|
Rai Languages
The Kiranti languages are a major family of Sino-Tibetan languages spoken in Nepal and India (notably Sikkim, Darjeeling, Kalimpong, and Kumai) by the Kirati people. External relationships George van Driem had formerly proposed that the Kiranti languages were part of a Mahakiranti family, although specialists are not completely certain of either the existence of a Kiranti subgroup or its precise membership. LaPolla (2003), though, proposes that Kiranti may be part of a larger "Rung" group. Languages There are about two dozen Kiranti languages. The better known are Limbu, Sunuwar, Bantawa Rai, Chamling Rai, Khaling Rai, Bahing Rai, Yakkha language, Vayu, Dungmali Rai, Lohorung Rai and Kulung Rai. Kiranti verbs are not easily segmentable, due in large part to the presence of portmanteau morphemes, crowded affix strings, and extensive (and often nonintuitive) allomorphy. Classification Overall, Kiranti languages are: * Limbu * Eastern Kiranti ** Greater Yakkha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rai People
The Rai are an ethnolinguistic group belonging to the Kirat family and primarily Tibeto-Burman linguistic ethnicity. They mainly reside in the eastern parts of Nepal, the Indian states of Sikkim, West Bengal (predominantly Darjeeling and Kalimpong Hills) and in south western Bhutan. The Rais are a set of groups, one of the cultivating tribes of Nepal. They inhabited the area between the Dudh Koshi and Tamur River in Nepal. They claim that their country alone is called ( Kiratdesh), and they call themselves Rai. In modern times, they have spread over Nepal, Sikkim and West Bengal. Rai are also known as "Jimdar" and in some places as "Khambu." "Jim" means "land" because they cultivated "Jim" or land, the Rais return cultivation as their traditional occupation. H. H Risley treats the Rais and Jimdar the as synonymous with the Khambus, but most of the Rais nowadays do admit Khambu and Jimdar to be synonymous terms connoting the same ethnic group. Rais are one of the dominant tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
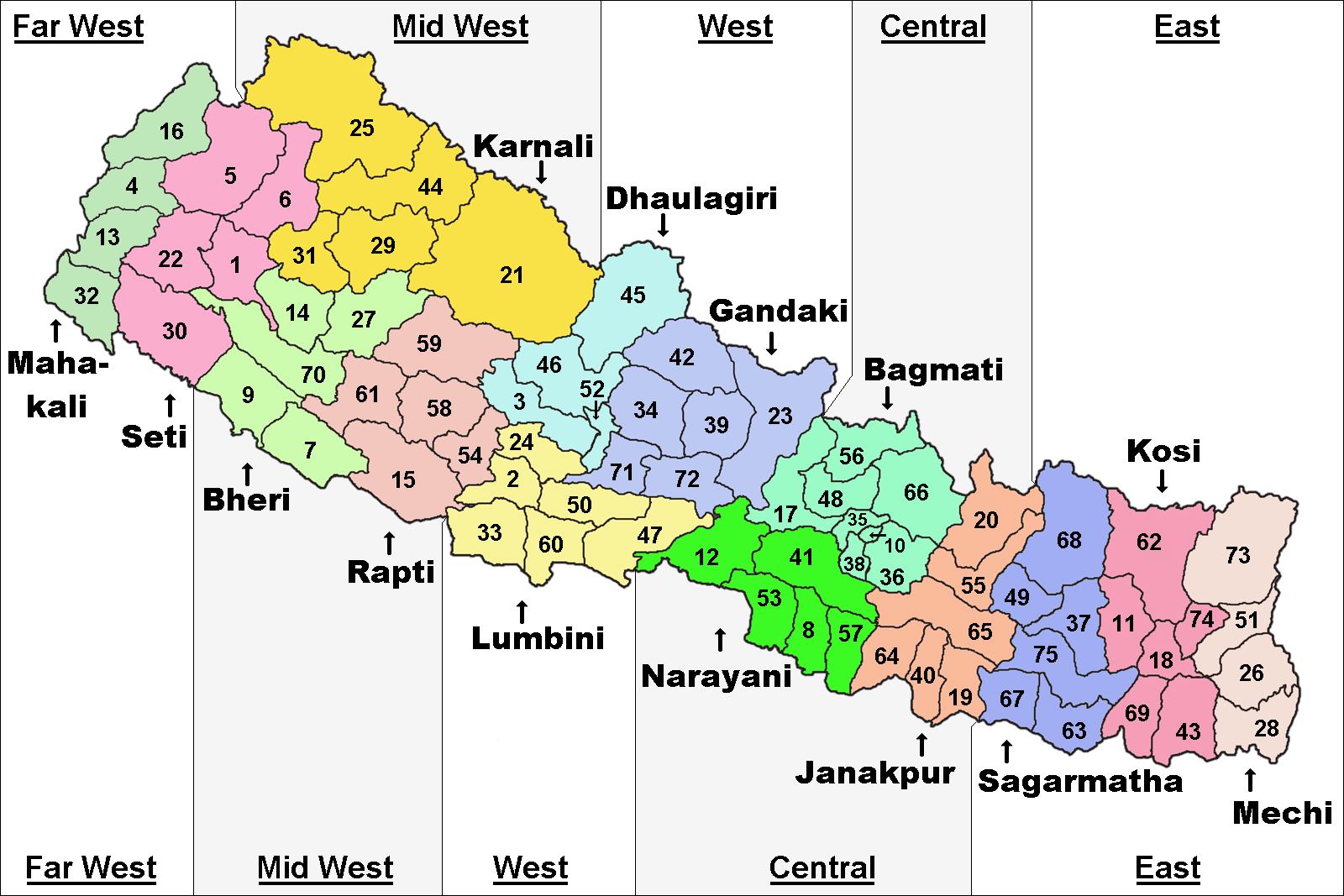
Eastern Nepal
The Eastern Development Region (Nepali: पुर्वाञ्चल विकास क्षेत्र, ''Purwānchal Bikās Kshetra'') was one of Nepal's five development regions. It is also known as Kirata region. It was located at the eastern end of the country with its headquarters at Dhankuta. The town of Dhankuta was the headquarter of the Eastern Region, as well as the headquarter of the Dhankuta District. History On April 13, 1961 Mahendra, the king of Nepal, divided the existing 35 districts into 75 districts and grouped them into 14 administrative zones. In 1972, the King of Nepal grouped 14 zones into total 4 development regions, thus Eastern Development Region came into existence. On 20 September 2015, Eastern Development Region including all other development regions of Nepal were abolished, when the new Constitution of Nepal-2015 was proclaimed. The total area of the region was 28,456 km². Administrative divisions The region administratively was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunuwar Language
Sunuwar, Sunuwar, or Kõinch (; ; other spellings are Koinch and Koincha), is a Kiranti language spoken in Nepal and India by the Sunuwar people. It was first comprehensively attested by the Himalayan Languages Project. It is also known as Kõits Lo ( ; ), Kiranti-Kõits ( ; ), Mukhiya ( ; ). The Sunwar language is one of the smaller members of the Tibeto-Burman language family. About 40,000 speakers are residing in eastern Nepal. Names The language is commonly known as ''Koic,'' for many ethnic Sunwar and Sunwar speakers also refer to the language as “''Sunuwar, Kõinch'' '', Koinch'' or ''Koincha'' (कोँइच); ''Kõits Lo'' (कोँइच लो), ''Kiranti-Kõits'' (किराँती-कोँइच) or ''Mukhiya'' (मुखिया).” Moreover, most Sunwar speakers have the surname (सुनुवार), ''Sunuvār'' in Latin script. Many affiliated Sunwar with Sunar; they share the initial syllable, ''sun'', “gold,” in Nepali, similar to the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allomorph
In linguistics, an allomorph is a variant phonetic form of a morpheme, or, a unit of meaning that varies in sound and spelling without changing the meaning. The term ''allomorph'' describes the realization of phonological variations for a specific morpheme. The different allomorphs that a morpheme can become are governed by morphophonemic rules. These phonological rules determine what phonetic form, or specific pronunciation, a morpheme will take based on the phonological or morphological context in which they appear. In English English has several morphemes that vary in sound but not in meaning, such as past tense morphemes, plural morphemes, and negative morphemes. Past tense allomorphs For example, an English past tense morpheme is ''-ed'', which occurs in several allomorphs depending on its phonological environment by assimilating the voicing of the previous segment or the insertion of a schwa after an alveolar stop: *as or in verbs whose stem ends with the alveolar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affix
In linguistics, an affix is a morpheme that is attached to a word stem to form a new word or word form. Affixes may be derivational, like English ''-ness'' and ''pre-'', or inflectional, like English plural ''-s'' and past tense ''-ed''. They are bound morphemes by definition; prefixes and suffixes may be separable affixes. Affixation is the linguistic process that speakers use to form different words by adding morphemes at the beginning (prefixation), the middle (infixation) or the end (suffixation) of words. Positional categories of affixes ''Prefix'' and ''suffix'' may be subsumed under the term ''adfix'', in contrast to ''infix.'' When marking text for interlinear glossing, as in the third column in the chart above, simple affixes such as prefixes and suffixes are separated from the stem with hyphens. Affixes which disrupt the stem, or which themselves are discontinuous, are often marked off with angle brackets. Reduplication is often shown with a tilde. Affixes whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morpheme
A morpheme is the smallest meaningful constituent of a linguistic expression. The field of linguistic study dedicated to morphemes is called morphology. In English, morphemes are often but not necessarily words. Morphemes that stand alone are considered roots (such as the morpheme ''cat''); other morphemes, called affixes, are found only in combination with other morphemes. For example, the ''-s'' in ''cats'' indicates the concept of plurality but is always bound to another concept to indicate a specific kind of plurality. This distinction is not universal and does not apply to, for example, Latin, in which many roots cannot stand alone. For instance, the Latin root ''reg-'' (‘king’) must always be suffixed with a case marker: ''rex'' (''reg-s''), ''reg-is'', ''reg-i'', etc. For a language like Latin, a root can be defined as the main lexical morpheme of a word. These sample English words have the following morphological analyses: * "Unbreakable" is composed of three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portmanteau
A portmanteau word, or portmanteau (, ) is a blend of wordsGarner's Modern American Usage , p. 644. in which parts of multiple words are combined into a new word, as in ''smog'', coined by blending ''smoke'' and ''fog'', or ''motel'', from ''motor'' and ''hotel''. In , a portmanteau is a single morph that is analyzed as representing two (or more) underlying s. When portmanteaus shorte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kulung Language (Nepal)
Kulung ( autonym: ''Kulu riŋ'', ulu rɪŋ is one of the Rai languages; it is spoken by an estimated 33,000 people. Van Driem (2001) includes Chukwa as a dialect. Locations Kulung in some ten villages along the upper reaches of the Huṅga or Hoṅgu River (a tributary of the Dūdhkosī), in Solukhumbu District of Sagarmāthā Zone, Nepal. The main Kulung-speaking villages are Chhemsi and Chheskam. The particular dialect of the language spoken in these two villages is considered by the Kulung to be the most original form of their language. Downstream, on both sides of the Huṅga river, in villages that are now called Luchcham, Gudel, Chocholung, Nāmluṅg, Pilmo, Bung, Chhekmā, and Sātdi, less prestigious varieties of Kulung are spoken. ''Ethnologue'' lists the following Kulung villages. * Hongu River valley, Solukhumbu District, Sagarmatha Zone: Bung, Pelmang, Chhemsing, Chheskam, Lucham, Chachalung, Satdi, Gudel, Namlung, Sotang, and Chekma villages * Sankhuwasabha dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lohorung Language
Lohorung, also spelled Lorung, Lohrung or Loharung, is a Kirati language of eastern Nepal. It has been described by George van Driem. Southern Lorung is also considered to be Southern Yamphu language. These varieties are all closely related. Geographical distribution Lohorung is spoken between the middle Arun valley and the Sabhakhola in central Sankhuwasabha District, Kosi Zone, in the villages of Pangma, Angala, Higuwa, Khorande, Bardeu, Gairiaula, Malta, Sitalpati, and Dhupu (''Ethnologue''). Southern Yamphu (Southern Lohorung) is spoken in Bodhe, Mounabudhuk, Bhedetar, and Rajaran villages in Dhankuta District, Kosi Zone (''Ethnologue''). It is also spoken in Devitar and Matsya Pokhari villages, northern Sankhuwasabha District Sankhuwasabha District ( ne, सङ्खुवासभा जिल्ला ) is one of 14 districts of Province No. 1 of eastern Nepal. The district's area is 3,480 km2 with a population of 159,203 in 2001 and 158,742 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dungmali Language
Dungmali, or Dungmali-Bantawa, is a Kirati languages language spoken in Nepal. It is largely cognate with Bantawa language, but differs grammatically and phonologically. Locations Dungmali is spoken in eastern Bhojpur District, Kosi Zone Kosi or Koshi ( ne, कोसी अञ्चल, ne, कोशी अञ्चल ) was one of the fourteen zones of Nepal until the restructure of zones to provinces. The headquarters of Kosi Zone was Biratnagar which was also its largest ci ..., in Thulo Dumba, Sano Dumba, and Bastim Similarly, Tiwari Bhanjyan, Chyangre, Yaku etc. which is also called Pouwakhesang Thum. VDC's ('' Ethnologue''). The Dungmali area extends all the way east to the Arun River. In present days Dungmali’s people are living in different countries India, Bhutan, United States of America (USA). According to kirat Rai Dungmalis Bhasa Sanskriti Samrachhan Mancha, Dungmalis were generated from Hangwang, Pungwat, Pawen, Chokhang and Salukathewa Pachhas ‘ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wayu Language
Vayu (वायु), Wayu or Hayu (हायु) is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken in Nepal by about 1740 people in Province No. 3. Dialects include Pali gau (पालि गाउ) Mudajor Sukajor Ramechhap Sindhuli and Marin Khola. The Vayu language features SOV ordering. There are strong Nepali influences in its phonology, lexicon, and grammar. Its writing system uses the Devanagari script. There are no known monolingual speakers of the language, as its speaking population also uses Nepali. Despite a lack of monolingual children, use of Vayu has survived into the 21st century Phonology Geographical distribution Vayu is spoken in the following locations of Nepal. * Ramechhap District, Province No. 3 Bagmati Province ( ne, बाग्मती प्रदेश, ''Bagmati Pradesh'') is one of the seven provinces of Nepal established by the constitution of Nepal. The province is Nepal's second-most populous province and fifth largest provinc ...: Mudajor and S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakkha Language
Yakkha (also erroneously spelled as Yakha) is a language spoken in parts of Nepal, Darjeeling district and Sikkim. The Yakkha-speaking villages are located to the East of the Arun river, in the southern part of the Sankhuwasabha district and in the northern part of the Dhankuta district of Nepal. About 14,000 people still speak the language, out of 17,003 ethnic Yakkha in Nepal. Genealogically, Yakkha belongs to the Eastern Kiranti languages and is in one subgroup with several Limbu languages, e.g. Belhare, Athpare, Chintang and Chulung. Ethnically however, the Yakkha people perceive themselves as distinct from the other Kiranti groups such as Limbu. Geographical distribution Mugali is spoken between Mugakhola and Sinuwakhola on the eastern banks of the Arun River in Dhankuta District, Province No. 1, Nepal, in the villages (VDC's) of Muga, Pakhribas, and Phalate. Phangduwali is spoken above the Mugakhola headwaters in Pakhribas VDC, Dhankuta District, Province No. 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |