|
Radar Angels
Radar angels are an effect seen on radar displays when there is a periodic structure in the view of the radar that is roughly the same length as the signal's wavelength. The angel appears to be a physically huge object on the display, often miles across, that can obscure real targets. These were first noticed in the 1940s and were a topic of considerable study in the 1950s. The underlying mechanism is due to Bragg's law. History and source Early radars were subject to strong returns from the ground and their plan position indicator displays often featured many permanent echos that blanked out portions of the screen. Angels appeared on these systems, but were difficult to distinguish from these ground returns and generally not noticed. Development of the COHO concept in the UK eliminated these permanent echos, at which point angels were clearly seen for the first time on a continual basis. One of the earliest examples was seen in 1953 on the Radar, Anti-Aircraft No. 4 Mk. 7, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S Band Angel 1959
S, or s, is the nineteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ess'' (pronounced ), plural ''esses''. History Origin Northwest Semitic šîn represented a voiceless postalveolar fricative (as in 'ip'). It originated most likely as a pictogram of a tooth () and represented the phoneme via the acrophonic principle. Ancient Greek did not have a phoneme, so the derived Greek letter sigma () came to represent the voiceless alveolar sibilant . While the letter shape Σ continues Phoenician ''šîn'', its name ''sigma'' is taken from the letter ''samekh'', while the shape and position of ''samekh'' but name of ''šîn'' is continued in the '' xi''. Within Greek, the name of ''sigma'' was influenced by its association with the Greek word (earlier ) "to hiss". The original name of the letter "sigma" may have been ''san'', but due to the complic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example of convection, specifically atmospheric convection. Thermals on Earth The Sun warms the ground, which in turn warms the air directly above. The warm air near the surface expands, becoming less dense than the surrounding air. The lighter air rises and cools due to its expansion in the lower pressure at higher altitudes. It stops rising when it has cooled to the same temperature, thus density, as the surrounding air. Associated with a thermal is a downward flow surrounding the thermal column. The downward-moving exterior is caused by colder air being displaced at the top of the thermal. The size and strength of thermals are influenced by the properties of the lower atmosphere (the ''troposphere''). When the air is cold, bubbles of warm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or speaker driver) is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. A ''speaker system'', also often simply referred to as a "speaker" or "loudspeaker", comprises one or more such speaker ''drivers'', an enclosure, and electrical connections possibly including a crossover network. The speaker driver can be viewed as a linear motor attached to a diaphragm which couples that motor's movement to motion of air, that is, sound. An audio signal, typically from a microphone, recording, or radio broadcast, is amplified electronically to a power level capable of driving that motor in order to reproduce the sound corresponding to the original unamplified electronic signal. This is thus the opposite function to the microphone; indeed the ''dynamic speaker'' driver, by far the most common type, is a linear motor in the same basic configuration as the dynamic microphone which uses such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doppler Shift
The Doppler effect or Doppler shift (or simply Doppler, when in context) is the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who described the phenomenon in 1842. A common example of Doppler shift is the change of pitch heard when a vehicle sounding a horn approaches and recedes from an observer. Compared to the emitted frequency, the received frequency is higher during the approach, identical at the instant of passing by, and lower during the recession. The reason for the Doppler effect is that when the source of the waves is moving towards the observer, each successive wave crest is emitted from a position closer to the observer than the crest of the previous wave. Therefore, each wave takes slightly less time to reach the observer than the previous wave. Hence, the time between the arrivals of successive wave crests at the observer is reduced, causing an increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
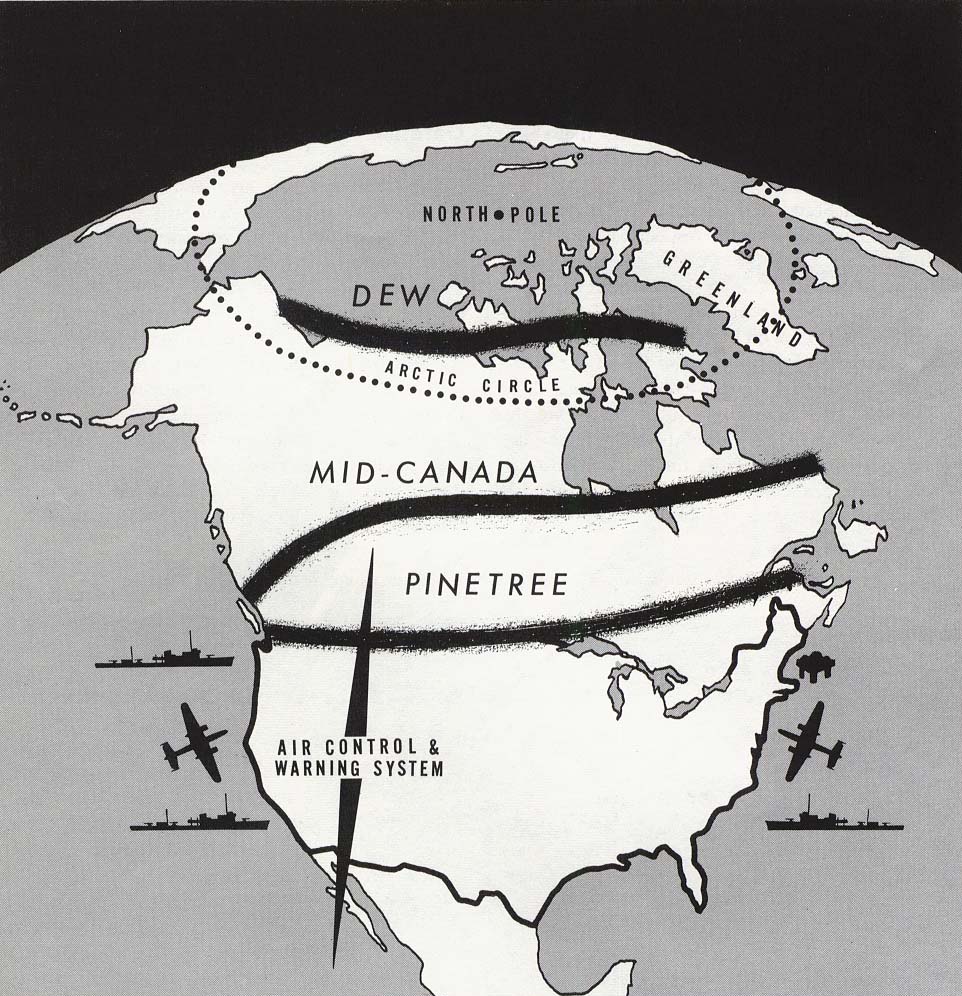
DEW Line
The Distant Early Warning Line, also known as the DEW Line or Early Warning Line, was a system of radar stations in the northern Arctic region of Canada, with additional stations along the north coast and Aleutian Islands of Alaska (see Project Stretchout and Project Bluegrass), in addition to the Faroe Islands, Greenland, and Iceland. It was set up to detect incoming bombers of the Soviet Union during the Cold War, and provide early warning of any sea-and-land invasion. The DEW Line was the northernmost and most capable of three radar lines in Canada and Alaska. The first of these was the joint Canadian-United States Pinetree Line, which ran from Newfoundland to Vancouver Island just north of the Canada–United States border, but even while it was being built there were concerns that it would not provide enough warning time to launch an effective counterattack. The Mid-Canada Line (MCL) was proposed as an inexpensive solution using bistatic radar. This provided a "trip wir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AN/FPS-23
The Motorola AN/FPS-23 was a short-range early warning radar deployed on the Distant Early Warning Line (DEW Line). It was used as a "gap filler", looking for aircraft attempting to sneak by the DEW line by flying between the main AN/FPS-19 stations at low altitude. It could detect aircraft flying at 200 feet over land or 50 feet over water. The system was known as Fluttar (flutter radar) during its development at the Lincoln Laboratory, and this name was widely used for the production units as well. It was also sometimes known as "Type F". MCL In the early 1950s, Canada undertook the development of a pioneering radar system as part of the Mid-Canada Line (MCL). This system was based on continuous wave radars that broadcast a signal between separate transmitter and receiver stations. When an aircraft passed through the space between the stations, some of the signal was reflected off the aircraft and back to the receiver. Today, this style of operation is known as a forward scat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Wave Radar
Continuous-wave radar (CW radar) is a type of radar system where a known stable frequency continuous wave radio energy is transmitted and then received from any reflecting objects. Individual objects can be detected using the Doppler effect, which causes the received signal to have a different frequency from the transmitted signal, allowing it to be detected by filtering out the transmitted frequency. Doppler-analysis of radar returns can allow the filtering out of slow or non-moving objects, thus offering immunity to interference from large stationary objects and slow-moving clutter. This makes it particularly useful for looking for objects against a background reflector, for instance, allowing a high-flying aircraft to look for aircraft flying at low altitude against the background of the surface. Because the very strong reflection off the surface can be filtered out, the much smaller reflection from a target can still be seen. CW radar systems are used at both ends of the rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-Canada Line
The Mid-Canada Line (MCL), also known as the McGill Fence, was a line of radar stations running east–west across the middle of Canada, used to provide early warning of a Soviet bomber attack on North America. It was built to supplement the Pinetree Line, which was located farther south. The majority of Mid-Canada Line stations were used only briefly from the late 1950s to the mid-1960s, as the attack threat changed from bombers to ICBMs. As the MCL was closed down, the early warning role passed almost entirely to the newer and more capable DEW Line farther north. The MCL was based on the bistatic radar principle, using separated transmitters and receivers. An aircraft flying anywhere between the stations would reflect some of the transmitted signal towards the receiver, where it would mix with the signal travelling directly from the transmitter. The mixing of the two signals produces a pattern that is very easy to detect using simple electronics. As the transmitter is not pul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Equation
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving information about the objects' locations and speeds. Radar was developed secretly for military use by several countries in the period before and during World War II. A key development was the cavity magnetron in the United Kingdom, which allowed the creation of relatively small systems with sub-meter resolution. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, recognising excellence in science, supporting outstanding science, providing scientific advice for policy, education and public engagement and fostering international and global co-operation. Founded on 28 November 1660, it was granted a royal charter by King Charles II as The Royal Society and is the oldest continuously existing scientific academy in the world. The society is governed by its Council, which is chaired by the Society's President, according to a set of statutes and standing orders. The members of Council and the President are elected from and by its Fellows, the basic members of the society, who are themselves elected by existing Fellows. , there are about 1,700 fellows, allowed to use the postnominal title FRS (Fellow of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starlings
Starlings are small to medium-sized passerine birds in the family Sturnidae. The Sturnidae are named for the genus ''Sturnus'', which in turn comes from the Latin word for starling, ''sturnus''. Many Asian species, particularly the larger ones, are called mynas, and many African species are known as glossy starlings because of their iridescent plumage. Starlings are native to Europe, Asia, and Africa, as well as northern Australia and the islands of the tropical Pacific. Several European and Asian species have been introduced to these areas, as well as North America, Hawaii, and New Zealand, where they generally compete for habitats with native birds and are considered to be invasive species. The starling species familiar to most people in Europe and North America is the common starling, and throughout much of Asia and the Pacific, the common myna is indeed common. Starlings have strong feet, their flight is strong and direct, and they are very gregarious. Their preferred habit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Baddow
Great Baddow is an urban village and civil parish in the Chelmsford borough of Essex, England. It is close to the city of Chelmsford, and, with a population of over 13,000,Great Baddow Parish Council published 2005, accessed 2011-10-13 is one of the largest villages in the country. History Great Baddow's name is believed to have been derived from the River Beadwan, now known as the , which marks the northern boundary of the village. ''Beadwan'' is thought to be a Celtic word of uncertain meaning, possibly "birch stream" or a reference to the goddess .[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)
