|
Raphignathoidea
Raphignathoidea is a superfamily of the Acari (mite) order Trombidiformes, comprising 1087 species in 62 genera and 12 families. Morphology Adult Raphignathoidea are generally oval or round in shape, with 2 pairs of vertical setae on the prodorsum (rarely 3), 2 pairs of scapular setae (rarely 1 or 3), and eyes and postocular bodies usually present. The second and third leg pairs are separated by a gap except in families Cryptognathidae and Raphignathidae. The legs usually bear tarsal claws at the ends. Females and males look similar except that males are often tapered posteriorly, the first and second pseudanal setae are often reduced, the genital and anal openings are fused, and an aedeagus (male reproductive organ) is present. Life cycle Most Raphignathoidea have five life stages: egg, larva, protonymph, deutonymph and adult. The species ''Agistemus exsertus'' also has a prelarval stage, while the genus ''Raphignathus'' and the family Xenocaligonellididae also have a th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stigmaeidae
Stigmaeidae is a family of prostigmatan mites in the order Trombidiformes. At over 600 species, it is the largest family in superfamily Raphignathoidea. It has a worldwide distribution. Description As mites, Stigmaeidae have unsegmented bodies with eight legs (six in larvae). They can be recognised by: prodorsum without transversal groove, sacs or tubes; suranal and aggenital shields separate; cheliceral bases usually separate (rarely fused or conjunct); palps stout with tibial claws at least 1/3 length of tarsus; peritreme absent. Males differ from females in being somewhat tapered posteriorly. Life cycle The stigmaeid life cycle has the five stages of egg, larva, protonymph, deutonymph and adult. The larva and two nymph stages are also each followed by a quiescent period. The whole life cycle takes no more than four weeks. Males usually reach adulthood slightly faster than females, allowing them to mate with females as soon as the latter have reached adulthood. Offspr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
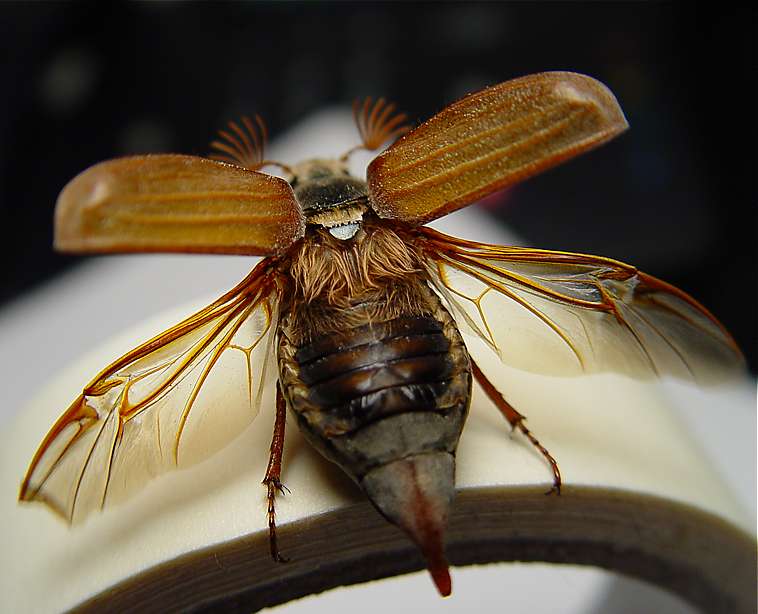
Dytiscacaridae
''Dytiscacarus'' is a genus of Trombidiformes, trombidiform mites that are sub-elytral parasites of diving beetles (Dytiscidae). It is in the Monotypic taxon, monotypic Family (biology), family Dytiscacaridae, and comprises three species. It has been recorded from Iran and the United States. Morphology The family has three distinctive features not found in other mites (Autapomorphy, autapomorphies): the infracapitulum has a pair of gnathosomatic neostigmata on its dorsal face, the movable Chelicerae, cheliceral stylets are sheathed and can be deeply retracted into the Cephalothorax, prosoma, and the pretarsi of all legs lack empodia and bear paired claws strongly modified into sclerotized tenent-like structures (to attach to hosts). These features occur in all of the active life stages. Dytiscacaridae are also Sexual dimorphism, sexually dimorphic: females have the fourth pair of legs elongated (possibly for greater mobility), while males have a caudal copulatory capsule. Biol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Families
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideally, families offer predictability, structure, and safety as members mature and learn to participate in the community. Historically, most human societies use family as the primary locus of attachment, nurturance, and socialization. Anthropologists classify most family organizations as matrifocal (a mother and her children), patrifocal (a father and his children), conjugal (a wife, her husband, and children, also called the nuclear family), avuncular (a man, his sister, and her children), or extended (in addition to parents and children, may include grandparents, aunts, uncles, or cousins). The field of genealogy aims to trace family lineages through history. The family is also an important economic unit studied in family economics. The w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caterpillar
Caterpillars ( ) are the larval stage of members of the order Lepidoptera (the insect order comprising butterflies and moths). As with most common names, the application of the word is arbitrary, since the larvae of sawflies (suborder Symphyta) are commonly called caterpillars as well. Both lepidopteran and symphytan larvae have eruciform body shapes. Caterpillars of most species eat plant material ( often leaves), but not all; some (about 1%) eat insects, and some are even cannibalistic. Some feed on other animal products. For example, clothes moths feed on wool, and horn moths feed on the hooves and horns of dead ungulates. Caterpillars are typically voracious feeders and many of them are among the most serious of agricultural pests. In fact, many moth species are best known in their caterpillar stages because of the damage they cause to fruits and other agricultural produce, whereas the moths are obscure and do no direct harm. Conversely, various species of caterpi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
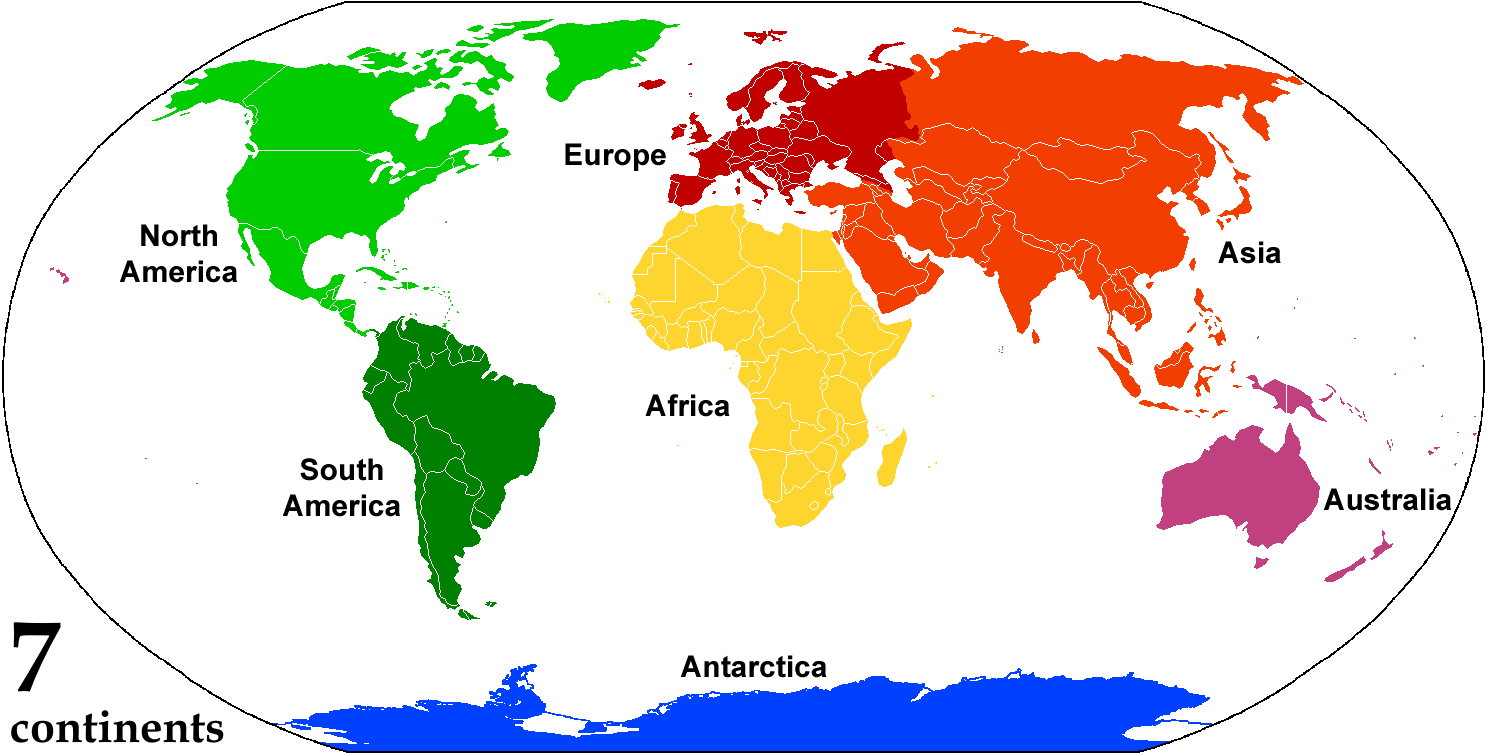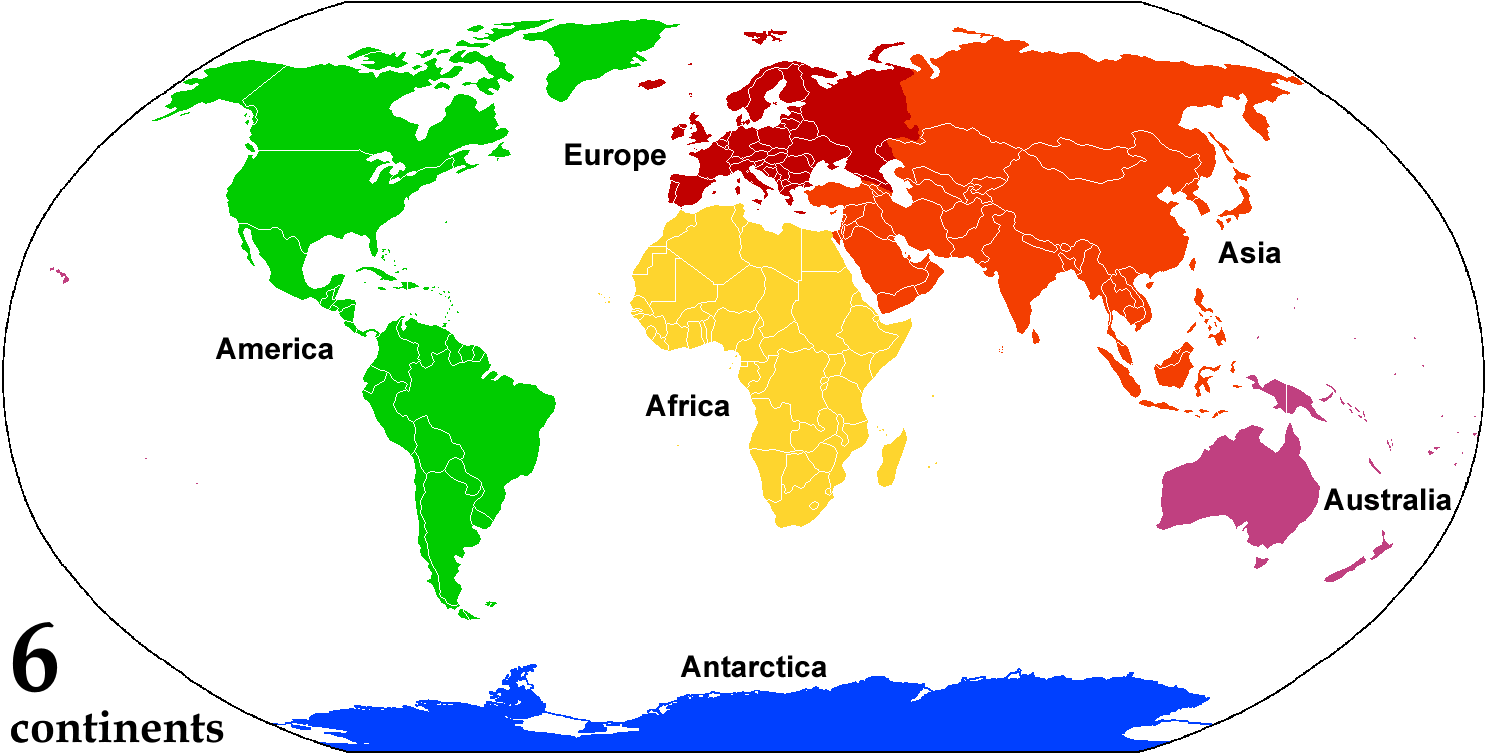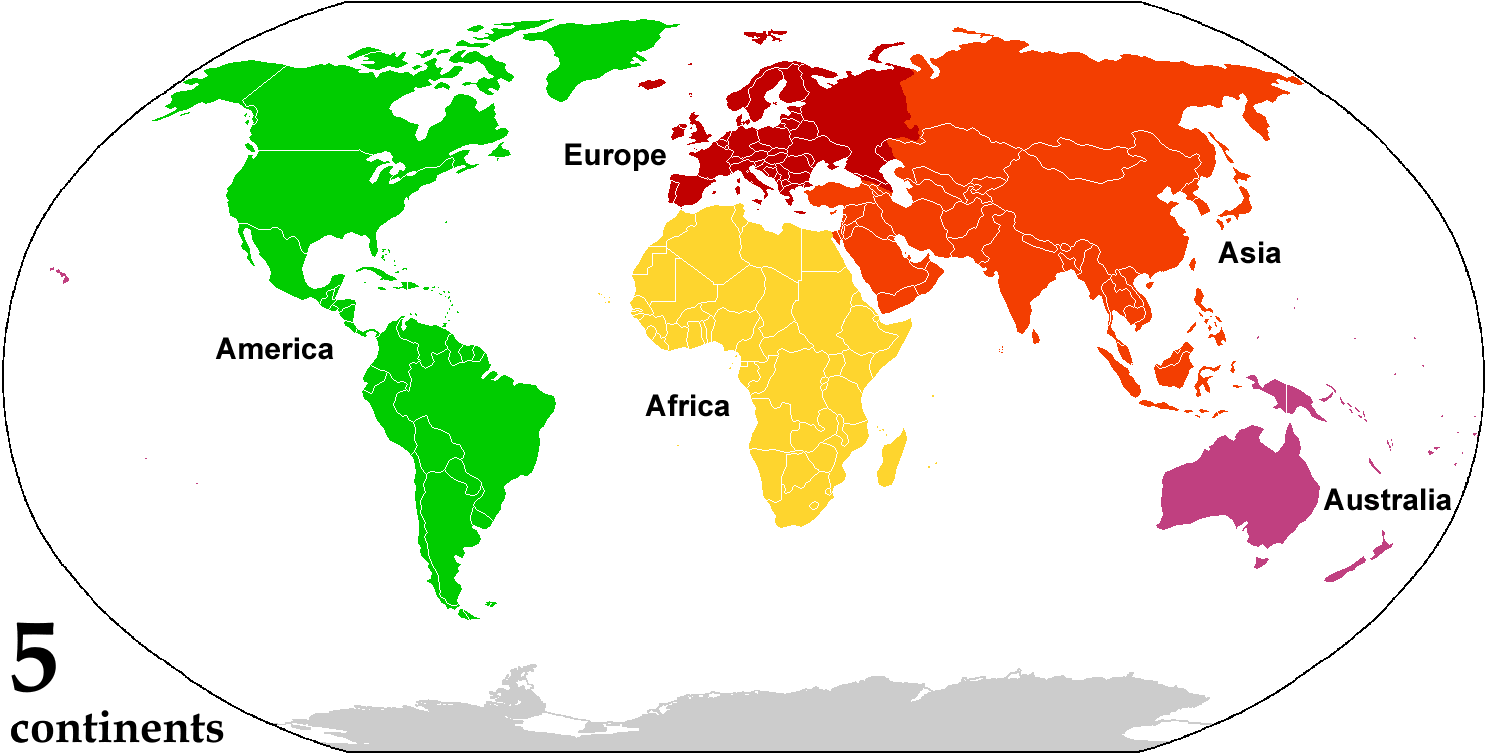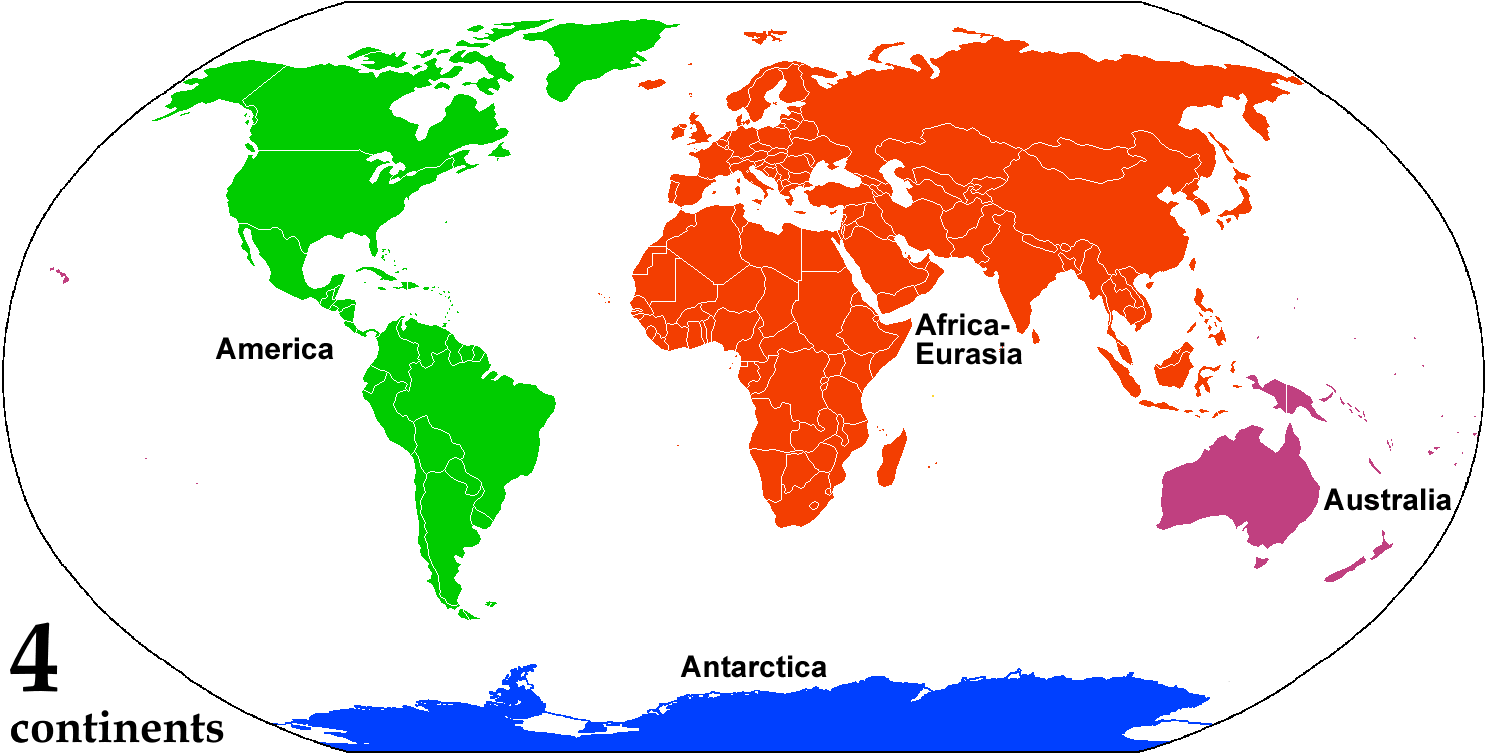
Continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven regions are: Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia. "Most people recognize seven continents—Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia, from largest to smallest—although sometimes Asia and Europe are considered a single continent, Eurasia." Variations with fewer continents may merge some of these, for example America, Eurasia, or Afro-Eurasia are sometimes treated as single continents, which can bring the total number as low as four. Zealandia, a largely submerged mass of continental crust, has also been described as a continent. Oceanic islands are frequently grouped with a nearby continent to divide all the world's land into geographical regions. Under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dytiscidae
The Dytiscidae – based on the Greek ''dytikos'' (δυτικός), "able to dive" – are the predaceous diving beetles, a family of water beetles. They occur in virtually any freshwater habitat around the world, but a few species live among leaf litter. The adults of most are between long, though much variation is seen between species. The European ''Dytiscus latissimus'' and Brazilian ''Megadytes ducalis'' are the largest, reaching up to and respectively. In contrast, the smallest is likely the Australian ''Limbodessus atypicali'' of subterranean waters, which only is about long. Most are dark brown, blackish, or dark olive in color with golden highlights in some subfamilies. The larvae are commonly known as water tigers due to their voracious appetite. They have short, but sharp mandibles and immediately upon biting, they deliver digestive enzymes into prey to suck their liquefied remains. The family includes more than 4,000 described species in numerous genera. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elytra
An elytron (; ; , ) is a modified, hardened forewing of beetles (Coleoptera), though a few of the true bugs (Hemiptera) such as the family Schizopteridae are extremely similar; in true bugs, the forewings are called hemelytra (sometimes alternatively spelled as "hemielytra"), and in most species only the basal half is thickened while the apex is membranous, but when they are entirely thickened the condition is referred to as "coleopteroid". An elytron is sometimes also referred to as a shard. Description The elytra primarily serve as protective wing-cases for the hindwings underneath, which are used for flying. To fly, a beetle typically opens the elytra and then extends the hindwings, flying while still holding the elytra open, though many beetles in the families Scarabaeidae and Buprestidae can fly with the elytra closed (e.g., most Cetoniinae; ). In a number of groups, the elytra are reduced to various degrees, (e.g., the beetle families Staphylinidae and Ripiphoridae), or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasites
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), Disease vector, vector-transmitted paras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
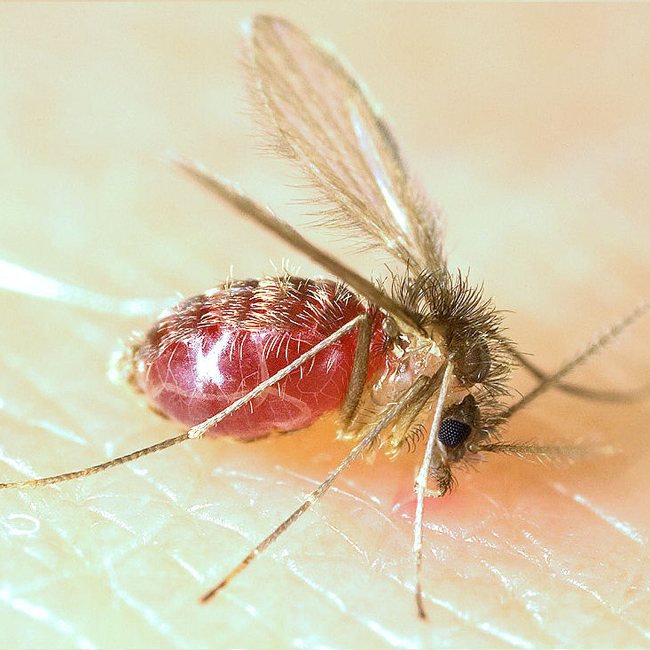
Phlebotominae
The Phlebotominae are a subfamily of the family Psychodidae. In several countries, their common name is sandfly; but that name is also applied to other flies. The Phlebotominae include many genera of blood-feeding (hematophagous) flies, including the primary vectors of leishmaniasis, bartonellosis and pappataci fever. In the New World, leishmaniasis is spread by sand flies in the genus ''Lutzomyia'', which commonly live in caves, where their main hosts are bats. In the Old World, sand flies in the genus ''Phlebotomus'' spread leishmaniasis. Phlebotomine females, and only females, suck blood from various mammals, reptiles and birds. Some species are selective, whereas others bite any suitable host they find. Some species can produce one clutch of eggs before their first blood meal; such females are said to practise autogenous or partly autogenous reproduction. Other species need a blood meal before they can produce any eggs at all; they are said to practise anautogenous reproduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |