|
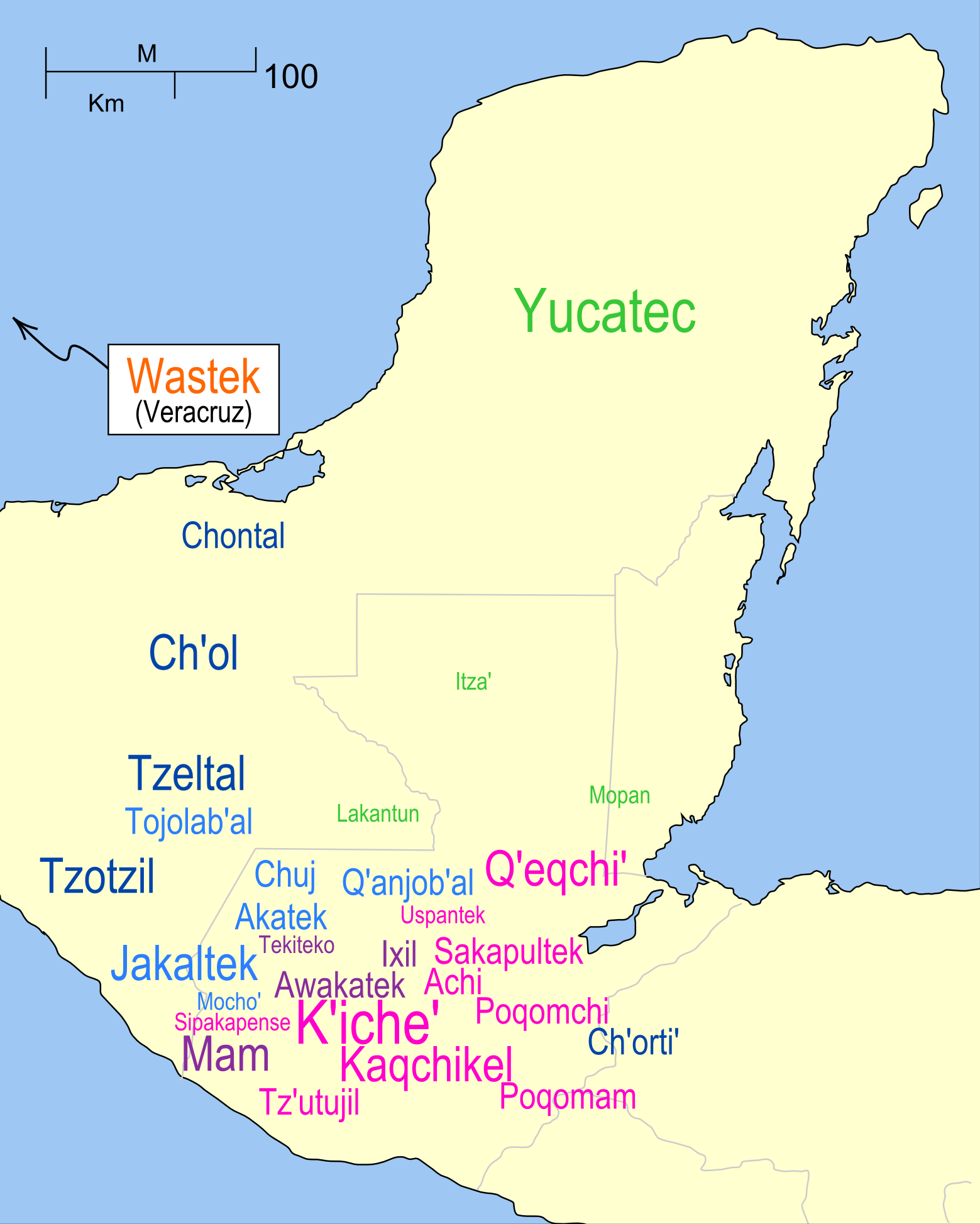
Qʼeqchiʼ
Qʼeqchiʼ () (Kʼekchiʼ in the former orthography, or simply Kekchi in many English-language contexts, such as in Belize) are a Maya people of Guatemala and Belize. Their indigenous language is the Qʼeqchiʼ language. Before the beginning of the Spanish conquest of Guatemala in the 1520s, Qʼeqchiʼ settlements were concentrated in what are now the departments of Alta Verapaz and Baja Verapaz. Over the course of the succeeding centuries a series of land displacements, resettlements, persecutions and migrations resulted in a wider dispersal of Qʼeqchiʼ communities into other regions of Guatemala ( Izabal, Petén, El Quiché), southern Belize (Toledo District), and smaller numbers in southern Mexico ( Chiapas, Campeche). While most notably present in northern Alta Verapaz and southern Petén, contemporary Qʼeqchiʼ language-speakers are the most widely spread geographically of all Maya peoples in Guatemala. History Not much is known about the lives and history of the Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qʼeqchiʼ Language
The Qʼeqchiʼ language, also spelled Kekchi, Kʼekchiʼ, or Kekchí, is one of the Mayan languages, spoken within Qʼeqchiʼ communities in Guatemala and Belize. Distribution The area where Qʼeqchiʼ is spoken spreads across northern Guatemala into southern Belize. There are also some Qʼeqchiʼ speaking communities in Mexico. It was calculated that the core of the Qʼeqchiʼ-speaking area in northern Guatemala extends over 24,662 square kilometers (about 9,522 square miles). The departments and specific municipalities where Qʼeqchiʼ is regularly spoken in Guatemala include: In the country of Belize, Qʼeqchiʼ is spoken in the Toledo District. Qʼeqchiʼ is the first language of many communities in the district, and the majority of Maya in Toledo speak it. Terrence Kaufman described Qʼeqchiʼ as having two principal dialect groups: the eastern and the western. The eastern group includes the varieties spoken in the municipalities of Lanquín, Chahal, Chahabón and Senah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Conquest Of Guatemala
In a protracted conflict during the Spanish colonization of the Americas, Spanish colonisers gradually incorporated the territory that became the modern country of Guatemala into the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain. Before the conquest, this territory contained a number of competing Mesoamerican kingdoms, the majority of which were Maya. Many conquistadors viewed the Maya as "infidels" who needed to be forcefully converted and pacified, disregarding the achievements of their civilization.Jones 2000, p. 356. The first contact between the Maya and European explorers came in the early 16th century when a Spanish ship sailing from Panama to Santo Domingo was wrecked on the east coast of the Yucatán Peninsula in 1511. Several Spanish expeditions followed in 1517 and 1519, making landfall on various parts of the Yucatán coast. The Spanish conquest of the Maya was a prolonged affair; the Maya kingdoms resisted integration into the Spanish Empire with such tenacity that their defeat t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya People
The Maya peoples () are an ethnolinguistic group of indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica. The ancient Maya civilization was formed by members of this group, and today's Maya are generally descended from people who lived within that historical region. Today they inhabit southern Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, El Salvador, and Honduras. "Maya" is a modern collective term for the peoples of the region, however, the term was not historically used by the indigenous populations themselves. There was no common sense of identity or political unity among the distinct populations, societies and ethnic groups because they each had their own particular traditions, cultures and historical identity. It is estimated that seven million Maya were living in this area at the start of the 21st century. Guatemala, southern Mexico and the Yucatán Peninsula, Belize, El Salvador, and western Honduras have managed to maintain numerous remnants of their ancient cultural heritage. Some are quite integrated int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summer Institute Of Linguistics
SIL International (formerly known as the Summer Institute of Linguistics) is an evangelical Christian non-profit organization whose main purpose is to study, develop and document languages, especially those that are lesser-known, in order to expand linguistic knowledge, promote literacy, translate the Christian Bible into local languages, and aid minority language development. Based on its language documentation work, SIL publishes a database, ''Ethnologue'', of its research into the world's languages, and develops and publishes software programs for language documentation, such as FieldWorks Language Explorer (FLEx) and Lexique Pro. Its main offices in the United States are located at the International Linguistics Center in Dallas, Texas. History William Cameron Townsend, a Presbyterian minister, founded the organization in 1934, after undertaking a Christian mission with the Disciples of Christ among the Kaqchikel Maya people in Guatemala in the early 1930s.George Thomas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Quiché
EL, El or el may refer to: Religion * El (deity), a Semitic word for "God" People * EL (rapper) (born 1983), stage name of Elorm Adablah, a Ghanaian rapper and sound engineer * El DeBarge, music artist * El Franco Lee (1949–2016), American politician * Ephrat Livni (born 1972), American street artist Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit * El, short for Eleven, a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things'' * El, family name of Kal-El (Superman) and his father Jor-El in ''Superman'' *E.L. Faldt, character in the road comedy film ''Road Trip'' Literature * ''Él'', 1926 autobiographical novel by Mercedes Pinto * ''Él'' (visual novel), a 2000 Japanese adult visual novel Music * Él Records, an independent record label from the UK founded by Mike Alway * ''Él'' (Lucero album), a 1982 album by Lucero * "Él", Spanish song by Rubén Blades from ''Caminando'' (album) * "Él" (Lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toledo District
Toledo District is the southernmost district in Belize, and Punta Gorda is the District capital. It is the second most developed region in the country (according to the Human Development Index (HDI)). The district has a diverse topography which features rainforests, extensive cave networks, coastal lowland plains, and offshore cays. Toledo is home to a wide range of cultures: Mopan and Kekchi Maya, Creole, the Garifuna, East Indians, Mennonites, Mestizos, and descendants of US Confederate settlers. Geography The District has many villages, including Monkey River Town and the Toledo Settlement; the Maya villages of San Pedro Columbia, Blue Creek, Indian Creek, Santa Cruz, San Antonio, San Jose, San Felipe; and the Garifuna village of Barranco. It also has a number of Maya ruins, including Lubaantun, Nim Li Punit, Uxbenka, and Pusilha. According to the 2010 census, Toledo District had a population of 30,538 people. Economy The economy of Toledo relies heavily upon a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiapas
Chiapas (; Tzotzil language, Tzotzil and Tzeltal language, Tzeltal: ''Chyapas'' ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Chiapas), is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and largest city is Tuxtla Gutiérrez. Other important population centers in Chiapas include Ocosingo, Tapachula, San Cristóbal de las Casas, Comitán, and Arriaga, Chiapas, Arriaga. Chiapas is the southernmost state in Mexico, and it borders the states of Oaxaca to the west, Veracruz to the northwest, and Tabasco to the north, and the Petén Department, Petén, Quiché Department, Quiché, Huehuetenango Department, Huehuetenango, and San Marcos Department, San Marcos departments of Guatemala to the east and southeast. Chiapas has a significant coastline on the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. In general, Chiapas has a humid, tropical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campeche
Campeche (; yua, Kaampech ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Campeche ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Campeche), is one of the 31 states which make up the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. Located in southeast Mexico, it is bordered by the states of Tabasco to the southwest, Yucatán to the northeast, and Quintana Roo to the east; to the southeast by the Orange Walk district of Belize, and by the Petén department of Guatemala to the south. It has a coastline to the west with the Gulf of Mexico. The state capital, also called Campeche, was declared a World Heritage Site in 1997. The formation of the state began with the city, which was founded in 1540 as the Spanish began the conquest of the Yucatán Peninsula. The city was a rich and important port during the colonial period, but it declined after Mexico's independence. Campeche was part of the province of Yucatán but split off in the mid-19th century, mostly due to political friction with the city of Mérida. Much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petén (department)
Petén or Peten may refer to: *Petén Department, a department of Guatemala *Petén Basin, the geographical/archaeological region of Mesoamerica and a center of the Maya civilization *Lake Petén Itzá Lake Petén Itzá (''Lago Petén Itzá'', ) is a lake in the northern Petén Department in Guatemala. It is the third largest lake in Guatemala, after Lake Izabal and Lake Atitlán. It is located around . It has an area of , and is some long and ..., a lake in the Petén Basin region * Peten Itza kingdom, a kingdom in modern-day Central America centered on the city of Nojpetén *The Hebrew name ( he, פתן) for the Boeing AH-64A Apache in Israeli service, meaning "Cobra" in English {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartolomé De Las Casas
Bartolomé de las Casas, OP ( ; ; 11 November 1484 – 18 July 1566) was a 16th-century Spanish landowner, friar, priest, and bishop, famed as a historian and social reformer. He arrived in Hispaniola as a layman then became a Dominican friar and priest. He was appointed as the first resident Bishop of Chiapas, and the first officially appointed "Protector of the Indians". His extensive writings, the most famous being ''A Short Account of the Destruction of the Indies'' and ''Historia de Las Indias'', chronicle the first decades of colonization of the West Indies. He described the atrocities committed by the colonizers against the indigenous peoples. Arriving as one of the first Spanish (and European) settlers in the Americas, Las Casas initially participated in, but eventually felt compelled to oppose, the abuses committed by colonists against the Native Americans. As a result, in 1515 he gave up his Native American slaves and '' encomienda'', and advocated, before King Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cristina Coc
Cristina Coc (born 1981) is a leader of the Maya community in southern Belize. She has served as co-spokesperson for the Maya Leadership Alliance and is the founder and executive director of the advocacy organization, the Julian Cho Society. In 2015, she and the MLA were awarded the Equator Prize for their efforts in protecting indigenous rights. Early life Cristina Coc was born on 21 December 1981 in Laguna, a traditional Mayan village in the Toledo District of Belize. She was the youngest of four other daughters born to Maria (née Baki) and Mateo Coc. Until she entered school, Coc was raised in Laguna, but seeking better education for their children, the family relocated to Punta Gorda, where Coc attended St. Peter Claver School. Her academic excellence led to a scholarship award to attend high school at the Toledo Community College, from which she graduated in 1998. Determined to continue her education, Coc applied St. John's College, Junior College (SJCJC) and was accepted, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |