|
Rang Avadhoot
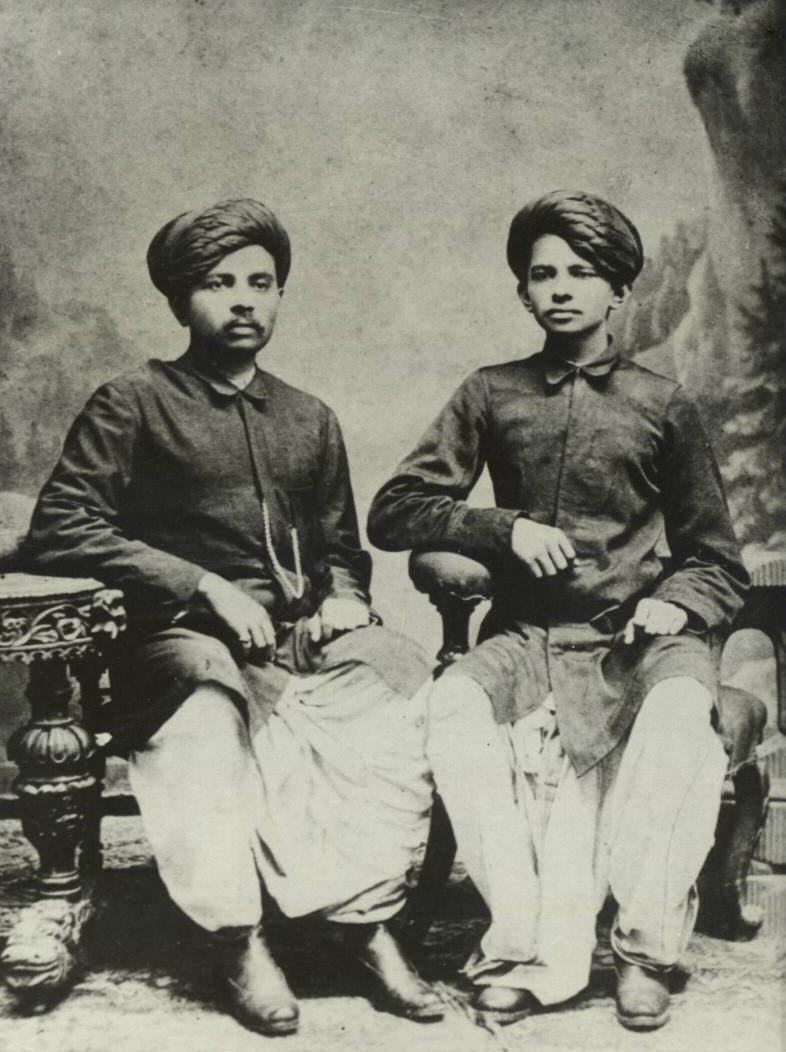
Rang Avadhoot, born Pandurang Vitthalapant Valame, (21 November 1898 – 19 November 1968) was a mystic saint-poet belonging to Datta-panth (Gurucharita tradition of Dattatreya) of Hinduism. He was a social worker and independence activist before accepting asceticism. He is credited with the expansion of Datta-panth in Gujarat state of India. He has written more than 45 works, mostly concerning spirituality and devotion. Early life Rang Avadhoot was born Pandurang Vitthalapant Valame on 21 November 1898 (Kartika Sud 9 according to Hindu calendar) in Godhra in a Marathi family of Vitthalpant Jairam Valame and Rukmini (née Kashi). His family belonged to Devle village (now in Sangameshwar taluka of Ratnagiri district in Maharashtra). His father moved to Godhra as a caretaker (pujari) of Viththal temple. His father died in a plague in 1902. He had a brother named Narayan. He met his spiritual teacher (guru) Vasudevanand Saraswati (Tembe Swami) in 1905. He was religiously inclin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global population, known as Hindus. The word ''Hindu'' is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, many practitioners refer to their religion as '' Sanātana Dharma'' ( sa, सनातन धर्म, lit='the Eternal Dharma'), a modern usage, which refers to the idea that its origins lie beyond human history, as revealed in the Hindu texts. Another endonym is ''Vaidika dharma'', the dharma related to the Vedas. Hinduism is a diverse system of thought marked by a range of philosophies and shared concepts, rituals, cosmological systems, pilgrimage sites, and shared textual sources that discuss theology, metaphysics, mythology, Vedic yajna, yoga, agamic rituals, and temple building, among other to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matriculated
Matriculation is the formal process of entering a university, or of becoming eligible to enter by fulfilling certain academic requirements such as a matriculation examination. Australia In Australia, the term "matriculation" is seldom used now. In the late 1960s and early 1970s, all states replaced the matriculation examination with either a certificate, such as the Higher School Certificate (HSC) in Victoria and NSW, or a university entrance exam such as the Tertiary Entrance Exam in Western Australia. These have all been renamed (except in NSW) as a state-based certificate, such as the Victorian Certificate of Education (VCE) or the Western Australian Certificate of Education (WACE). Bangladesh In Bangladesh, the "Matriculation" is the Secondary School Examination (SSC) taken at year 10, and the Intermediate Exams is the Higher Secondary Examination (HSC) taken at year 12. Bangladesh, like the rest of Indian sub-continent, still uses terms such as Matriculation Exams and Inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapas (Indian Religions)
Tapas (Sanskrit: तपस्) is a variety of austere spiritual meditation practices in Indian religions. In Jainism, it means asceticism (austerities, body mortification); in Buddhism, it denotes spiritual practices including meditation and self-discipline; and in the different traditions within Hinduism it means a spectrum of practices ranging from asceticism, inner cleansing to self-discipline by meditation practices. The ''Tapas'' practice often involves solitude, and is a part of monastic practices that are believed to be a means to moksha (liberation, salvation). In the Vedas literature of Hinduism, fusion words based on ''tapas'' are widely used to expound several spiritual concepts that develop through heat or inner energy, such as meditation, any process to reach special observations and insights, the spiritual ecstasy of a yogin or ''Tāpasa'' (a vṛddhi derivative meaning "a practitioner of austerities, an ascetic"), even warmth of sexual intimacy.Kaelber, W. O. (197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navajivan Trust
''Navajivan Trust'' is a publishing house based in Ahmedabad, India. It was founded by Mahatma Gandhi in 1929 and has published more than 800 titles in , , and other languages to date. Earlier, ''Navajivan'' referred to a weekly newspaper published by Gandhi, in , from 1919 (September 7) to 1931, from Ahmedabad. Object ...
|
Swami Anand
Swami Anand (1887 – 25 January 1976) was a monk, a Gandhian activist and a Gujarati writer from India. He was the manager of Gandhi's publications such as ''Navajivan'' and ''Young India'' and inspired Gandhi to write his autobiography, ''The Story of My Experiments with Truth''. He wrote sketches, memoir, biographies, philosophy, travelogues and translated some works. Biography Early life Swami Anand was born Himmatlal on 8 September 1887 at Shiyani village near Wadhwan to Ramchandra Dave (Dwivedi) and Parvati in Audichya Brahmin family. His father was a teacher. He was among seven siblings. He was brought up and educated in Bombay. At the age of ten, he left home in opposition to marriage and due to an offer by a monk to show him God. He wandered for three years with several different monks. He took a vow of renunciation while still in his teens, took on the name Swami Anand and became a monk with the Ramakrishna Mission. He also lived at the Advaita Ashram where he s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
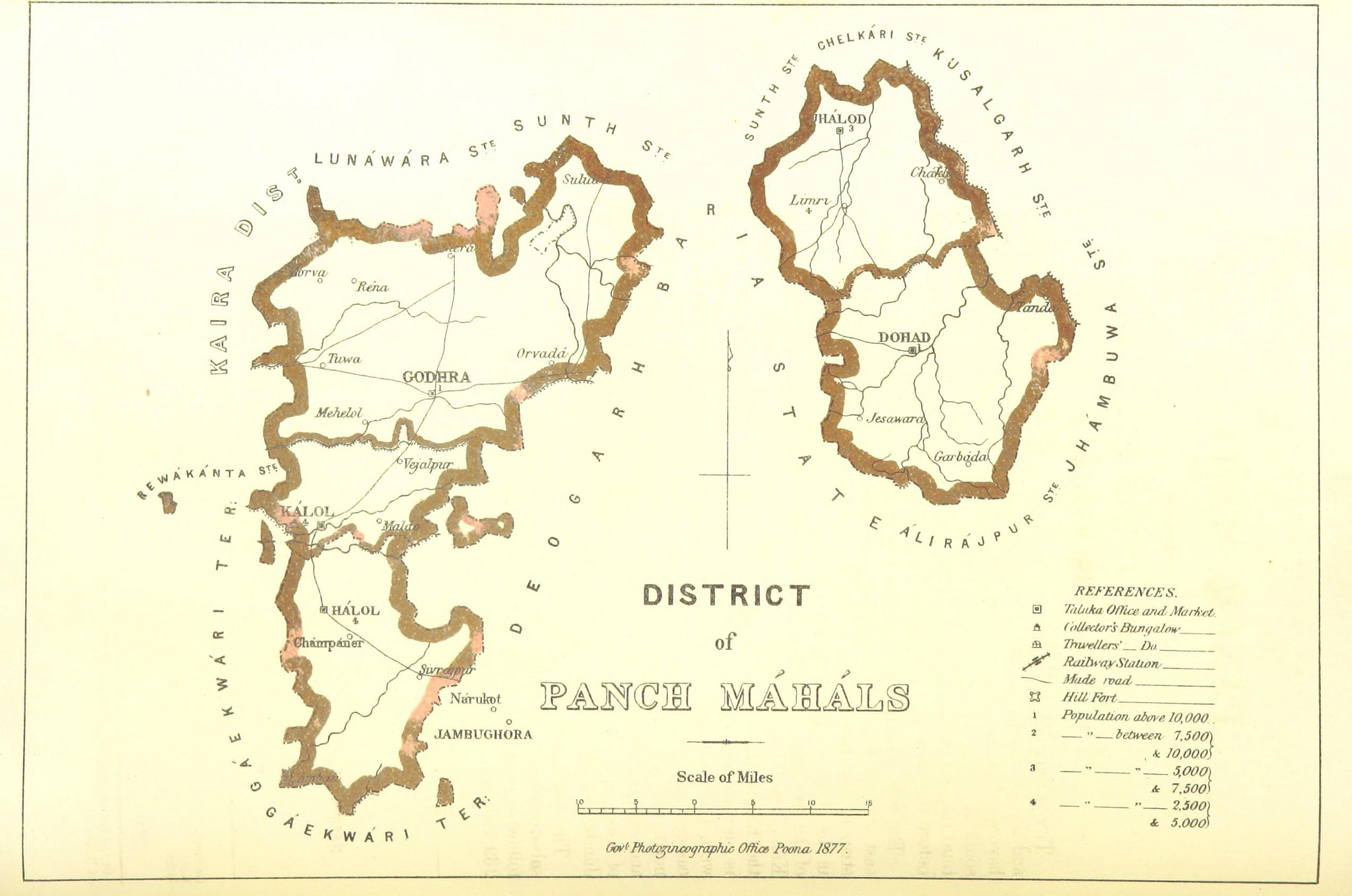
Panchmahal District
Panchmahal, also known as Panch Mahals, is a district in the eastern portion of Gujarat State western India. ''Panch-mahal'' means "five tehsils/talukas" (5 sub-divisions), and refers to the five sub-divisions that were transferred by the Maharaja Jivajirao Scindia of Gwalior State to the British: Godhra, Dahod, Halol, Kalol and Jhalod, Devgadh Baria. The district had a population of 2,390,776 of which 12.51% were urban as of 2001. The district is located on eastern end of the state. It is bordered by Dahod district to the north-east & east, Vadodara district to the southwest and Chhota Udaipur district to southeast, Kheda district to the west and Mahisagar district to the north. Name ''Panch-mahal'' is a Hindustani or Gujarati word derived from Panch ("five") and Mahal which adopted from its original usage in Arabic for a place or type of building, later adopted in Hindi to refer to a province, district or its division, an estate etc. The district was originally called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat Vidyapith
Gujarat Vidyapith is a deemed university in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. It was founded in 1920 by Mahatma Gandhi, the leader of the Indian independence movement, and deemed a university in 1963. Etymology "Vidyapith," in many languages of India, means university. History The university was founded on 18 October 1920 as a 'Rashtriya Vidyapith' ('National University') by Mahatma Gandhi, who would serve throughout his life as the ''kulpati'' (chancellor) and all needs of Fund collected by sardar Vallabhbhai Patel by his personal relations and capacity. The Gujarat Vidyapith was started in Dahyabhai Mehta's bungalow behind the Kocharab Ashram (the Kocharab Aashram was started in barrister Jivanlal Desai's bungalow). Its purpose was to promote educational institutions run by Indians for Indians outside the financial and governing control of British authorities. The university helped nationalists establish a system of education for all Indians, thus proving the country's indep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-cooperation Movement
The Non-cooperation movement was a political campaign launched on 4 September 1920, by Mahatma Gandhi to have Indians revoke their cooperation from the British government, with the aim of persuading them to grant self-governance.Noncooperation movement " ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', December 15, 2015. Retrieved 2021-08-10.Wright, Edmund, ed. 2006. non-cooperation (in British India) " ''A Dictionary of World History'' (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780192807007. This came as result of the |
Mahatma Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (; ; 2 October 1869 – 30 January 1948), popularly known as Mahatma Gandhi, was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist Quote: "... marks Gandhi as a hybrid cosmopolitan figure who transformed ... anti-colonial nationalist politics in the twentieth-century in ways that neither indigenous nor westernized Indian nationalists could." and political ethicist Quote: "Gandhi staked his reputation as an original political thinker on this specific issue. Hitherto, violence had been used in the name of political rights, such as in street riots, regicide, or armed revolutions. Gandhi believes there is a better way of securing political rights, that of nonviolence, and that this new way marks an advance in political ethics." who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from British rule, and to later inspire movements for civil rights and freedom across the world. The honorific ''Mahātmā'' (Sanskrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |