|
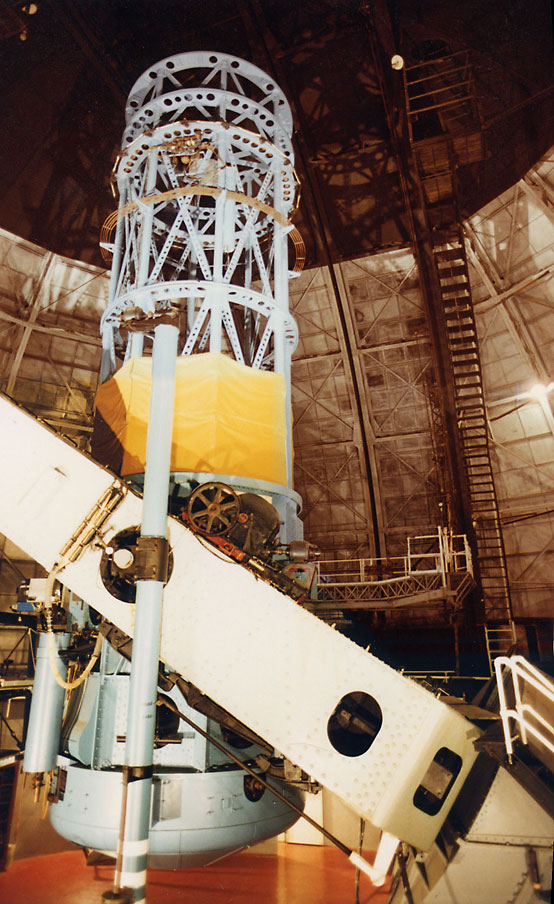
R. F. Joyce Observatory
R. F. Joyce Observatory is the home observatory of the Canterbury Astronomical Society (CAS) and is situated near West Melton, Christchurch, New Zealand. The observatory is the result of the bequest of R. F. Joyce, a founding member and former President of the CAS. The primary instruments in use are a 16" Meade RCX400, a 14.5" Cassegrain telescope, two 11" Schmidt-Cassegrain telescopes, and a 120mm refractor A refracting telescope (also called a refractor) is a type of optical telescope that uses a lens (optics), lens as its objective (optics), objective to form an image (also referred to a dioptrics, dioptric telescope). The refracting telescope d .... External linksCanterbury Astronomical Society webpage {{Astronomical observatories in New Zealand Astronomical observatories in New Zealand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Melton, New Zealand
West Melton is a town in the Selwyn District, in the Canterbury region of New Zealand's South Island. It is located west of Christchurch and is part of the Christchurch metropolitan area. The town has a population of 2,640 (June 2022), making it the 124th-largest urban area in New Zealand, the 16th-largest in Canterbury and fifth-largest in the Selwyn District (behind Darfield and before Leeston). History West Melton was first settled in the 1870s, where it has long been associated with horse racing (trotting), cropping, and sheep farming. Recently, it has become associated with wine growing and deer farming. In 1881, Alfred Saunders arrived in West Melton, where he bought a farm that he referred to as a “bleak and wild looking property”. On 26 October 2014, West Melton residents celebrated the town's 150th anniversary. Urban expansion In 2007, West Melton saw the start of its urban expansion. Gainsborough and Halkett Grove subdivisions were the first developmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christchurch
Christchurch ( ; mi, Ōtautahi) is the largest city in the South Island of New Zealand and the seat of the Canterbury Region. Christchurch lies on the South Island's east coast, just north of Banks Peninsula on Pegasus Bay. The Avon River / Ōtākaro flows through the centre of the city, with an urban park along its banks. The city's territorial authority population is people, and includes a number of smaller urban areas as well as rural areas. The population of the urban area is people. Christchurch is the second-largest city by urban area population in New Zealand, after Auckland. It is the major urban area of an emerging sub-region known informally as Greater Christchurch. Notable smaller urban areas within this sub-region include Rangiora and Kaiapoi in Waimakariri District, north of the Waimakariri River, and Rolleston and Lincoln in Selwyn District to the south. The first inhabitants migrated to the area sometime between 1000 and 1250 AD. They hunted moa, which led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observatory
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysical, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed. Historically, observatories were as simple as containing an astronomical sextant (for measuring the distance between stars) or Stonehenge (which has some alignments on astronomical phenomena). Astronomical observatories Astronomical observatories are mainly divided into four categories: space-based, airborne, ground-based, and underground-based. Ground-based observatories Ground-based observatories, located on the surface of Earth, are used to make observations in the radio and visible light portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Most optical telescopes are housed within a dome or similar structure, to protect the delicate instruments from the elements. Telescope domes have a slit or other opening in the roof that can be opened during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
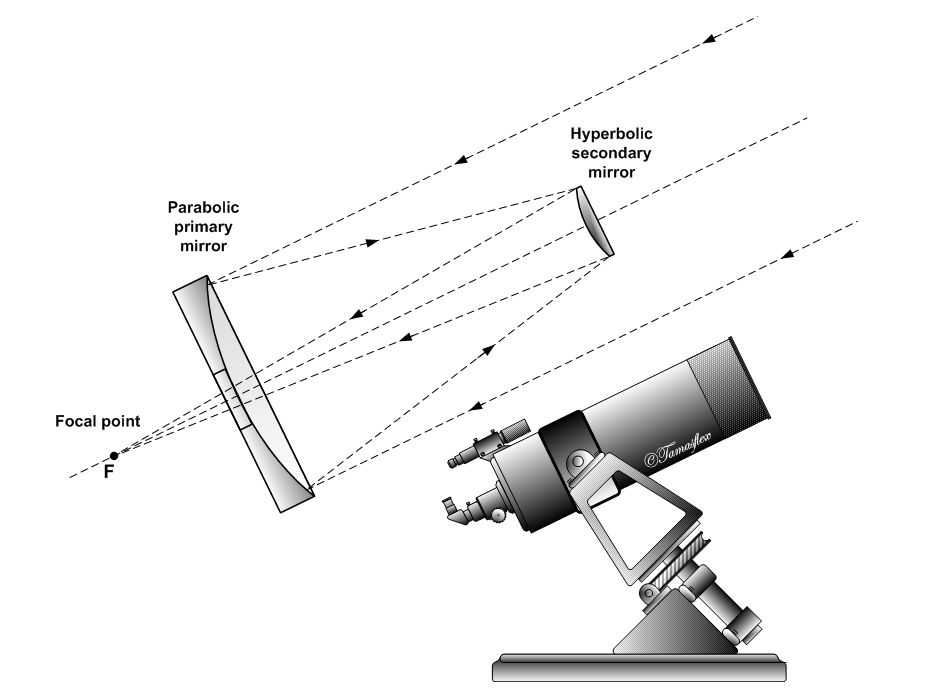
Cassegrain Reflector
The Cassegrain reflector is a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror, often used in optical telescopes and radio antennas, the main characteristic being that the optical path folds back onto itself, relative to the optical system's primary mirror entrance aperture. This design puts the focal point at a convenient location behind the primary mirror and the convex secondary adds a telephoto effect creating a much longer focal length in a mechanically short system. In a symmetrical Cassegrain both mirrors are aligned about the optical axis, and the primary mirror usually contains a hole in the center, thus permitting the light to reach an eyepiece, a camera, or an image sensor. Alternatively, as in many radio telescopes, the final focus may be in front of the primary. In an asymmetrical Cassegrain, the mirror(s) may be tilted to avoid obscuration of the primary or to avoid the need for a hole in the primary mirror (or both). The classic Cassegrain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally meaning only an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe distant objects, the word ''telescope'' now refers to a wide range of instruments capable of detecting different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, and in some cases other types of detectors. The first known practical telescopes were refracting telescopes with glass lenses and were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 17th century. They were used for both terrestrial applications and astronomy. The reflecting telescope, which uses mirrors to collect and focus light, was invented within a few decades of the first refracting telescope. In the 20th century, many new types of telescopes were invented, including radio telescopes in the 1930s and infrared telescopes in the 1960s. Etymology The word ''telescope'' was coin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractor
A refracting telescope (also called a refractor) is a type of optical telescope that uses a lens (optics), lens as its objective (optics), objective to form an image (also referred to a dioptrics, dioptric telescope). The refracting telescope design was originally used in spyglasses and astronomy, astronomical telescopes but is also used for long-focus lens, long-focus camera lenses. Although large refracting telescopes were very popular in the second half of the 19th century, for most research purposes, the refracting telescope has been superseded by the reflecting telescope, which allows larger apertures. A refractor's magnification is calculated by dividing the focal length of the objective lens by that of the eyepiece. Refracting telescopes typically have a lens at the front, then a optical train, long tube, then an eyepiece or instrumentation at the rear, where the telescope view comes to focus. Originally, telescopes had an objective of one element, but a century later, tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |