|
Ramón Herrera Y Rodado
Ramón Herrera y Rodado (1799–1882) was a Chilean soldier who held important public positions in Peru during the government of José de la Riva Agüero and later during the Peru–Bolivian Confederation, being president of the South Peru and one of the trusted men of the protector Andrés de Santa Cruz. Biography He was the son of the couple Francisco Manuel de Herrera and Francisca de Paula Rodado, both natives of Peninsular Spain. His family had moved to America when his father began a bureaucratic career as a Crime Prosecutor of the Real Audiencia of Buenos Aires in the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata in 1787, later holding the same position in the Captaincy General of Chile where in 1799 his son Ramón was born. Following in the footsteps of his older brother Francisco de Paula Pedro Regalado, generally known as Pedro Herrera, he enlisted in the royalist army, later moving to Peru where he was part of the Concordia regiment stationed in Lima; His brother Pedro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of South Peru
The Republic of South Peru ( es, República Sud-Peruana) was one of the three constituent Republics of the short-lived Peru–Bolivian Confederation of 1836–39. South Peru was formed from the division of the Republic of Peru into the Republic of North Peru and the Republic of South Peru. These two Republics were founded in 1836 to be (with the Republic of Bolivia) constituent Republics of the Peru–Bolivian Confederation. The Confederation came to an end three years later after continuous border wars with Argentina and Chile in the War of the Confederation, and after a chaotic civil conflict between North and South Peruvians. In August 1839, Agustín Gamarra declared the Confederation dissolved; as a result, South Peru and North Peru reverted to being a unified Republic of Peru. Background The Peru–Bolivian Confederation was a plan that attempted to reunite the ''Alto Perú'' ("Upper Peru", now Bolivia) and ''Bajo Perú'' ("Lower Peru", now simply Peru) into a single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg , image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg , other_symbol = Great Seal of the State , other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal , national_motto = "Firm and Happy for the Union" , national_anthem = "National Anthem of Peru" , march = "March of Flags" , image_map = PER orthographic.svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Lima , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Peruvian Spanish, Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages = , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2017 , demonym = Peruvians, Peruvian , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Semi-presidential system, semi-presidential republic , leader_title1 = President of Peru, President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
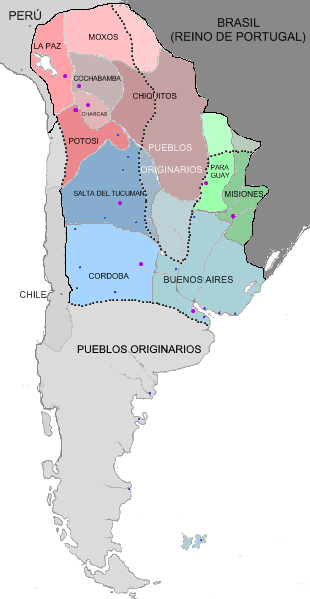
Upper Peru
Upper Peru (; ) is a name for the land that was governed by the Real Audiencia of Charcas. The name originated in Buenos Aires towards the end of the 18th century after the Audiencia of Charcas was transferred from the Viceroyalty of Peru to the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata in 1776.Crespo Rodas, Alberto (1981). ''El ejército de San Martín y las guerrillas del Alto Perú''. La Paz. p. 379 It comprised the Governorate, governorships of Potosí, La Paz, Cochabamba, Chiquitania, Chiquitos, Moxos Province, Moxos and Charcas Province, Charcas (since renamed Sucre). Following the Bolivian War of Independence, the region became an independent country and was renamed Bolivia in honor of Simón Bolívar. History By 1821, the Spanish Empire, Spanish colonial empire in Latin America Napoleonic_Wars#Subsidiary_wars, was falling apart because of the Peninsular War, Napoleonic occupation of Spain and the troops of generals Simón Bolívar, Bolivar and Antonio José de Sucre, Sucre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joaquín De La Pezuela
Joaquín or Joaquin is a male given name, the Spanish version of Joachim. Given name * Joaquín (footballer, born 1956), Spanish football midfielder * Joaquín (footballer, born 1981), Spanish football winger * Joaquín (footballer, born 1982), Spanish football forward * Joaquín Almunia, Spanish politician * Joaquín Andújar, professional baseball player in the Houston Astros organization * Joaquín Arias, professional baseball player in the San Francisco Giants organization * Joaquín Balaguer, President of the Dominican Republic * Joaquín Belgrano, Argentine patriot * Joaquín Benoit, professional baseball player for the San Diego Padres * Joaquin Castro, American politician from San Antonio, Texas * Joaquín Cortés, Spanish flamenco dancer * Joaquín De Luz, Spanish New York City Ballet principal dancer * Joaquin Domagoso, Filipino actor and model * Joaquín "El Chapo" Guzmán, Mexican drug lord * Joaquín Hernández, Mexican footballer * Joaquín "Jack" García, Cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sucre
Sucre () is the Capital city, capital of Bolivia, the capital of the Chuquisaca Department and the List of cities in Bolivia, 6th most populated city in Bolivia. Located in the south-central part of the country, Sucre lies at an elevation of . This relatively high altitude gives the city a subtropical highland climate with cool temperatures year-round. Its pre-Columbian name was Chuquisaca; during the Spanish Empire it was called La Plata. Before the arrival of the Spanish, the city of Chuquisaca had its own autonomy with respect to the Inca Empire (the Charca people, Charcas were the only people that did not pay the ransom for the Inca captive). Today, the region is of predominantly Quechua people, Quechua background, with some Aymara people, Aymara communities and influences. Today Sucre remains a city of major national importance and is an educational and government center, being the location of the Bolivian Supreme Court. Its pleasant climate and low crime rates have made th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lima
Lima ( ; ), originally founded as Ciudad de Los Reyes (City of The Kings) is the capital and the largest city of Peru. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón River, Chillón, Rímac River, Rímac and Lurín Rivers, in the desert zone of the central coastal part of the country, overlooking the Pacific Ocean. Together with the seaside city of Callao, it forms a contiguous urban area known as the Lima Metropolitan Area. With a population of more than 9.7 million in its urban area and more than 10.7 million in its metropolitan area, Lima is one of the largest cities in the Americas. Lima was named by natives in the agricultural region known by native Peruvians as ''Limaq''. It became the capital and most important city in the Viceroyalty of Peru. Following the Peruvian War of Independence, it became the capital of the Republic of Peru (República del Perú). Around one-third of the national population now lives in its Lima Metropolitan Area, metropolitan area. The city of Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viceroyalty Of Peru
The Viceroyalty of Peru ( es, Virreinato del Perú, links=no) was a Spanish imperial provincial administrative district, created in 1542, that originally contained modern-day Peru and most of the Spanish Empire in South America, governed from the capital of Lima. The Viceroyalty of Peru was officially called the Kingdom of Peru. Peru was one of the two Spanish Viceroyalties in the Americas from the sixteenth to the eighteenth centuries. The Spanish did not resist the Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian established by the Treaty of Tordesillas. The treaty was rendered meaningless between 1580 and 1640 while Spain controlled Portugal. The creation during the 18th century of Viceroyalties of New Granada and Río de la Plata (at the expense of Peru's territory) reduced the importance of Lima and shifted the lucrative Andean trade to Buenos Aires, while the fall of the mining and textile production accelerated the progressive decay of the Viceroyalty of Peru. Even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royalist (Spanish American Independence)
The royalists were the people of Hispanic America (mostly from native and indigenous peoples) and European that fought to preserve the integrity of the Spanish monarchy during the Spanish American wars of independence. In the early years of the conflict, when King Ferdinand VII was captive in France, royalists supported the authority in the Americas of the Supreme Central Junta of Spain and the Indies and the Cortes of Cádiz that ruled in the King's name during the Peninsular War. During the Trienio Liberal in 1820, after the restoration of Ferdinand VII in 1814, the royalists were split between Absolutists, those that supported his insistence to rule under traditional law, and liberals, who sought to reinstate the reforms enacted by the Cortes of Cádiz. Political evolution The creation of juntas in Spanish America in 1810 was a direct reaction to developments in Spain during the previous two years. In 1808 Ferdinand VII had been convinced to abdicate by Napoleon in hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viceroyalty Of The Río De La Plata
The Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata ( es, Virreinato del Río de la Plata or es, Virreinato de las Provincias del Río de la Plata) meaning "River of the Silver", also called "Viceroyalty of the River Plate" in some scholarly writings, in southern South America, was the last to be organized and also the shortest-lived of the Viceroyalties of the Spanish Empire in the Americas. The name ''"Provincias del Río de la Plata"'' was formally adopted in 1810 during the Cortes of Cádiz to designate the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata The Viceroyalty was established in 1776 from several former Viceroyalty of Perú dependencies that mainly extended over the Río de la Plata Basin, roughly the present-day territories of Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, Paraguay and Uruguay, extending inland from the Atlantic Coast. The colony of Spanish Guinea (present-day Equatorial Guinea) also depended administratively on the Viceroyalty of Rio de la Plata. Buenos Aires, located on the western sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Audiencia Of Buenos Aires
The Real Audiencia de Buenos Aires, were two '' audiencias'', or highest courts, of the Spanish crown, which lived in Buenos Aires. The authority of the first extended to the territory of the Governorate of the Río de la Plata and operated from 1661 to 1671. The second began to function in 1783 and had as its territory the areas of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata not covered by the Audiencia de Charcas, that is to say the intendancies of Buenos Aires, Córdoba del Tucumán, Salta del Tucumán and Paraguay. In 1810, after the May Revolution, it was suspended, and in 1813 the Assembly of the Year XIII permanently disbanded it. The Audiencias lived in the city's ''cabildo'' building. History Audiencia of Buenos Aires during the Governorate Created by Philip IV by decree (''real cédula'') in 1661, it covered the governorates of Río de la Plata, Paraguay (established in 1617) and Tucumán. This Audiencia was dissolved in 1671. The Recompilation of Laws of the Indies o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish America
Spanish America refers to the Spanish territories in the Americas during the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The term "Spanish America" was specifically used during the territories' Spanish Empire, imperial era between 15th century, 15th and 19th century, 19th centuries. To the end of its imperial rule, Spain called its overseas possessions in the Americas and the Philippines "The Indies", an enduring remnant of Columbus's notion that he had reached Asia by sailing west. When these territories reach a high level of importance, the crown established the Council of the Indies in 1524, following the conquest of the Aztec Empire, asserting permanent royal control over its possessions. Regions with dense indigenous populations and sources of mineral wealth attracting Spanish settlers became colonial centers, while those without such resources were peripheral to crown interest. Once regions incorporated into the empire and their importance assessed, overseas possessions came unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peninsular Spain
Peninsular Spain refers to that part of Spanish territory located within the Iberian Peninsula, thus excluding other parts of Spain: the Canary Islands, the Balearic Islands, Ceuta, Melilla, and a number of islets and crags off the coast of Morocco known collectively as ''plazas de soberanía'' (places of sovereignty). In Spain it is mostly known simply as ''la Península''. It has land frontiers with France and Andorra to the north; Portugal to the west; and the British territory of Gibraltar to the south. Characteristics Peninsular Spain is 492,175 km2 in area - and in population - 43,731,572. It contains 15 of the autonomous communities of Spain. Occupying the central part of Spain, it possesses much greater resources and better interior and exterior communications than other parts of the country. To redress this imbalance, Spanish residents outside the peninsula receive a state subsidy for transport to and from the peninsula. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
%2C_Guamán_Poma%2C_1616.jpg)