|
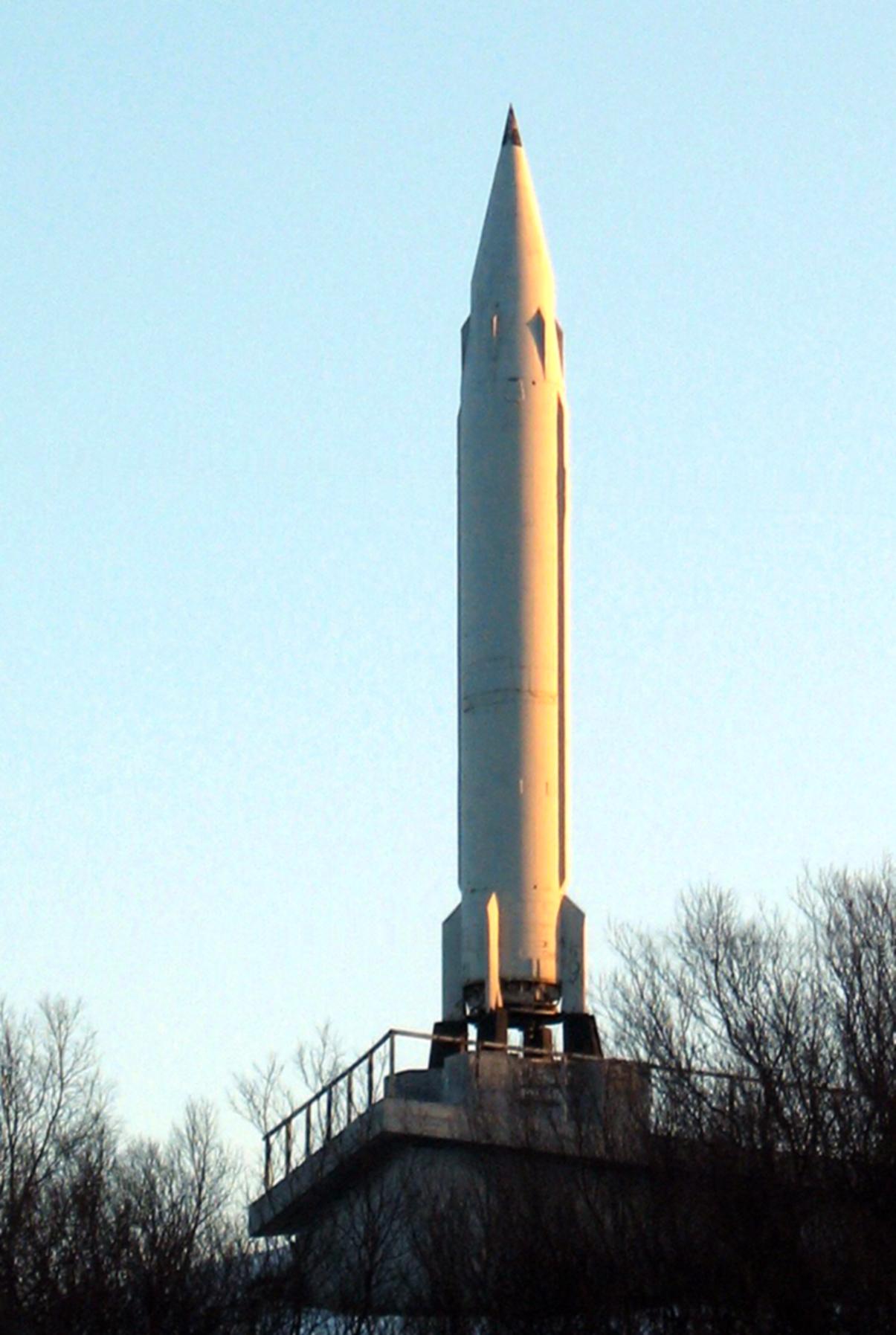
R-13 (missile)
The R-13 (russian: ракета-13) was a submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) developed by the Soviet Union starting around 1955. It was assigned the NATO reporting name SS-N-4 Sark and carried the GRAU index 4K50. History Development of the R-13 was authorised by the Soviet Supreme Council on 25 July 1955 for use on the Project 629 and Project 658 submarines. The design work was started by OKB-1 under Sergei Korolev before being transferred to CB Miasskoe engineering / Makeyev Rocket Design Bureau (chief designer - Viktor Makeyev). Final technical specifications was approved by 11 January 1956. Serial production was undertaken at Zlatoust Machine-Building Plant in 1959. The R-13 was a single-stage liquid-fuel rocket and entered service in 1961. This missile was somewhat similar in design to the R-11FM missile, which caused some confusion in Western intelligence services during the Cold War. The missiles were phased out from 1965 to 1975. This missile was the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severomorsk R-13 Monument
Severomorsk (russian: Северомо́рск), known as Vayenga () until April 18, 1951, is a closed town in Murmansk Oblast, Russia. Severomorsk is the main administrative base of the Russian Northern Fleet. The town is located on the coast of the Barents Sea along the Kola Bay northeast of Murmansk, the administrative centre of the oblast, to which it is connected by railway and a motorway. History Early settlement The first settlement on the site of the modern city arose between 1896 and 1897. It was named Vayenga (), after the river, the name of which itself comes from the Sami "vayongg", meaning "doe" or "reindeer". In 1917, only thirteen people lived in the settlement, who engaged in hunting, fishing and animal husbandry. The founding of the Northern Fleet Base In 1926, the Murmansk office of logging was founded, one of the artels of which was sent to Vayenga. A barracks, a dormitory, and a banya were built, and a telephone line was laid through the village. In 1933, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because there was no large-scale fighting directly between the two superpowers, but they each supported major regional conflicts known as proxy wars. The conflict was based around the ideological and geopolitical struggle for global influence by these two superpowers, following their temporary alliance and victory against Nazi Germany and Imperial Japan in 1945. Aside from the nuclear arsenal development and conventional military deployment, the struggle for dominance was expressed via indirect means such as psychological warfare, propaganda campaigns, espionage, far-reaching embargoes, rivalry at sports events, and technological competitions such as the Space Race. The Western Bloc was led by the United States as well as a number of other First W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Missiles
Below is a list of missiles, sorted alphabetically into large categories and subcategories by name and purpose. Other missile lists Types of missiles: * Conventional guided missiles ** Air-to-air missile ** Air-to-surface missile ** Anti-radiation missile ** Anti-ballistic missile ** Anti-satellite weapon ** Anti-ship missile (list) ** Anti-submarine missile ** Anti-tank guided missile (list) ** Land-attack missile ** Shoulder-launched missiles ** Surface-to-air missile (list) ** Surface-to-surface missile ** Wire-guided missile * Cruise missiles ** Air-launched cruise missile ** Ground-launched cruise missile ** Submarine-launched cruise missile * Ballistic missiles ** Tactical ballistic missile ** Short-range ballistic missile ** Theatre ballistic missile ** Medium-range ballistic missile ** Intermediate-range ballistic missile ** Intercontinental ballistic missile (List of ICBMs/Comparison of ICBMs) ** Submarine-launched ballistic missile ** Air-launched ballistic missile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
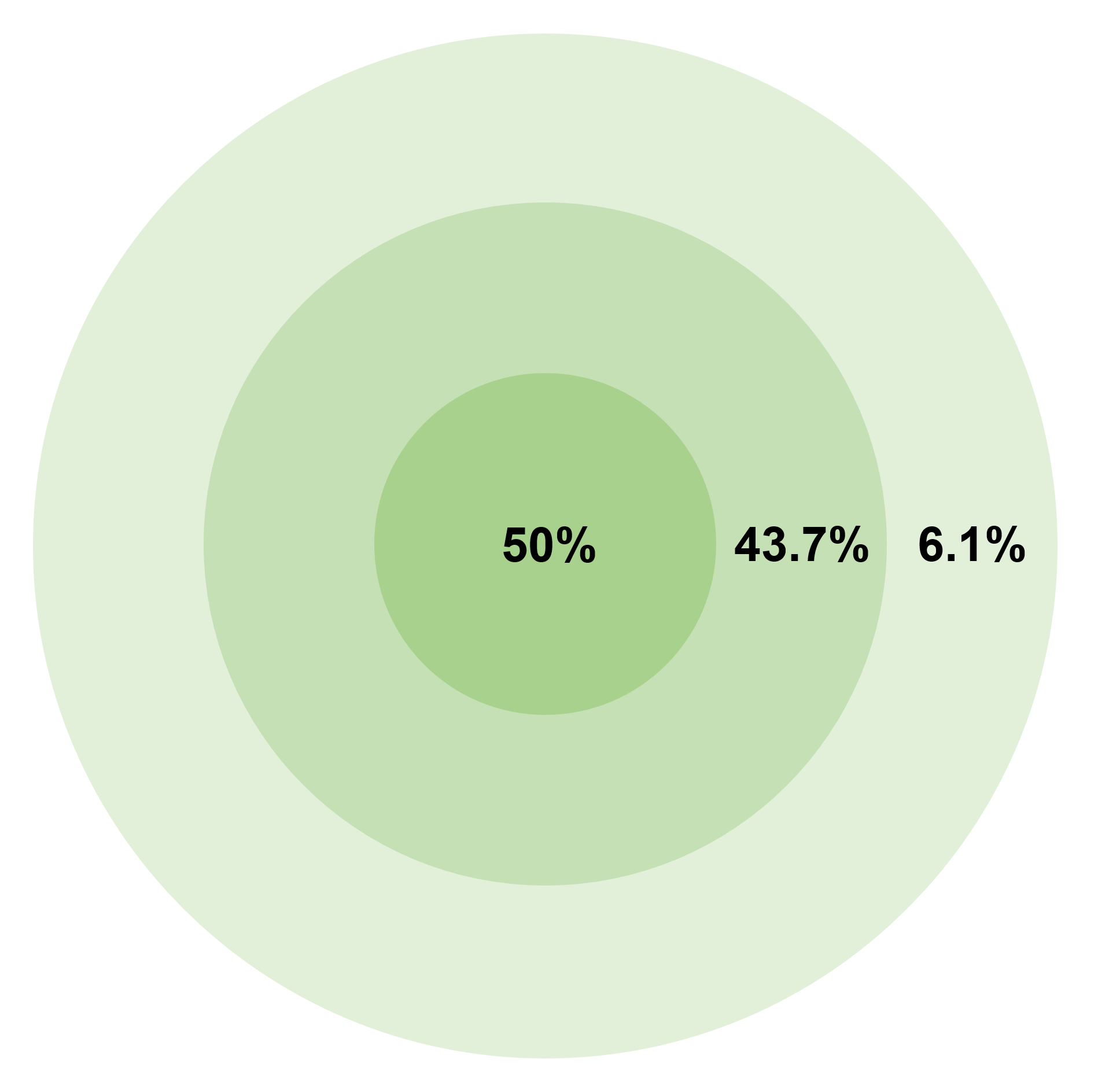
Circular Error Probable
In the military science of ballistics, circular error probable (CEP) (also circular error probability or circle of equal probability) is a measure of a weapon system's precision. It is defined as the radius of a circle, centered on the mean, whose perimeter is expected to include the landing points of 50% of the rounds; said otherwise, it is the median error radius. That is, if a given munitions design has a CEP of 100 m, when 100 munitions are targeted at the same point, 50 will fall within a circle with a radius of 100 m around their average impact point. (The distance between the target point and the average impact point is referred to as bias.) There are associated concepts, such as the DRMS (distance root mean square), which is the square root of the average squared distance error, and R95, which is the radius of the circle where 95% of the values would fall in. The concept of CEP also plays a role when measuring the accuracy of a position obtained by a navigati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonka (fuel)
Tonka (also TONKA-250 and R-Stoff) is the name given to a German-designed rocket propellant first used in the Wasserfall missile, and recently used by North Korea. It was used in the Soviet Union under the name TG-02, for example in the engine designs of the A.M. Isayev Chemical Engineering Design Bureau. Its name is a reference to the tonka bean. Being invented during the Second World War, it has no connection to the similarly named toys. Its composition is approximately 50% triethylamine and 50% xylidine, most commonly used with nitric acid or its anhydrous nitric oxide derivatives (classified as the AK-2x family in the Soviet Union) as the oxidiser; the combination is hypergolic and has a maximum practical specific impulse of approximately at sea level, with the latter figure stated as a specification for the R-21 Submarine Launched Ballistic Missile, first fielded in 1963. The Soviet Union reverse-engineered the Wasserfall missile and investigated the use of hypergolic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Fuming Nitric Acid
Red fuming nitric acid (RFNA) is a storable oxidizer used as a rocket propellant. It consists of 84% nitric acid (), 13% dinitrogen tetroxide and 1–2% water. The color of red fuming nitric acid is due to the dinitrogen tetroxide, which breaks down partially to form nitrogen dioxide. The nitrogen dioxide dissolves until the liquid is saturated, and produces toxic fumes with a suffocating odor. RFNA increases the flammability of combustible materials and is highly exothermic when reacting with water. It is usually used with an inhibitor (with various, sometimes secret, substances, including hydrogen fluoride; any such combination is called ''inhibited RFNA'', ''IRFNA'') because nitric acid attacks most container materials. Hydrogen fluoride for instance will passivate the container metal with a thin layer of metal fluoride, making it nearly impervious to the nitric acid. It can also be a component of a monopropellant; with substances like amine nitrates dissolved in it, it can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stabilizer (aircraft)
An aircraft stabilizer is an aerodynamic surface, typically including one or more movable control surfaces, that provides longitudinal (pitch) and/or directional (yaw) stability and control. A stabilizer can feature a fixed or adjustable structure on which any movable control surfaces are hinged, or it can itself be a fully movable surface such as a stabilator. Depending on the context, "stabilizer" may sometimes describe only the front part of the overall surface. In the conventional aircraft configuration, separate vertical (fin) and horizontal (tailplane) stabilizers form an empennage positioned at the tail of the aircraft. Other arrangements of the empennage, such as the V-tail configuration, feature stabilizers which contribute to a combination of longitudinal and directional stabilization and control. Longitudinal stability and control may be obtained with other wing configurations, including canard, tandem wing and tailless aircraft. Some types of aircraft are stabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight Control Surfaces
Aircraft flight control surfaces are aerodynamic devices allowing a pilot to adjust and control the aircraft's flight attitude. Development of an effective set of flight control surfaces was a critical advance in the development of aircraft. Early efforts at fixed-wing aircraft design succeeded in generating sufficient lift to get the aircraft off the ground, but once aloft, the aircraft proved uncontrollable, often with disastrous results. The development of effective flight controls is what allowed stable flight. This article describes the control surfaces used on a fixed-wing aircraft of conventional design. Other fixed-wing aircraft configurations may use different control surfaces but the basic principles remain. The controls (stick and rudder) for rotary wing aircraft (helicopter or autogyro) accomplish the same motions about the three axes of rotation, but manipulate the rotating flight controls (main rotor disk and tail rotor disk) in a completely different manner. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerodynamic
Aerodynamics, from grc, ἀήρ ''aero'' (air) + grc, δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dynamics and its subfield of gas dynamics. The term ''aerodynamics'' is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, the difference being that "gas dynamics" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, and is not limited to air. The formal study of aerodynamics began in the modern sense in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag were recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics were directed toward achieving heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Otto Lilienthal in 1891. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer simulations has formed a rational basis for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vernier Thruster
A vernier thruster is a rocket engine used on a spacecraft for fine adjustments to the attitude or velocity of a spacecraft. Depending on the design of a craft's maneuvering and stability systems, it may simply be a smaller thruster complementing the main propulsion system, or it may complement larger attitude control thrusters, or may be a part of the reaction control system. The name is derived from vernier calipers (named after Pierre Vernier) which have a primary scale for gross measurements, and a secondary scale for fine measurements. Vernier thrusters are used when a heavy spacecraft requires a wide range of different thrust levels for attitude or velocity control, as for maneuvering during docking with other spacecraft. On space vehicles with two sizes of attitude control thrusters, the main ACS (Attitude Control System) thrusters are used for larger movements, while the verniers are reserved for smaller adjustments. Due to their weight and the extra plumbing required ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(1966).png)
.png)