentricity''. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focus (geometry)
In geometry, focuses or foci (), singular focus, are special points with reference to which any of a variety of curves is constructed. For example, one or two foci can be used in defining conic sections, the four types of which are the circle, ellipse, parabola, and hyperbola. In addition, two foci are used to define the Cassini oval and the Cartesian oval, and more than two foci are used in defining an ''n''-ellipse. Conic sections Defining conics in terms of two foci An ellipse can be defined as the locus of points for which the sum of the distances to two given foci is constant. A circle is the special case of an ellipse in which the two foci coincide with each other. Thus, a circle can be more simply defined as the locus of points each of which is a fixed distance from a single given focus. A circle can also be defined as the circle of Apollonius, in terms of two different foci, as the locus of points having a fixed ratio of distances to the two foci. A parabola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eccentricity (mathematics)
In mathematics, the eccentricity of a conic section is a non-negative real number that uniquely characterizes its shape. More formally two conic sections are similar if and only if they have the same eccentricity. One can think of the eccentricity as a measure of how much a conic section deviates from being circular. In particular: * The eccentricity of a circle is zero. * The eccentricity of an ellipse which is not a circle is greater than zero but less than 1. * The eccentricity of a parabola is 1. * The eccentricity of a hyperbola is greater than 1. * The eccentricity of a pair of lines is \infty Definitions Any conic section can be defined as the locus of points whose distances to a point (the focus) and a line (the directrix) are in a constant ratio. That ratio is called the eccentricity, commonly denoted as . The eccentricity can also be defined in terms of the intersection of a plane and a double-napped cone associated with the conic section. If the cone is orie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordinate Axes
A Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular oriented lines, measured in the same unit of length. Each reference coordinate line is called a ''coordinate axis'' or just ''axis'' (plural ''axes'') of the system, and the point where they meet is its ''origin'', at ordered pair . The coordinates can also be defined as the positions of the perpendicular projections of the point onto the two axes, expressed as signed distances from the origin. One can use the same principle to specify the position of any point in three-dimensional space by three Cartesian coordinates, its signed distances to three mutually perpendicular planes (or, equivalently, by its perpendicular projection onto three mutually perpendicular lines). In general, ''n'' Cartesian coordinates (an element of real ''n''-space) specify the point in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetry
Symmetry (from grc, συμμετρία "agreement in dimensions, due proportion, arrangement") in everyday language refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, "symmetry" has a more precise definition, and is usually used to refer to an object that is invariant under some transformations; including translation, reflection, rotation or scaling. Although these two meanings of "symmetry" can sometimes be told apart, they are intricately related, and hence are discussed together in this article. Mathematical symmetry may be observed with respect to the passage of time; as a spatial relationship; through geometric transformations; through other kinds of functional transformations; and as an aspect of abstract objects, including theoretic models, language, and music. This article describes symmetry from three perspectives: in mathematics, including geometry, the most familiar type of symmetry for many people; in science and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptote
In analytic geometry, an asymptote () of a curve is a line such that the distance between the curve and the line approaches zero as one or both of the ''x'' or ''y'' coordinates tends to infinity. In projective geometry and related contexts, an asymptote of a curve is a line which is tangent to the curve at a point at infinity. The word asymptote is derived from the Greek ἀσύμπτωτος (''asumptōtos'') which means "not falling together", from ἀ priv. + σύν "together" + πτωτ-ός "fallen". The term was introduced by Apollonius of Perga in his work on conic sections, but in contrast to its modern meaning, he used it to mean any line that does not intersect the given curve. There are three kinds of asymptotes: ''horizontal'', ''vertical'' and ''oblique''. For curves given by the graph of a function , horizontal asymptotes are horizontal lines that the graph of the function approaches as ''x'' tends to Vertical asymptotes are vertical lines near which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branch (mathematics)
In mathematics, a principal branch is a function which selects one branch ("slice") of a multi-valued function. Most often, this applies to functions defined on the complex plane. Examples Trigonometric inverses Principal branches are used in the definition of many inverse trigonometric functions, such as the selection either to define that :\arcsin:1,+1rightarrow\left \frac,\frac\right/math> or that :\arccos:1,+1rightarrow ,\pi/math>. Exponentiation to fractional powers A more familiar principal branch function, limited to real numbers, is that of a positive real number raised to the power of . For example, take the relation , where is any positive real number. This relation can be satisfied by any value of equal to a square root of (either positive or negative). By convention, is used to denote the positive square root of . In this instance, the positive square root function is taken as the principal branch of the multi-valued relation . Complex logarithms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Navigation
Hyperbolic navigation is a class of radio navigation systems in which a navigation receiver instrument is used to determine location based on the difference in timing ( phase) of radio waves received from radio navigation beacon transmitters. Such systems rely on the ability of two widely separated stations to broadcast a signal that is highly correlated in time. Typical systems either broadcast short pulses at the same time, or continual signals that are identical in phase. A receiver located at the midpoint between the two stations will receive the signals at the same time or have identical phase, but at any other location the signal from the closer station will be received first or have a different phase. Determining the location of a receiver requires that the two synchronized stations be tuned in at the same time so the signals can be compared. This reveals a ''difference'' in time, corresponding to a relative distance closer to one station or the other. Plotting all the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subatomic Particle
In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that composes an atom. According to the Standard Model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon). Particle physics and nuclear physics study these particles and how they interact. Experiments show that light could behave like a stream of particles (called photons) as well as exhibiting wave-like properties. This led to the concept of wave–particle duality to reflect that quantum-scale behave like both particles and waves; they are sometimes called wavicles to reflect this. Another concept, the uncertainty principle, states that some of their properties taken together, such as their simultaneous position and momentum, cannot be measured exactly. The wave–particle duality has been shown to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutherford Scattering
In particle physics, Rutherford scattering is the elastic scattering of charged particles by the Coulomb interaction. It is a physical phenomenon explained by Ernest Rutherford in 1911 that led to the development of the planetary Rutherford model of the atom and eventually the Bohr model. Rutherford scattering was first referred to as Coulomb scattering because it relies only upon the static electricity, static electric (Coulomb) potential, and the minimum distance between particles is set entirely by this potential. The classical Rutherford scattering process of alpha particles against gold atomic nucleus, nuclei is an example of "elastic scattering" because neither the alpha particles nor the gold nuclei are internally excited. The Rutherford formula (see below) further neglects the recoil kinetic energy of the massive target nucleus. The initial discovery was made by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden in 1909 when they performed the Geiger–Marsden experiment, gold foil experime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |