|
Railroads' War Board
The Railroads' War Board was a committee of US railroad executives, created voluntarily by the railroad industry in early 1917, in an attempt to improve railroad operations as the United States entered World War I. Following the declaration of war by the United States on April 6, 1917, the railroad companies organized the war board on April 11, 1917 to support the war effort. The board comprised five members, chaired by Fairfax Harrison, president of the Southern Railway. The additional members were: * Howard Elliott, chairman, Northern Pacific Railway * Hale Holden, president, Chicago, Burlington & Quincy Railroad * Julius Kruttschnitt, chairman, Southern Pacific Railway * Samuel Rea, president, Pennsylvania Railroad. The board had limited success and in late 1917 supported the decision by President Woodrow Wilson to nationalize the railroads to support the war effort. Wilson established the United States Railroad Administration The United States Railroad Administration (USRA) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairfax Harrison
Fairfax Harrison (March 13, 1869 – February 2, 1938) was an American lawyer, businessman, and writer. The son of the secretary to Confederate President Jefferson Davis, Harrison studied law at Yale University and Columbia University before becoming a lawyer for the Southern Railway Company in 1896. By 1906 he was Southern's vice-president of finance, and in 1907 he helped secure funding to keep the company solvent. In 1913 he was elected president of Southern, where he instituted a number of reforms in the way the company operated. By 1916, under Harrison's leadership, the Southern had expanded to an network across 13 states, its greatest extent until the 1950s. Following the United States' entry into World War I, the federal government took control of the railroads in December 1917, running them through the United States Railroad Administration, on which Harrison served. An economic boom after the war helped the company to expand its operations; Harrison worked to impro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Railway (US)
The Southern Railway (also known as Southern Railway Company and now known as the Norfolk Southern Railway) was a class 1 railroad based in the Southern United States between 1894 and 1982, when it merged with the Norfolk & Western to form Norfolk Southern. The railroad was the product of nearly 150 predecessor lines that were combined, reorganized and recombined beginning in the 1830s, formally becoming the Southern Railway in 1894. At the end of 1971, the Southern operated of railroad, not including its Class I subsidiaries Alabama Great Southern (528 miles or ); Central of Georgia (1729 miles); Savannah & Atlanta (167 miles); Cincinnati, New Orleans and Texas Pacific Railway (415 miles); Georgia Southern & Florida (454 miles); and twelve Class II subsidiaries. That year, the Southern itself reported 26,111 million net ton-miles of revenue freight and 110 million passenger-miles. Alabama Great Southern reported 3,854 million net ton-miles of revenue freight and 11 million pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howard Elliott (railroad Executive)
Howard Elliott (December 6, 1860 – July 8, 1928) was President of Northern Pacific Railway 1903-1913, and also President of New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad beginning in 1913. Biography Elliott was born on December 6, 1860, in New York, and received a degree from Harvard University. He entered railway service during the summer of 1880, during college break as a rodman on the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad. After graduation from Lawrence Scientific School in 1881 with a degree in civil engineering, he became a clerk in the president's office of the St. Louis, Keokuk and Northwestern Railway. From 1887 to 1891, he was a general freight and passenger agent, and from 1891 to 1896, also of the Hannibal and St. Joseph and Kansas City, St. Joseph and Council Bluffs lines. From 1896 to 1902, he became general manager, and from 1902 to 1903, second vice-president of the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy lines. In 1903 he was elected president of the Northern Pacific Railro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
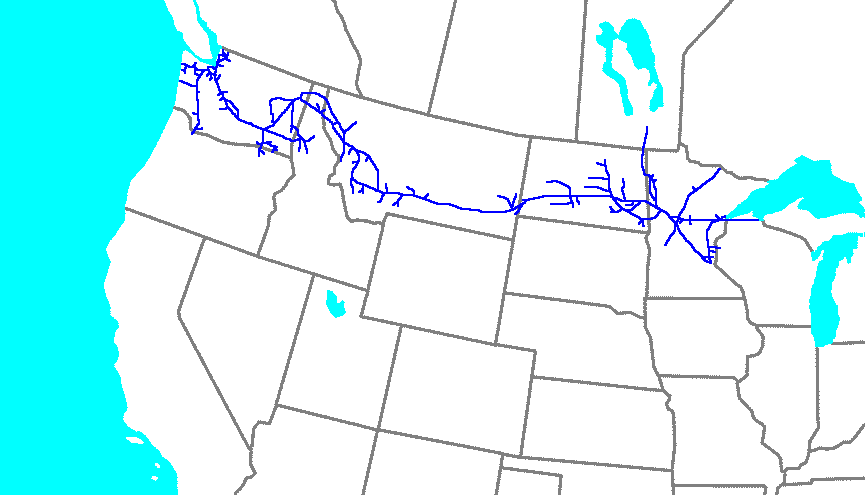
Northern Pacific Railway
The Northern Pacific Railway was a transcontinental railroad that operated across the northern tier of the western United States, from Minnesota to the Pacific Northwest. It was approved by Congress in 1864 and given nearly of land grants, which it used to raise money in Europe for construction. Construction began in 1870 and the main line opened all the way from the Great Lakes to the Pacific when former President Ulysses S. Grant drove in the final "golden spike" in western Montana on September 8, 1883. The railroad had about of track and served a large area, including extensive trackage in the states of Idaho, Minnesota, Montana, North Dakota, Oregon, Washington, and Wisconsin. In addition, the NP had an international branch to Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. The main activities were shipping wheat and other farm products, cattle, timber, and minerals; bringing in consumer goods, transporting passengers; and selling land. The Northern Pacific was headquartered in Minnesota, fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hale Holden
Hale Holden (August 11, 1869 – September 23, 1940) was president of the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad (CB&Q) from 1914 to 1918 and 1920 to 1929, and chairman of the board of directors for Southern Pacific Railroad from 1932 to 1939. He was one of the lawyers working for James J. Hill's defense team in the Minnesota Rate Cases. In later years he served as a director for a number of large companies including American Telephone & Telegraph, New York Life Insurance Company and the Chemical Bank & Trust. Early life Hale Holden was born on August 11, 1869, in Kansas City, Missouri, the son of Howard Malcomb and Mary Finley (Oburn) Holden. He received his education at Williams College (graduated 1890) and Harvard Law School (entered September 22, 1890; left 1892). Although he graduated from Williams College, he was forced to withdraw from Harvard due to family finances. Career Holden practiced law as a partner in Dean, McLeod & Holden in Kansas City; it was his work in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago, Burlington & Quincy Railroad
The Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad was a railroad that operated in the Midwestern United States. Commonly referred to as the Burlington Route, the Burlington, or as the Q, it operated extensive trackage in the states of Colorado, Illinois, Iowa, Missouri, Nebraska, Wisconsin, Wyoming, and also in Texas through subsidiaries Colorado and Southern Railway, Fort Worth and Denver Railway, and Burlington-Rock Island Railroad. Its primary connections included Chicago, Minneapolis–Saint Paul, St. Louis, Kansas City, and Denver. Because of this extensive trackage in the midwest and mountain states, the railroad used the advertising slogans "Everywhere West", "Way of the ''Zephyrs''", and "The Way West". In 1967, it reported 19,565 million net ton-miles of revenue freight and 723 million passenger miles; corresponding totals for C&S were 1,100 and 10 and for FW&D were 1,466 and 13. At the end of the year, CB&Q operated 8,538 route-miles, C&S operated 708, and FW&D operated 136 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Kruttschnitt
Julius Kruttschnitt (July 30, 1854 – June 15, 1925) was a German American railroad executive. Biography He was born on July 30, 1854 in New Orleans, Louisiana. He graduated from Washington and Lee University in 1873 and worked briefly as a schoolteacher before beginning his railroad career. He joined the Southern Pacific Railroad in 1885 and served in a variety of roles, culminating in chairman from 1913. He retired on May 31, 1925 as chairman of the executive committee of the Southern Pacific Railroad. He died on June 15, 1925 in New Orleans, Louisiana of a heart attack. References See also * List of Wells Fargo directors *Pecos River High Bridge The Pecos River High Bridge carries the Union Pacific Railroad across the Pecos River gorge and is the second high-level crossing on this site. History The first Pecos River Bridge, designed by SP chief engineer Julius Kruttschnitt, was buil ... 1854 births 1925 deaths Southern Pacific Railroad people American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Pacific Railway
The Southern Pacific (or Espee from the railroad initials- SP) was an American Class I railroad network that existed from 1865 to 1996 and operated largely in the Western United States. The system was operated by various companies under the names Southern Pacific Railroad, Southern Pacific Company and Southern Pacific Transportation Company. The original Southern Pacific began in 1865 as a land holding company. The last incarnation of the Southern Pacific, the Southern Pacific Transportation Company, was founded in 1969 and assumed control of the Southern Pacific system. The Southern Pacific Transportation Company was acquired in 1996 by the Union Pacific Corporation and merged with their Union Pacific Railroad. The Southern Pacific legacy founded hospitals in San Francisco, Tucson, and Houston. In the 1970s, it also founded a telecommunications network with a state-of-the-art microwave and fiber optic backbone. This telecommunications network became part of Sprint, a compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Rea
Samuel Rea (September 21, 1855 – March 24, 1929) was an American engineer and the ninth president of the Pennsylvania Railroad, serving from 1913 to 1925. He joined the PRR in 1871, when the railroad had hardly outgrown its 1846 charter to build from Harrisburg to Pittsburgh, and helped it grow to a 12,000-mile (19,000 km) system with access to Manhattan, upstate New York, and New England. Rea was awarded the Franklin Medal in 1926, and was elected as an honorary member of the Institution of Civil Engineers in 1928. Early life and career Samuel Rea was born on September 21, 1855, in Hollidaysburg, Pennsylvania. His parents were James D. Rea and Ruth Blair Moore. His paternal grandfather, General John Rea, was the United States representative from Bedford and Franklin, Pennsylvania, during the terms of Thomas Jefferson and James Madison. Through the marriage of his father's siblings, he was related to the Asa Childs and the Henry Clay Frick families. His father died when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
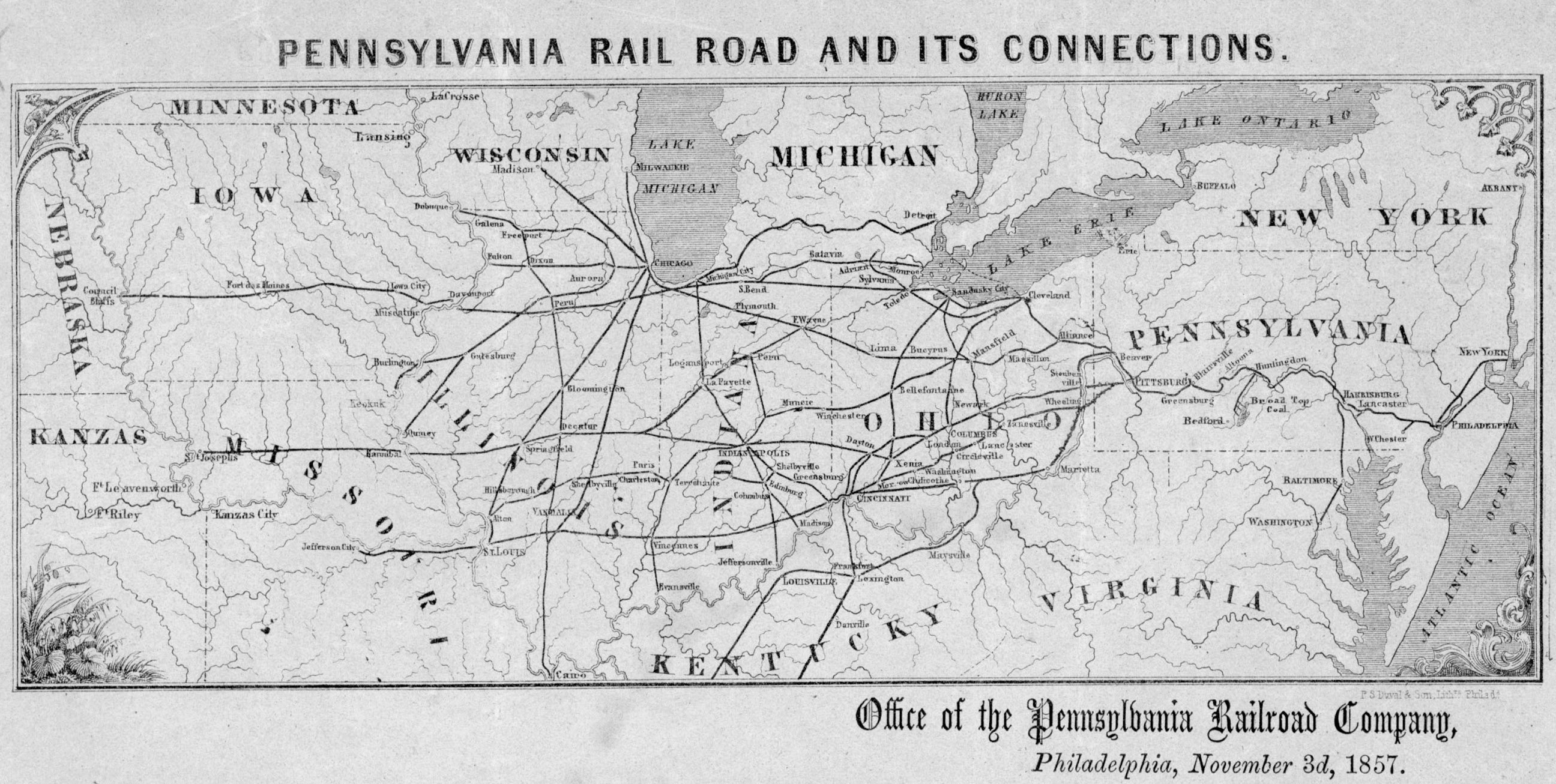
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named for the commonwealth in which it was established. By 1882, Pennsylvania Railroad had become the largest railroad (by traffic and revenue), the largest transportation enterprise, and the largest corporation in the world. Its budget was second only to the U.S. government. Over the years, it acquired, merged with, or owned part of at least 800 other rail lines and companies. At the end of 1926, it operated of rail line;This mileage includes companies independently operated. PRR miles of all tracks, which includes first (or main), second, third, fourth, and sidings, totalled 28,040.49 at the end of 1926. in the 1920s, it carried nearly three times the traffic as other railroads of comparable length, such as the Union Pacific and Atchison, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of Princeton University and as the governor of New Jersey before winning the 1912 presidential election. As president, Wilson changed the nation's economic policies and led the United States into World War I in 1917. He was the leading architect of the League of Nations, and his progressive stance on foreign policy came to be known as Wilsonianism. Wilson grew up in the American South, mainly in Augusta, Georgia, during the Civil War and Reconstruction. After earning a Ph.D. in political science from Johns Hopkins University, Wilson taught at various colleges before becoming the president of Princeton University and a spokesman for progressivism in higher education. As governor of New Jersey from 1911 to 1913, Wilson broke with party bosse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |