|
RQOPS
Reliable Quantum Operations Per Second (rQOPS) is a metric that measures the capabilities and error rates of a quantum computer. It combines several key factors to measure how many reliable operations a computer can execute in a single second: logical error rates, clock speed, and number of reliable qubits. The quantities included in rQOPS can be measured in all quantum computer architectures, allowing different architectures to be compared with one standard metric. A larger rQOPS measurement indicates a faster and more accurate device capable of solving more complex problems. Microsoft suggest that a machine with 1 million rQOPS qualifies as a quantum supercomputer. Alternative benchmarks include quantum volume, cross-entropy benchmarking, Circuit Layer Operations Per Second (CLOPS) proposed by IBM and IonQ's Algorithmic Qubits. However, as opposed to considering qubit performance alone, rQOPS measures how capable a quantum system is at solving tangible problems. Definition r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Volume
Quantum volume is a metric that measures the capabilities and error rates of a quantum computer. It expresses the maximum size of square quantum circuits that can be implemented successfully by the computer. The form of the circuits is independent from the quantum computer architecture, but compiler can transform and optimize it to take advantage of the computer's features. Thus, quantum volumes for different architectures can be compared. Introduction Quantum computers are difficult to compare. Quantum volume is a single number designed to show all around performance. It is a measurement and not a calculation, and takes into account several features of a quantum computer, starting with its number of qubits—other measures used are gate and measurement errors, crosstalk and connectivity. IBM defined its Quantum Volume metric because a classical computer's transistor count and a quantum computer's quantum bit count aren't the same. Qubits decohere with a resulting loss of performan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Computer
A quantum computer is a computer that exploits quantum mechanical phenomena. On small scales, physical matter exhibits properties of both particles and waves, and quantum computing takes advantage of this behavior using specialized hardware. Classical physics cannot explain the operation of these quantum devices, and a scalable quantum computer could perform some calculations exponentially faster than any modern "classical" computer. Theoretically a large-scale quantum computer could break some widely used encryption schemes and aid physicists in performing physical simulations; however, the current state of the art is largely experimental and impractical, with several obstacles to useful applications. The basic unit of information in quantum computing, the qubit (or "quantum bit"), serves the same function as the bit in classical computing. However, unlike a classical bit, which can be in one of two states (a binary), a qubit can exist in a superposition of its two " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
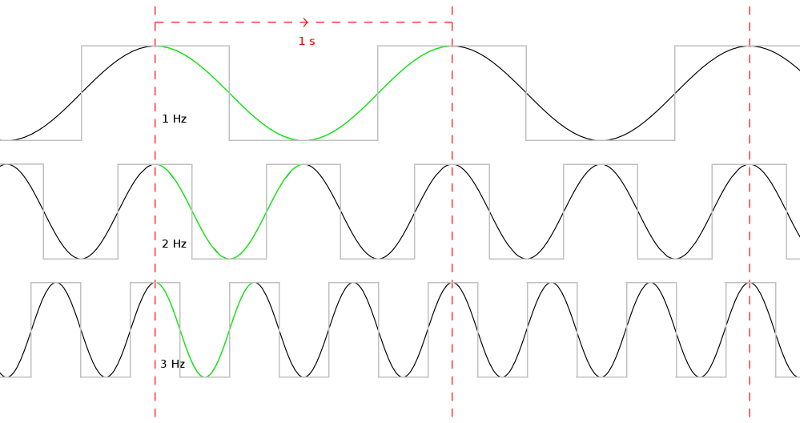
Clock Speed
Clock rate or clock speed in computing typically refers to the frequency at which the clock generator of a processor can generate pulses used to synchronize the operations of its components. It is used as an indicator of the processor's speed. Clock rate is measured in the SI unit of frequency hertz (Hz). The clock rate of the first generation of computers was measured in hertz or kilohertz (kHz), the first personal computers from the 1970s through the 1980s had clock rates measured in megahertz (MHz). In the 21st century the speed of modern CPUs is commonly advertised in gigahertz (GHz). This metric is most useful when comparing processors within the same family, holding constant other features that may affect performance. Determining factors Binning Manufacturers of modern processors typically charge higher prices for processors that operate at higher clock rates, a practice called binning. For a given CPU, the clock rates are determined at the end of the manufac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qubits
In quantum computing, a qubit () or quantum bit is a basic unit of quantum information—the quantum version of the classic binary bit physically realized with a two-state device. A qubit is a two-state (or two-level) quantum-mechanical system, one of the simplest quantum systems displaying the peculiarity of quantum mechanics. Examples include the spin of the electron in which the two levels can be taken as spin up and spin down; or the polarization of a single photon in which the two spin states (left-handed and the right-handed circular polarization) can also be measured as horizontal and vertical linear polarization. In a classical system, a bit would have to be in one state or the other. However, quantum mechanics allows the qubit to be in a coherent superposition of multiple states simultaneously, a property that is fundamental to quantum mechanics and quantum computing. Etymology The coining of the term ''qubit'' is attributed to Benjamin Schumacher. In the acknowledgmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Azure Quantum
Microsoft Azure Quantum is a public cloud-based quantum computing platform developed by Microsoft, that offers quantum hardware, software, and solutions for developers to build quantum applications. It supports variety of quantum hardware architectures from partners including Quantinuum, IonQ, and Atom Computing. To run applications on the cloud platform, Microsoft developed the Q# quantum programming language. Azure Quantum also includes a platform for scientific research, Azure Quantum Elements. It uses artificial intelligence, high-performance computing and quantum processors to run molecular simulations and calculations in computational chemistry and materials science. Azure Quantum was first announced at Microsoft Ignite in 2019. The platform was opened for public preview in 2021, and Azure Quantum Elements was launched in 2023. Hardware In addition to its hardware partners on the platform, Microsoft is developing a topological quantum computer with qubits that are inh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-entropy Benchmarking
Cross-entropy benchmarking (also referred to as XEB) is a quantum benchmarking protocol which can be used to demonstrate quantum supremacy. In XEB, a random quantum circuit is executed on a quantum computer multiple times in order to collect a set of k samples in the form of bitstrings \. The bitstrings are then used to calculate the cross-entropy benchmark fidelity (F_) via a classical computer, given by :F_= 2^ \langle P(x_) \rangle_ - 1 = \frac \left(\sum_^, \langle 0^, C, x_\rangle, ^\right) - 1, where n is the number of qubits in the circuit and P(x_) is the probability of a bitstring for an ideal quantum circuit C. If F_ = 1, the samples were collected from a noiseless quantum computer. If F_ = 0, then the samples could have been obtained via random guessing. This means that if a quantum computer did generate those samples, then the quantum computer is too noisy and thus has no chance of performing beyond-classical computations. Since it takes an exponential amount of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IonQ
IonQ, Inc. is an American quantum computing hardware and software company headquartered in College Park, Maryland. The company develops general-purpose trapped ion quantum computers and accompanying software to generate, optimize, and execute quantum circuits. History IonQ was co-founded by Christopher Monroe and Jungsang Kim, professors at Duke University, in 2015, with the help of Harry Weller and Andrew Schoen, partners at venture firm New Enterprise Associates. The company is an offshoot of the co-founders’ 25 years of academic research in quantum information science. Monroe's quantum computing research began as a Staff Researcher at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) with Nobel-laureate physicist David Wineland where he led a team using trapped ions to produce the first controllable qubits and the first controllable quantum logic gate, culminating in a proposed architecture for a large-scale trapped ion computer. Kim and Monroe began collabora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical And Logical Qubits
In quantum computing, a ''qubit'' is a unit of information analogous to a bit (binary digit) in classical computing, but it is affected by quantum mechanical properties such as superposition and entanglement which allow qubits to be in some ways more powerful than classical bits for some tasks. Qubits are used in quantum circuits and quantum algorithms composed of quantum logic gates to solve computational problems, where they are used for input/output and intermediate computations. A physical qubit is a physical device that behaves as a two-state quantum system, used as a component of a computer system. A logical qubit is a physical or abstract qubit that performs as specified in a quantum algorithm or quantum circuit subject to unitary transformations, has a long enough coherence time to be usable by quantum logic gates (cf. propagation delay for classical logic gates). Since the development of the first quantum computer in 1998, most technologies used to implement qubits f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The early 1980s and home computers, rise of personal computers through software like Windows, and the company has since expanded to Internet services, cloud computing, video gaming and other fields. Microsoft is the List of the largest software companies, largest software maker, one of the Trillion-dollar company, most valuable public U.S. companies, and one of the List of most valuable brands, most valuable brands globally. Microsoft was founded by Bill Gates and Paul Allen to develop and sell BASIC interpreters for the Altair 8800. It rose to dominate the personal computer operating system market with MS-DOS in the mid-1980s, followed by Windows. During the 41 years from 1980 to 2021 Microsoft released 9 versions of MS-DOS with a median frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noisy Intermediate-scale Quantum Era
The current state of quantum computing is referred to as the noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) era, characterized by quantum processors containing up to 1,000 qubits which are not advanced enough yet for fault-tolerance or large enough to achieve quantum advantage. These processors, which are sensitive to their environment (noisy) and prone to quantum decoherence, are not yet capable of continuous quantum error correction. This intermediate-scale is defined by the quantum volume, which is based on the moderate number of qubits and gate fidelity. The term NISQ was coined by John Preskill in 2018. According to Microsoft Azure Quantum's scheme, NISQ computation is considered level 1, the lowest of the quantum computing implementation levels. In October 2023, the 1,000 qubit mark was passed for the first time by Atom Computing's 1,180 qubit quantum processor. However, as of 2024, only two quantum processors have over 1,000 qubits, with sub-1,000 quantum processors still rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Error Correction
Quantum error correction (QEC) is a set of techniques used in quantum computing to protect quantum information from errors due to decoherence and other quantum noise. Quantum error correction is theorised as essential to achieve fault tolerant quantum computing that can reduce the effects of noise on stored quantum information, faulty quantum gates, faulty quantum state preparation, and faulty measurements. Effective quantum error correction would allow quantum computers with low qubit fidelity to execute algorithms of higher complexity or greater circuit depth. Classical error correction often employs redundancy. The simplest albeit inefficient approach is the repetition code. A repetition code stores the desired (logical) information as multiple copies, and—if these copies are later found to disagree due to errors introduced to the system—determines the most likely value for the original data by majority vote. For instance, suppose we copy a bit in the one (on) state thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threshold Theorem
In quantum computing, the threshold theorem (or quantum fault-tolerance theorem) states that a quantum computer with a physical error rate below a certain threshold can, through application of quantum error correction schemes, suppress the logical error rate to arbitrarily low levels. This shows that quantum computers can be made fault-tolerant, as an analogue to von Neumann's threshold theorem for classical computation. This result was proven (for various error models) by the groups of Dorit Aharanov and Michael Ben-Or; Emanuel Knill, Raymond Laflamme, and Wojciech Zurek; and Alexei Kitaev independently. These results built on a paper of Peter Shor, which proved a weaker version of the threshold theorem. Explanation The key question that the threshold theorem resolves is whether quantum computers in practice could perform long computations without succumbing to noise. Since a quantum computer will not be able to perform gate operations perfectly, some small constant error ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |