|
Quileute Canyon
Quileute Canyon (also ''Quillayute Canyon'') is a submarine canyon, off of Washington state, United States. Its location It is just north of Quinault Canyon. Quileute Canyon is offshore, from both La Push and Forks. Quillayute River pours into the Pacific Ocean, onshore, near Rialto Beach, and Quillayute Needles National Wildlife Refuge is also near, onshore. The Quileute Indian Reservation is near, onshore. Exploration As of September 2017, the area is being explored. Aquatic life Large sponges and large jellyfish have been found, living there. Nearby submarine canyons All of the following submarine canyons are near, headed north to south: * Clayoquot Canyon * Father Charles Canyon * Loudon Canyon * Barkely Canyon * Nitinat Canyon * Juan de Fuca Canyon * Quileute Canyon * Quinault Canyon * Grays Canyon * Guide Canyon * Willapa Canyon * Astoria Canyon See also Local geography * Abyssal fan * Astoria Canyon * Astoria Fan * Cascadia Basin * Cascadia Channel * Cascadia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine Canyon
A submarine canyon is a steep-sided valley cut into the seabed of the continental slope, sometimes extending well onto the continental shelf, having nearly vertical walls, and occasionally having canyon wall heights of up to 5 km, from canyon floor to canyon rim, as with the Great Bahama Canyon. Just as above-sea-level canyons serve as channels for the flow of water across land, submarine canyons serve as channels for the flow of turbidity currents across the seafloor. Turbidity currents are flows of dense, sediment laden waters that are supplied by rivers, or generated on the seabed by storms, submarine landslides, earthquakes, and other soil disturbances. Turbidity currents travel down slope at great speed (as much as 70 km/h), eroding the continental slope and finally depositing sediment onto the abyssal plain, where the particles settle out.Continental Margin Sedimentation: From Sediment Transport to Sequence Stratigraphy (Special Publication 37 of the IAS) Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitinat Canyon
Ditidaht (also Nitinaht, Nitinat, Southern Nootkan) or diitiidʔaaʔtx̣ is a South Wakashan (Nootkan) language spoken on the southern part of Vancouver Island. Nitinaht is related to the other South Wakashan languages, Makah and the neighboring Nuu-chah-nulth. Status and history The number of native Ditidaht speakers dwindled from about thirty in the 1990sMithun, Marianne. (1999). ''The languages of Native North America''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. to just eight by 2006.Kwong, Matthew. (2006-07-22).Standing by their words. The Globe and Mail. In 2003 the Ditidaht council approved construction of a $4.2 million community school to teach students on the Ditidaht ( Malachan) reserve their language and culture from kindergarten to Grade 12. The program was successful in its first years and produced its first high-school graduate in 2005. In 2014, the number of fluent Ditidaht speakers was 7, the number of individuals who have a good grasp on the language 6, and there w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitinat Fan
Ditidaht (also Nitinaht, Nitinat, Southern Nootkan) or diitiidʔaaʔtx̣ is a South Wakashan (Nootkan) language spoken on the southern part of Vancouver Island. Nitinaht is related to the other South Wakashan languages, Makah and the neighboring Nuu-chah-nulth. Status and history The number of native Ditidaht speakers dwindled from about thirty in the 1990sMithun, Marianne. (1999). ''The languages of Native North America''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. to just eight by 2006.Kwong, Matthew. (2006-07-22).Standing by their words. The Globe and Mail. In 2003 the Ditidaht council approved construction of a $4.2 million community school to teach students on the Ditidaht ( Malachan) reserve their language and culture from kindergarten to Grade 12. The program was successful in its first years and produced its first high-school graduate in 2005. In 2014, the number of fluent Ditidaht speakers was 7, the number of individuals who have a good grasp on the language 6, and there w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan De Fuca Channel
Juan de Fuca Channel is a submarine channel off the shore of Washington state, United States and the Strait of Juan de Fuca. The geography of Juan de Fuca Channel The Juan de Fuca Channel is a submarine canyon running from the shelf break, off southern Vancouver Island to Juan de Fuca Strait. The canyon is both narrow and deep and has sides that are steep. Over its width at the rim it drops from in depth to over deep at the thalweg. Along a track, seismic profiles over Juan de Fuca Channel show the canyon consists of two distinct parts. The upper canyon is narrow, extending southwestward down the continental slope. This area has an average gradient of . It is there carved in consolidated or semi-consolidated material of the slope. The lower part of the channel trends northwestward, parallel to the shelf edge, with a gradient of only , terminating at the apex of Nitinat fan. The lower channel represents a small fan and valley feature. Further, Nitinat Fan was construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cascadia Subduction Zone
The Cascadia subduction zone is a convergent plate boundary that stretches from northern Vancouver Island in Canada to Northern California in the United States. It is a very long, sloping subduction zone where the Explorer, Juan de Fuca, and Gorda plates move to the east and slide below the much larger mostly continental North American Plate. The zone varies in width and lies offshore beginning near Cape Mendocino, Northern California, passing through Oregon and Washington, and terminating at about Vancouver Island in British Columbia. The Explorer, Juan de Fuca, and Gorda plates are some of the remnants of the vast ancient Farallon Plate which is now mostly subducted under the North American Plate. The North American Plate itself is moving slowly in a generally southwest direction, sliding over the smaller plates as well as the huge oceanic Pacific Plate (which is moving in a northwest direction) in other locations such as the San Andreas Fault in central and southern Califo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cascadia Channel
Cascadia Channel is the most extensive deep-sea channel currently known (as of 1969) of the Pacific Ocean. It extends across Cascadia Abyssal Plain, through the Blanco Fracture Zone, and into Tufts Abyssal Plain. Notably, Cascadia Channel has tributaries, akin to river tributaries. Cascadia Channel has two contributing tributaries—Juan de Fuca Channel from the north, and the outflow of Quinault and Willapa Channels in the south. The channel is believed to be over long. Formation Headed north-south, Cascadia Channel initially formed on the eastern flank of the Juan de Fuca Ridge, which was actively spreading. In the late Cenozoic, the volcanic basement was covered by transparent pelagic and hemipelagic sediment, which horizontally deposited turbidites covered. During late Pleistocene glaciation and the lowering of sea level, much sand and gravel from the shore deposited on either the upper slope or the outer shelf, which initiated turbidity currents, converting the lower an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cascadia Basin
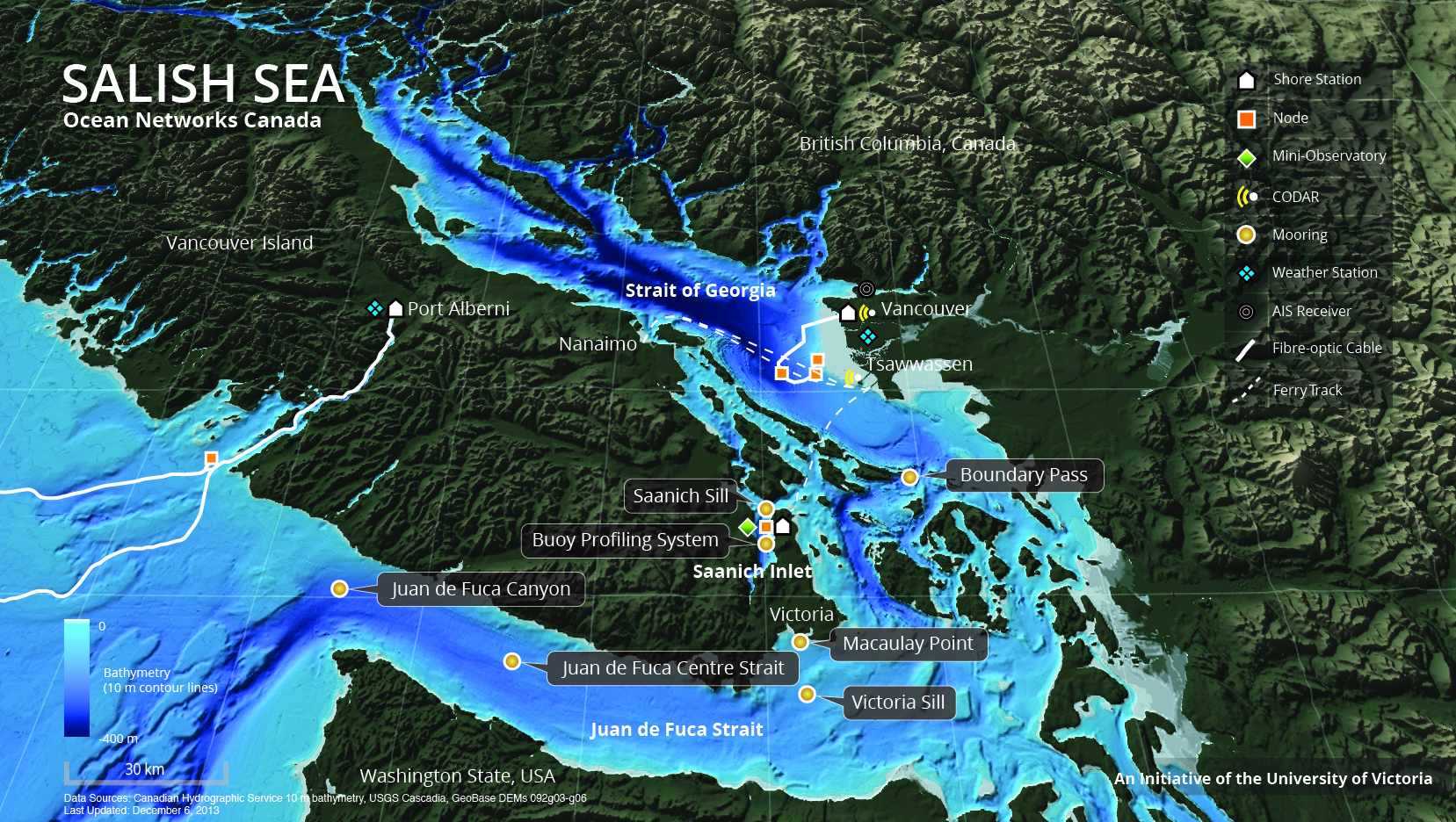
Ocean Networks Canada is a University of Victoria initiative that operates the NEPTUNE and VENUS cabled ocean observatories in the northeast Pacific Ocean and the Salish Sea. Additionally, Ocean Networks Canada operates smaller community-based observatories offshore from Cambridge Bay, Nunavut., Campbell River, Kitamaat Village and Digby Island. These observatories collect data on physical, chemical, biological, and geological aspects of the ocean over long time periods. As with other ocean observatories such as ESONET, Ocean Observatories Initiative, MACHO and DONET, scientific instruments connected to Ocean Networks Canada are operated remotely and provide continuous streams of freely available data to researchers and the public. Over 200 gigabytes of data are collected every day. The VENUS Observatory is situated at three main sites in the Salish Sea, including Saanich Inlet (depth 100 m), the eastern and central Strait of Georgia (depths 170–300 m), and the Fraser River d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astoria Fan
The Astoria Fan is a submarine fan. It has sediment, radiating asymmetrically southward from the mouth of the Astoria Canyon. From Astoria Canyon's mouth, the fan extends about to its western end, which is the Cascadia Channel. The fan proper ends south of the canyon mouth, although its depositional basin extends southward another to the Blanco Fracture Zone. Astoria Fan is generally asymmetrical. It extends roughly west of the mouth of Astoria Canyon, and about north, to Willapa Channel. Others trace different dimensions. Headed west, the fan crosses the continental shelf, trending sinuously down to the base of the continental slope. Near Astoria Canyon, it is at a depth of . The fan is approximately long. It varies in width from to . It has numerous tributaries. The fan extends about to its western boundary, which is the Cascadia Channel. Ash from the eruption of Mount Mazama has been found, in Astoria Fan. It may have been cut in the Pleistocene. It appears the Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abyssal Fan
Abyssal fans, also known as deep-sea fans, underwater deltas, and submarine fans, are underwater geological structures associated with large-scale sediment deposition and formed by turbidity currents. They can be thought of as an underwater version of alluvial fans and can vary dramatically in size, with widths from several kilometres to several thousands of kilometres The largest is the Bengal Fan, followed by the Indus Fan, but major fans are also found at the outlet of the Amazon, Congo, Mississippi and elsewhere. Formation Abyssal (or submarine) fans are formed from turbidity currents. These currents begin when a geologic activity pushes sediments over the edge of a continental shelf and down the continental slope, creating an underwater landslide. A dense slurry of muds and sands speeds towards the foot of the slope, until the current slows. The decreasing current, having a reduced ability to transport sediments, deposits the grains it carries, thus creating a su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astoria Canyon
Astoria Canyon is a submarine canyon 10 miles (16 km) offshore from the mouth of the Columbia River. See also * Astoria Fan The Astoria Fan is a submarine fan. It has sediment, radiating asymmetrically southward from the mouth of the Astoria Canyon. From Astoria Canyon's mouth, the fan extends about to its western end, which is the Cascadia Channel. The fan proper en ... External links * https://web.archive.org/web/20050902223250/http://newport.pmel.noaa.gov/heceta/oceanexploration.htm Geography of the Pacific Northwest Submarine canyons of the Pacific Ocean {{marine-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willapa Canyon , a geologic, physiographic, and geographic region in southwest Washington
{{disambiguation ...
Willapa may refer to: * Willapa people, an Athapaskan-speaking people in Washington, United States * Willapa River, river on the Pacific coast of southwestern Washington, United States * ''General Miles'', a ship * Willapa Electric Company, an electric railway and electric utility company incorporated on August 2, 1913 * Willapa Bay, a bay located on the southwest Pacific coast of Washington state in the United States * Willapa Hills The Willapa Hills is a geologic, physiographic, and geographic region in southwest Washington. When described as a physiographical province, the Willapa Hills are bounded by the Pacific Ocean to the west, the Columbia River to the south, the Ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |