|
RML 9 Pounder 8 And 6 Cwt Guns
The RML 9-pounder 8 cwt gun and the RML 9-pounder 6 cwt gun were British Rifled, Muzzle Loading (RML) field, horse and naval artillery guns manufactured in England in the 19th century, which fired a projectile weighing approximately . "8 cwt" and "6 cwt" refers to the weight of the gun to differentiate it from other 9-pounder guns. Service history The 9-pounder 8 cwt Rifled Muzzle Loader was the field gun selected by the Royal Artillery in 1871 to replace the more sophisticated RBL 12 pounder 8 cwt Armstrong gun, which had acquired a reputation for unreliability. The gun was rifled using the system developed by William Palliser, in which studs protruding from the side of the shell engaged with three spiral grooves in the barrel.Skaarup, Harold A (2012)''Shelldrake: Canadian Artillery Museums and Gun Monuments''iUniverse.com, (p. 131) In 1874, a 6 cwt version was introduced for horse artillery and was later adopted for field artillery use, replacing the 8 cwt version. All v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
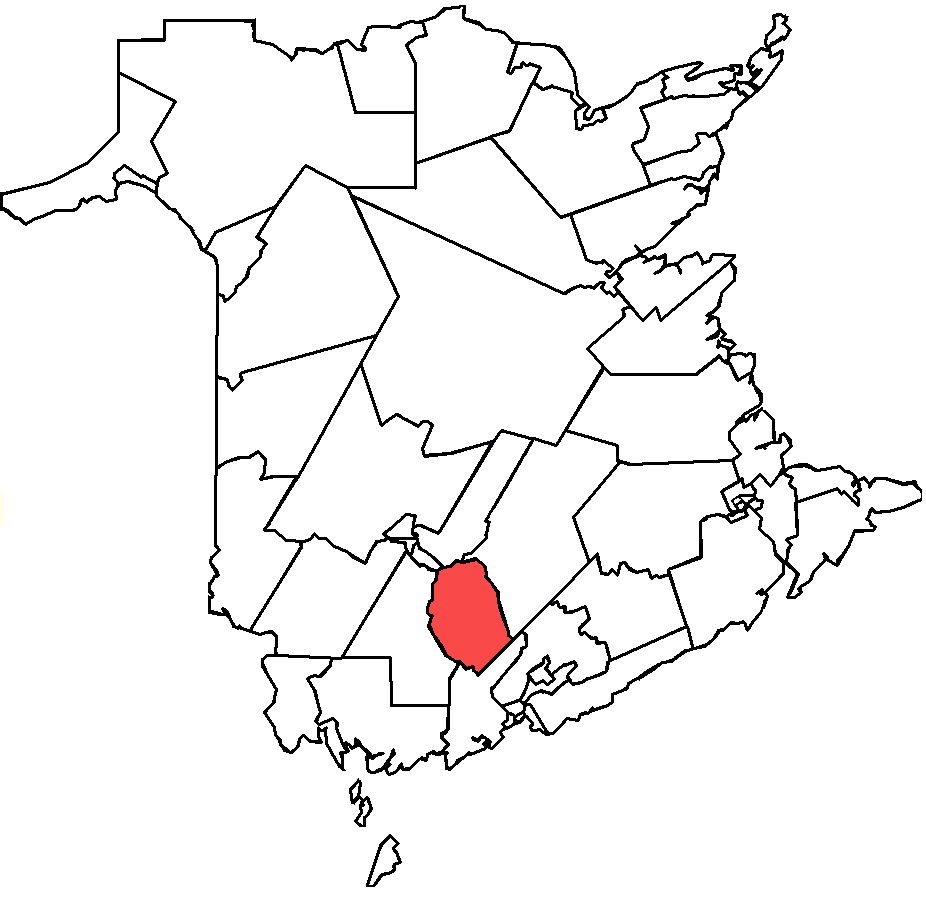
CFB Gagetown
5th Canadian Division Support Base (5 CDSB) Gagetown, formerly known as and commonly referred to as CFB Gagetown, is a large Canadian Forces Base covering an area over , located in southwestern New Brunswick. Construction of the base At the beginning of the Cold War, Canadian defence planners recognized the need for providing the Canadian Army with a suitable training facility where brigade and division-sized armoured, infantry, and artillery units could exercise in preparation for their role in defending western Europe under Canada's obligations to the North Atlantic Treaty. The facility would need to be located relatively close to an all-season Atlantic port and have suitable railway connections. Existing training facilities dating from the First and Second World Wars in eastern Canada were relatively small ( Camp Debert, Camp Aldershot, Sussex Military Camp, Camp Valcartier, Camp Petawawa, Camp Utopia), thus a new facility was considered. At the same time, regional econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrapnel Shell
Shrapnel shells were anti-personnel artillery munitions which carried many individual bullets close to a target area and then ejected them to allow them to continue along the shell's trajectory and strike targets individually. They relied almost entirely on the shell's velocity for their lethality. The munition has been obsolete since the end of World War I for anti-personnel use; high-explosive shells superseded it for that role. The functioning and principles behind Shrapnel shells are fundamentally different from high-explosive shell fragmentation. Shrapnel is named after Lieutenant-General Henry Shrapnel (1761–1842), a British artillery officer, whose experiments, initially conducted on his own time and at his own expense, culminated in the design and development of a new type of artillery shell. Usage of term "shrapnel" has changed over time to also refer to fragmentation of the casing of shells and bombs. This is its most common modern usage, which strays from the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Artillery Museum
The Royal Artillery Museum, which was one of the world's oldest military museums, was first opened to the public in Woolwich in southeast London in 1820. It told the story of the development of artillery through the ages by way of a collection of artillery pieces from across the centuries. The museum had its roots in an earlier institution, the Royal Military Repository (established in Woolwich in the 1770s as a training collection for cadets of the Royal Military Academy, Woolwich, Royal Military Academy); items which were once displayed in the Repository form the nucleus of the Royal Artillery Museum collection. Following the closure in 2016 of the museum, branded since 2001 as 'Firepower – The Royal Artillery Museum', its collection has been placed in storage pending the establishment of a new Royal Artillery Museum. The Royal Artillery Museum collections are designated as being of national and international significance by Arts Council England. History The museum has it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cascabel (artillery)
A cascabel is a subassembly of a muzzle-loading cannon, a knob to which to attach arresting ropes to deal with the recoil of firing the cannon. Description A cannon's cascabel comprises the knob (A) and the neck (B), with some models also having a filet (C). By some definitions the cascabel additionally includes the base of the breech (D). Cascabels varied in design and appearance, and were a common feature of cannons from the 17th century until the advent of the breech loading cannon in the late 19th century. Many naval guns had a heavy metal loop on the cascabel, the pomellion, through which a wide rope was passed. Bronze cascabels from captured guns have been used to make Victoria Cross The Victoria Cross (VC) is the highest and most prestigious award of the British honours system. It is awarded for valour "in the presence of the enemy" to members of the British Armed Forces and may be awarded posthumously. It was previously ... medals. It was long thought that Russ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrought Iron
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.08%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4%). It is a semi-fused mass of iron with fibrous slag Inclusion (mineral), inclusions (up to 2% by weight), which give it a wood-like "grain" that is visible when it is etched, rusted, or bent to structural failure, failure. Wrought iron is tough, malleable, ductile, corrosion resistant, and easily forge welding, forge welded, but is more difficult to welding, weld electrically. Before the development of effective methods of steelmaking and the availability of large quantities of steel, wrought iron was the most common form of malleable iron. It was given the name ''wrought'' because it was hammered, rolled, or otherwise worked while hot enough to expel molten slag. The modern functional equivalent of wrought iron is Carbon steel#Mild or low-carbon steel, mild steel, also called low-carbon steel. Neither wrought iron nor mild steel contain enough carbon to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun Carriage
A gun carriage is a frame and mount that supports the gun barrel of an artillery piece, allowing it to be maneuvered and fired. These platforms often had wheels so that the artillery pieces could be moved more easily. Gun carriages are also used on ships to facilitate the movement and aiming of large cannons. Early guns The earliest guns were laid directly onto the ground, with earth being piled up under the muzzle end of the barrel to increase the elevation. As the size of guns increased, they began to be attached to heavy wooden frames or beds that were held down by stakes. These began to be replaced by wheeled carriages in the early 16th century. Smoothbore gun carriages From the 16th to the mid-19th century, the main form of artillery remained the smoothbore cannon. By this time, the trunnion (a short axle protruding from either side of the gun barrel) had been developed, with the result that the barrel could be held in two recesses in the carriage and secured with an iro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Horse Artillery
The Royal Horse Artillery (RHA) was formed in 1793 as a distinct arm of the Royal Regiment of Artillery (commonly termed Royal Artillery) to provide horse artillery support to the cavalry units of the British Army. (Although the cavalry link remained part of its defining character, as early as the Battle of Waterloo the RHA was sometimes deployed more along the lines of conventional field artillery, fighting from comparatively fixed positions). The Royal Horse Artillery, currently consists of three regiments, ( 1 RHA, 3 RHA and 7 RHA) and one ceremonial unit (King's Troop, Royal Horse Artillery). Almost all the batteries of the Royal Horse Artillery have served continuously since the French Revolutionary Wars or Napoleonic Wars, except the King's Troop, created in 1946, and M Battery which was 'reanimated' in 1993. Horses are still in service for ceremonial purposes but were phased out from operational deployment in the 1930s. History In 1793, in the course of the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Indian Navy
The Royal Indian Navy (RIN) was the naval force of British India and the Dominion of India. Along with the Presidency armies, later the Indian Army, and from 1932 the Royal Indian Air Force, it was one of the Armed Forces of British India. From its origins in 1612 as the East India Company's Marine, the Navy underwent various changes, including changes to its name. Over time it was named the Bombay Marine (1686), the Bombay Marine Corps (1829), the Indian Navy (1830), Her Majesty's Indian Navy (1858), the Bombay and Bengal Marine (1863), the Indian Defence Force (1871), Her Majesty's Indian Marine (1877) and the Royal Indian Marine (1892). It was finally named the Royal Indian Navy in 1934. However, it remained a relatively small force until the Second World War, when it was greatly expanded. After the partition of India into two independent states in 1947, the Navy was split between Pakistan and India. One-third of the assets and personnel were assigned to Royal Pakistan Nav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Ayrshire And Galloway Artillery Volunteers
The 1st Ayrshire and Galloway Artillery Volunteer Corps was formed in 1859 as a response to a French invasion threat. It transferred to the Territorial Force (TF) in 1908 and its successor units fought with the 52nd (Lowland) Infantry Division in Palestine during World War I, and in North West Europe and Burma during World War II. It continued in the Territorial Army (TA) until amalgamation in 1967. Frederick, pp. 649, 661. Litchfield, pp. 278–9. Artillery Volunteers The enthusiasm for the Volunteer movement following an invasion scare in 1859 saw the creation of many Rifle and Artillery Volunteer Corps composed of part-time soldiers eager to supplement the Regular British Army in time of need. The 1st Administrative Brigade of Ayrshire Artillery Volunteers was formed with its headquarters (HQ) at Irvine, North Ayrshire, in November 1860. It comprised the following Ayrshire Artillery Volunteer Corps (AVCs):Beckett, Appendix VIII.Grierson, pp. 146–8.Litchfield & Westlake, pp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Egyptian War
The British conquest of Egypt (1882), also known as Anglo-Egyptian War (), occurred in 1882 between Egyptian and Sudanese forces under Ahmed ‘Urabi and the United Kingdom. It ended a nationalist uprising against the Khedive Tewfik Pasha. It established firm British influence over Egypt at the expense of the Egyptians, the French, and the Ottoman Empire, whose already weak authority became nominal. Background In 1881, an Egyptian army officer, Ahmed ‘Urabi (then known in English as Arabi Pasha), mutinied and initiated a coup against Tewfik Pasha, the Khedive of Egypt and Sudan, because of grievances over disparities in pay between Egyptians and Europeans, as well as other concerns. In January 1882 the British and French governments sent a "Joint Note" to the Egyptian government, declaring their recognition of the Khedive's authority. On 20 May, British and French warships arrived off the coast of Alexandria. On 11 June, an anti-Christian riot occurred in Alexandria that k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Boer War
The First Boer War ( af, Eerste Vryheidsoorlog, literally "First Freedom War"), 1880–1881, also known as the First Anglo–Boer War, the Transvaal War or the Transvaal Rebellion, was fought from 16 December 1880 until 23 March 1881 between the United Kingdom and Boers of the Transvaal (as the South African Republic was known while under British administration). The war resulted in a Boer victory and eventual independence of the South African Republic. Background In the 19th century a series of events occurred in the southern part of the African continent, with the British from time to time attempting to set up a single unified state there, while at other times wanting to control less territory. Three prime factors fuelled British expansion into Southern Africa: * the desire to control the trade routes to India that passed around the Cape of Good Hope * the discovery in 1868 of huge mineral deposits of diamonds around Kimberley on the joint borders of the South African R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







_p245_BOMBARDEMENT_OF_ALEXANDRIA_-_JULY_1882.jpg)
