|
Radio Beacon
In navigation, a radio beacon or radiobeacon is a kind of beacon, a device that marks a fixed location and allows direction-finding equipment to find relative bearing. But instead of employing visible light, radio beacons transmit electromagnetic radiation in the radio wave band. They are used for direction-finding systems on ships, aircraft and vehicles. Radio beacons transmit a continuous or periodic radio signal with limited information (for example, its identification or location) on a specified radio frequency. Occasionally, the beacon's transmission includes other information, such as telemetric or meteorological data. Radio beacons have many applications, including air and sea navigation, propagation research, robotic mapping, radio-frequency identification (RFID), near-field communication (NFC) and indoor navigation, as with real-time locating systems (RTLS) like Syledis or simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM). Types Radio-navigation beacons The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borough Hill Mast
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely. History In the Middle Ages, boroughs were settlements in England that were granted some self-government; burghs were the Scottish equivalent. In medieval England, boroughs were also entitled to elect members of parliament. The use of the word ''borough'' probably derives from the burghal system of Alfred the Great. Alfred set up a system of defensive strong points (Burhs); in order to maintain these particular settlements, he granted them a degree of autonomy. After the Norman Conquest, when certain towns were granted self-governance, the concept of the burh/borough seems to have been reused to mean a self-governing settlement. The concept of the borough has been used repeatedly (and often differently) throughout the world. Often, a borough is a single town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syledis
Syledis (SYstem LEger pour mesure la DIStance) was a terrestrial radio navigation and locating system. The system operated in the UHF segment of 420-450 MHz. It was manufactured in France by Sercel S.A., headquarters Carquefou, and was operational during the 1980s and until about 1995, providing positioning and navigational support for the petroleum sector in the North Sea and to other scientific projects. Syledis has been replaced by GPS. Functioning Determination of the position of mobile vehicles, like f.e. vessels, using Syledis is accomplished by measurement of transit time of radio waves between mobiles and radio stations at known points. There are two modes of operation, ''active range mode'' and ''passive pseudo-range mode''. Further explanation of the functioning of the Syledis positioning system A vessel is equipped with a transmitter that transmits a coded signal to at least three radio beacons each placed at a known point. The beacons send the code back to the transm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amateur Radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communications. The term "amateur" is used to specify "a duly authorised person interested in radioelectric practice with a purely personal aim and without pecuniary interest;" (either direct monetary or other similar reward) and to differentiate it from commercial broadcasting, public safety (such as police and fire), or professional two-way radio services (such as maritime, aviation, taxis, etc.). The amateur radio service (''amateur service'' and ''amateur-satellite service'') is established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) through the Radio Regulations. National governments regulate technical and operational characteristics of transmissions and issue individual station licenses with a unique identifying call sign, which m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amateur Radio Propagation Beacon
An amateur radio propagation beacon is a radio beacon, whose purpose is the investigation of the propagation of radio signals. Most radio propagation beacons use amateur radio frequencies. They can be found on LF, MF, HF, VHF, UHF, and microwave frequencies. Microwave beacons are also used as signal sources to test and calibrate antennas and receivers. The International Amateur Radio Union (IARU) and its member societies coordinate beacons established by radio amateurs. Transmission characteristics Most beacons operate in continuous wave (A1A) and transmit their identification (call sign and location). Some of them send long dashes to facilitate signal strength measurement. A small number of beacons transmit Morse code by frequency-shift keying (F1A). A few beacons transmit signals in digital modulation modes, like radioteletype (F1B) and PSK31 (G1B). Legality In the US, unattended beacons on frequencies lower than the 10-meter band are not legal. 2200-meter beacons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
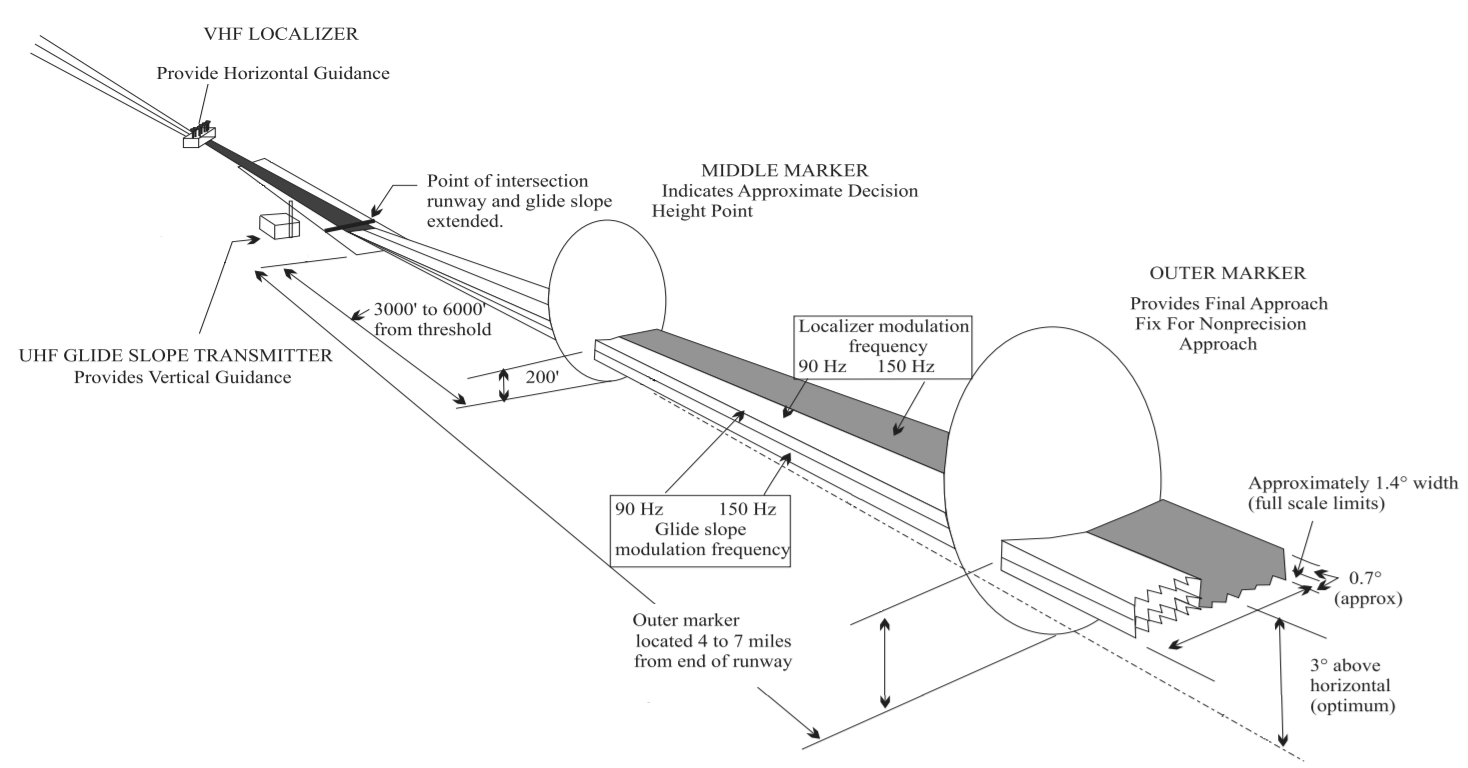
Instrument Landing System
In aviation, the instrument landing system (ILS) is a precision radio navigation system that provides short-range guidance to aircraft to allow them to approach a runway at night or in bad weather. In its original form, it allows an aircraft to approach until it is over the ground, within a of the runway. At that point the runway should be visible to the pilot; if it is not, they perform a missed approach. Bringing the aircraft this close to the runway dramatically increases the range of weather conditions in which a safe landing can be made. Other versions of the system, or "categories", have further reduced the minimum altitudes, runway visual ranges (RVRs), and transmitter and monitoring configurations designed depending on the normal expected weather patterns and airport safety requirements. ILS uses two directional radio signals, the ''localizer'' (108 to 112 MHz frequency), which provides horizontal guidance, and the ''glideslope'' (329.15 to 335 MHz frequenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marker Beacon
A marker beacon is a particular type of VHF radio beacon used in aviation, usually in conjunction with an instrument landing system (ILS), to give pilots a means to determine position along an established route to a destination such as a runway. According to ''Article 1.107'' of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) a marker beacon is defined as "a transmitter in the aeronautical radionavigation service which radiates vertically a distinctive pattern for providing position information to aircraft". History From the 1930s until the 1950s, markers were used extensively along airways to provide an indication of an aircraft's specific position along the route, but from the 1960s they have become increasingly limited to ILS approach installations. They are now very gradually being phased out of service, especially in more developed parts of the world, as GPS and other technologies have made marker beacons increasingly redundant. Types The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Station
Radio broadcasting is transmission of audio (sound), sometimes with related metadata, by radio waves to radio receivers belonging to a public audience. In terrestrial radio broadcasting the radio waves are broadcast by a land-based radio station, while in satellite radio the radio waves are broadcast by a satellite in Earth orbit. To receive the content the listener must have a broadcast radio receiver (''radio''). Stations are often affiliated with a radio network which provides content in a common radio format, either in broadcast syndication or simulcast or both. Radio stations broadcast with several different types of modulation: AM radio stations transmit in AM ( amplitude modulation), FM radio stations transmit in FM (frequency modulation), which are older analog audio standards, while newer digital radio stations transmit in several digital audio standards: DAB (digital audio broadcasting), HD radio, DRM ( Digital Radio Mondiale). Television bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AM Radio
AM broadcasting is radio broadcasting using amplitude modulation (AM) transmissions. It was the first method developed for making audio radio transmissions, and is still used worldwide, primarily for medium wave (also known as "AM band") transmissions, but also on the longwave and shortwave radio bands. The earliest experimental AM transmissions began in the early 1900s. However, widespread AM broadcasting was not established until the 1920s, following the development of vacuum tube receivers and transmitters. AM radio remained the dominant method of broadcasting for the next 30 years, a period called the "Golden Age of Radio", until television broadcasting became widespread in the 1950s and received most of the programming previously carried by radio. Subsequently, AM radio's audiences have also greatly shrunk due to competition from FM ( frequency modulation) radio, Digital Audio Broadcasting (DAB), satellite radio, HD (digital) radio, Internet radio, music streaming ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential GPS
Differential Global Positioning Systems (DGPSs) supplement and enhance the positional data available from global navigation satellite systems (GNSSs). A DGPS for GPS can increase accuracy by about a thousandfold, from approximately to . DGPSs consist of networks of fixed position, ground-based reference stations. Each reference station calculates the difference between its highly accurate known position and its less accurate satellite-derived position. The stations broadcast this data locally—typically using ground-based transmitters of shorter range. Non-fixed (mobile) receivers use it to correct their position by the same amount, thereby improving their accuracy. The United States Coast Guard (USCG) and the Canadian Coast Guard (CCG) each run DGPSs in the United States and Canada on longwave radio frequencies between and near major waterways and harbors. The USCG's DGPS was named NDGPS (Nationwide DGPS) and was jointly administered by the Coast Guard and the U.S. Departme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerodrome
An aerodrome (Commonwealth English) or airdrome (American English) is a location from which aircraft flight operations take place, regardless of whether they involve air cargo, passengers, or neither, and regardless of whether it is for public or private use. Aerodromes include small general aviation airfields, large commercial airports, and military air bases. The term ''airport'' may imply a certain stature (having satisfied certain certification criteria or regulatory requirements) that not all aerodromes may have achieved. That means that all airports are aerodromes, but not all aerodromes are airports. Usage of the term "aerodrome" remains more common in Ireland and Commonwealth nations, and is conversely almost unknown in American English, where the term "airport" is applied almost exclusively. A water aerodrome is an area of open water used regularly by seaplanes, floatplanes or amphibious aircraft for landing and taking off. In formal terminology, as defined by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Direction Finder
Direction finding (DF), or radio direction finding (RDF), isin accordance with International Telecommunication Union (ITU)defined as radio location that uses the reception of radio waves to determine the direction in which a radio station or an object is located. This can refer to radio or other forms of wireless communication, including radar signals detection and monitoring (ELINT/ESM). By combining the direction information from two or more suitably spaced receivers (or a single mobile receiver), the source of a transmission may be located via triangulation. Radio direction finding is used in the navigation of ships and aircraft, to locate emergency transmitters for search and rescue, for tracking wildlife, and to locate illegal or interfering transmitters. RDF was important in combating German threats during both the World War II Battle of Britain and the long running Battle of the Atlantic. In the former, the Air Ministry also used RDF to locate its own fighter grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instrument Approach
In aviation, an instrument approach or instrument approach procedure (IAP) is a series of predetermined maneuvers for the orderly transfer of an aircraft operating under instrument flight rules from the beginning of the initial approach to a landing, or to a point from which a landing may be made visually. These approaches are approved in the European Union by EASA and the respective country authorities and in the United States by the FAA or the United States Department of Defense for the military. The ICAO defines an instrument approach as, "a series of predetermined maneuvers by reference to flight instruments with specific protection from obstacles from the initial approach fix, or where applicable, from the beginning of a defined arrival route to a point from which a landing can be completed and thereafter, if landing is not completed, to a position at which holding or enroute obstacle clearance criteria apply." There are three categories of instrument approach procedures: p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |