|
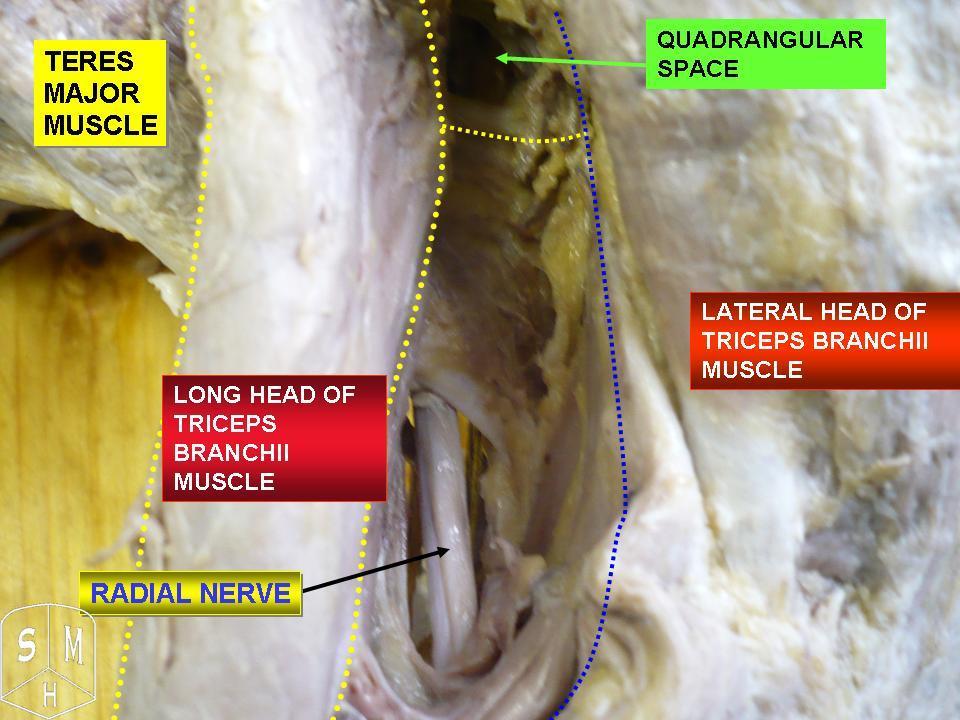
Radial Nerve
The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin. It originates from the brachial plexus, carrying fibers from the ventral roots of spinal nerves C5, C6, C7, C8 & T1. The radial nerve and its branches provide motor innervation to the dorsal arm muscles (the triceps brachii and the anconeus) and the extrinsic extensors of the wrists and hands; it also provides cutaneous sensory innervation to most of the back of the hand, except for the back of the little finger and adjacent half of the ring finger (which are innervated by the ulnar nerve). The radial nerve divides into a deep branch, which becomes the posterior interosseous nerve, and a superficial branch, which goes on to innervate the dorsum (back) of the hand. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suprascapular Nerve
The suprascapular nerve is a nerve that branches from the upper trunk of the brachial plexus. It is responsible for the innervation of two of the muscles that originate from the scapula, namely the supraspinatus muscle, supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles. Structure The suprascapular nerve arises from the upper trunk of the brachial plexus which is formed by the union of the Anterior ramus of spinal nerve, ventral rami of the fifth and sixth cervical nerves. After branching from the upper trunk, the nerve passes across the posterior triangle of the neck parallel to the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle and deep to the trapezius muscle. It then runs along the Scapula#Borders, superior border of the scapula through the suprascapular canal, in which it enters via the suprascapular notch inferior to the superior transverse scapular ligament and enters the supraspinous fossa. It then passes beneath the supraspinatus, and curves around the lateral border of the spine of the scapul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Compartment Of The Arm
The fascial compartments of arm refers to the specific anatomical term of the compartments within the upper segment of the upper limb (the arm) of the body. The upper limb is divided into two segments, the arm and the forearm. Each of these segments is further divided into two compartments which are formed by deep fascia – tough connective tissue septa (walls). Each compartment encloses specific muscles and nerves. The compartments of the arm are the anterior compartment of the arm and the posterior compartment of the arm, divided by the lateral and the medial intermuscular septa. The compartments of the forearm are the anterior compartment of the forearm and posterior compartment of the forearm. Intermuscular septa The lateral intermuscular septum extends from the lower part of the crest of the greater tubercle of the humerus, along the lateral supracondylar ridge, to the lateral epicondyle; it is blended with the tendon of the deltoid muscle, gives attachment to the tricep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Cutaneous Nerve Of The Forearm
The posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm is a nerve found in humans and other animals. It is also known as the dorsal antebrachial cutaneous nerve, the external cutaneous branch of the musculospiral nerve, and the posterior antebrachial cutaneous nerve. It is a cutaneous nerve (a nerve that supplies skin) of the forearm. Origin It arises from the radial nerve in the posterior compartment of the arm, often along with the posterior cutaneous nerve of the arm. Course It perforates the lateral head of the triceps brachii muscle at the triceps' attachment to the humerus. The upper and smaller branch of the nerve passes to the front of the elbow, lying close to the cephalic vein, and supplies the skin of the lower half of the arm. The lower branch pierces the deep fascia below the insertion of the Deltoideus, and descends along the lateral side of the arm and elbow, and then along the back of the forearm to the wrist, supplying the skin in its course, and joining, near its termination, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Cutaneous Nerve Of The Arm
The posterior cutaneous nerve of arm (internal cutaneous branch of musculospiral, posterior brachial cutaneous nerve) is a branch of the radial nerve that provides sensory innervation for much of the skin on the back of the arm. It arises in the axilla. It is of small size, and passes through the axilla to the medial side of the area supplying the skin on its dorsal surface nearly as far as the olecranon. In its course it crosses behind and communicates with the intercostobrachial. See also * Superior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm * Inferior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm * Medial cutaneous nerve of arm * Posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm The posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm is a nerve found in humans and other animals. It is also known as the dorsal antebrachial cutaneous nerve, the external cutaneous branch of the musculospiral nerve, and the posterior antebrachial cutaneous n ... Additional images File:Gray413_color.png, Cross-section through the middle of upper ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on each "hand" and fingerprints extremely similar to human fingerprints) are often described as having "hands" instead of paws on their front limbs. The raccoon is usually described as having "hands" though opposable thumbs are lacking. Some evolutionary anatomists use the term ''hand'' to refer to the appendage of digits on the forelimb more generally—for example, in the context of whether the three digits of the bird hand involved the same homologous loss of two digits as in the dinosaur hand. The human hand usually has five digits: four fingers plus one thumb; these are often referred to collectively as five fingers, however, whereby the thumb is included as one of the fingers. It has 27 bones, not including the sesamoid bone, the number of whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachioradialis
The brachioradialis is a muscle of the forearm that flexes the forearm at the elbow. It is also capable of both pronation and supination, depending on the position of the forearm. It is attached to the distal styloid process of the radius by way of the brachioradialis tendon, and to the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus. Structure The brachioradialis is a superficial, fusiform muscle on the lateral side of the forearm. It originates proximally on the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus. It inserts distally on the radius, at the base of its styloid process. Near the elbow, it forms the lateral limit of the cubital fossa, or elbow pit. Nerve supply Despite the bulk of the muscle body being visible from the anterior aspect of the forearm, the brachioradialis is a posterior compartment muscle and consequently is innervated by the radial nerve. Of the muscles that receive innervation from the radial nerve, it is one of only four that receive input directly from the ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachialis
The brachialis (brachialis anticus), also known as the Teichmann muscle, is a muscle in the upper arm that flexes the elbow. It lies deeper than the biceps brachii, and makes up part of the floor of the region known as the cubital fossa (elbow pit). The brachialis is the prime mover of elbow flexion generating about 50% more power than the biceps.Saladin, Kenneth S, Stephen J. Sullivan, and Christina A. Gan. Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function. 2015. Print. Structure The brachialis originates from the anterior surface of the distal half of the humerus, near the insertion of the deltoid muscle, which it embraces by two angular processes. Its origin extends below to within 2.5 cm of the margin of the articular surface of the humerus at the elbow joint. Its fibers converge to a thick tendon, which is inserted into the tuberosity of the ulna and the rough depression on the anterior surface of the coronoid process of the ulna. Blood supply The brachialis is supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubital Fossa
The cubital fossa, chelidon, or elbow pit, is the triangular area on the anterior side of the upper limb between the arm and forearm of a human or other hominid animals. It lies anteriorly to the elbow (Latin ) when in standard anatomical position. Boundaries * superior (proximal) boundary – an imaginary horizontal line connecting the medial epicondyle of the humerus to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus * medial (ulnar) boundary – lateral border of pronator teres muscle originating from the medial epicondyle of the humerus. * lateral (radial) boundary – medial border of brachioradialis muscle originating from the lateral supraepicondylar ridge of the humerus. * apex – it is directed inferiorly, and is formed by the meeting point of the lateral and medial boundaries * superficial boundary (roof) – skin, superficial fascia containing the median cubital vein, the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm and the medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm, deep fascia reinforce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascial Compartments Of Arm
The fascial compartments of arm refers to the specific anatomical term of the compartments within the upper segment of the upper limb (the arm) of the body. The upper limb is divided into two segments, the arm and the forearm. Each of these segments is further divided into two compartments which are formed by deep fascia – tough connective tissue septa (walls). Each compartment encloses specific muscles and nerves. The compartments of the arm are the anterior compartment of the arm and the posterior compartment of the arm, divided by the lateral and the medial intermuscular septa. The compartments of the forearm are the anterior compartment of the forearm and posterior compartment of the forearm. Intermuscular septa The lateral intermuscular septum extends from the lower part of the crest of the greater tubercle of the humerus, along the lateral supracondylar ridge, to the lateral epicondyle; it is blended with the tendon of the deltoid muscle, gives attachment to the tricep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltoid Tuberosity
In human anatomy, the deltoid tuberosity is a rough, triangular area on the anterolateral (front-side) surface of the middle of the humerus. It is a site of attachment of deltoid muscle. Structure Variation The deltoid tuberosity has been reported as very prominent in less than 10% of people. Development The deltoid tuberosity develops through endochondral ossification in a two-phase process. The initiating signal is tendon-dependent, whilst the growth phase is muscle-dependent. Clinical significance The deltoid tuberosity is at risk of avulsion fracture. These fractures may be managed conservatively with rest. Other animals In mammals, the humerus displays a wide morphological variation. The size and orientation of its functionally important features, including the deltoid tubercle, greater tubercle, and medial epicondyle, are pivotal to an animal's style of locomotion and habitat. In cursorial (running) animals such as the pronghorn, the deltoid tubercle is located ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Artery Of Arm
The deep artery of arm (also known as arteria profunda brachii and the deep brachial artery) is a large vessel which arises from the lateral and posterior part of the brachial artery, just below the lower border of the teres major. Structure It follows closely the radial nerve, running at first backward between the long and medial heads of the triceps brachii, then along the groove for the radial nerve (the radial sulcus), where it is covered by the lateral head of the triceps brachii, to the lateral side of the arm; there it pierces the lateral intermuscular septum, and, descending between the brachioradialis and the brachialis to the front of the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, ends by anastomosing with the radial recurrent artery. Branches and anastomoses It gives branches to the deltoid muscle (which, however, primarily is supplied by the posterior circumflex humeral artery) and to the muscles between which it lies; it supplies an occasional nutrient artery which enters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Sulcus
The radial groove (also known as the musculospiral groove, radial sulcus, or spiral groove) is a broad but shallow oblique depression for the radial nerve and deep brachial artery. It is located on the center of the lateral border of the humerus bone. Although it provides protection to the radial nerve, it is often involved in compressions on the nerve (due to external pressure due to surgery) that can cause radial nerve palsy. See also * Intertubercular groove * Triceps brachii muscle The triceps, or triceps brachii (Latin for "three-headed muscle of the arm"), is a large muscle on the back of the upper limb of many vertebrates. It consists of 3 parts: the medial, lateral, and long head. It is the muscle principally responsibl ... Additional images File:Gray413_color.png, Cross-section through the middle of upper arm. File:Gray525.png, The brachial artery. File:Gray818.png, The suprascapular, axillary, and radial nerves. References Bibliography Humerus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |