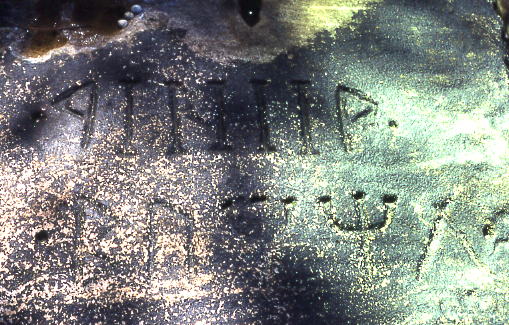|
Quenya
Quenya ()Tolkien wrote in his "Outline of Phonology" (in '' Parma Eldalamberon'' 19, p. 74) dedicated to the phonology of Quenya: is "a sound as in English ''new''". In Quenya is a combination of consonants, ibidem., p. 81. is a constructed language, one of those devised by J. R. R. Tolkien for the Elves in his Middle-earth fiction. Tolkien began devising the language around 1910, and restructured its grammar several times until it reached its final state. The vocabulary remained relatively stable throughout the creation process. He successively changed the language's name from ''Elfin'' and ''Qenya'' to the eventual ''Quenya''. Finnish had been a major source of inspiration, but Tolkien was also fluent in Latin and Old English, and was familiar with Greek, Welsh (the primary inspiration for Sindarin, Tolkien's other major Elvish language), and other ancient Germanic languages, particularly Gothic, during his development of Quenya. Tolkien developed a complex internal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Quenya Grammar
Quenya is a constructed language devised by J. R. R. Tolkien, and used in his fictional universe, Middle-earth. Here is presented a resume of the grammar of late Quenya as established from Tolkien's writings c. 1951–1973. It is almost impossible to extrapolate the morphological rules of the Quenya tongue from published data because Quenya is a fictional and irregular language that was heavily influenced by natural languages, such as Finnish and Latin, not an international auxiliary language with a regular morphology. Tolkien wrote several synchronic grammars of Quenya, describing its state at specific moments during its development, but only one has been published in full: ''The Early Qenya Grammar''. J.R.R. Tolkien, Carl F. Hostetter, and Bill Welden. 23 December 2003. ''The Early Qenya Grammar'', ''Parma Eldalamberon'' 14, pp. 37-88 Apart from that, he wrote several diachronic studies of Quenya and its proto-language Common Eldarin, three of which have been published: ''The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Elvish Languages (Middle-earth)
The Elvish languages of Middle-earth, Constructed languages, constructed by J. R. R. Tolkien, include Quenya and Sindarin. These were the various languages spoken by the Elves in Middle-earth, Elves of Middle-earth as they developed as a society throughout the Ages. In his pursuit for realism and in his love of language, Tolkien was especially fascinated with the development and evolution of language through time. Tolkien created two almost fully developed languages and a dozen more in various beginning stages as he studied and reproduced the way that language adapts and morphs. A philology, philologist by profession, he spent much time on his constructed languages. In the collection of letters he had written, posthumously published by his son, Christopher Tolkien, he stated that he began stories set within this secondary world, the realm of Middle-earth, not with the characters or narrative as one would assume, but with a created set of languages. The stories and characters serve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cirth
The Cirth (, meaning "runes"; sg. certh ) is a semi‑artificial script, based on real‑life runic alphabets, one of Tolkien's scripts, several scripts invented by J. R. R. Tolkien for the constructed languages he devised and used in his works. ''Cirth'' is written with a capital letter when referring to the writing system; the letters themselves can be called ''cirth''. In the fictional history of Middle-earth, the original ''Certhas'' was created by the Sindar (or Grey Elves) for their language, Sindarin. Its extension and elaboration was known as the ''Angerthas Daeron'', as it was attributed to the Sinda Daeron, despite the fact that it was most probably arranged by the Noldor in order to represent the sounds of other languages like Quenya and Telerin. Although it was later largely replaced by the Tengwar, the Cirth was nonetheless adopted by the Dwarf (Middle-earth), Dwarves to write down both their Khuzdul language (''Angerthas Moria'') and the languages of Man (Middle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sindarin
Sindarin is one of Languages constructed by J. R. R. Tolkien, the constructed languages devised by J. R. R. Tolkien for use in his fantasy stories set in Arda (Tolkien), Arda, primarily in Middle-earth. Sindarin is one of the many languages spoken by the Elf (Middle-earth), Elves. The word is Quenya for Grey-elven, since it was the language of the Grey Elves of Beleriand. These were Elves of the Third Clan who remained behind in Beleriand after the Great Journey. Their language became estranged from that of their kin who sailed over sea. Sindarin derives from an earlier language called Common Telerin, which evolved from Common Eldarin, the tongue of the Eldar (Middle-earth), Eldar before their divisions, e.g., those Elves who decided to follow the Vala Oromë and undertook the Great March to Valinor. Even before that the Eldar Elves spoke the original speech of all Elves, or Primitive Quendian. In the Third Age (the setting of ''The Lord of the Rings''), Sindarin was the languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tengwar
The Tengwar () script is an artificial script, one of Tolkien's scripts, several scripts created by J. R. R. Tolkien, the author of ''The Lord of the Rings''. Within the context of Tolkien's fictional world, the Tengwar were invented by the Elf (Middle-earth), Elf Fëanor, and used first to write the Elvish languages Quenya and Telerin. Later a great number of Tolkien's constructed languages were written using the Tengwar, including Sindarin. Tolkien used Tengwar to write English language, English: most of Tolkien's Tengwar samples are actually in English. Internal history and terminology Within the context of Middle-earth, Tolkien's fictional world, the Tengwar were invented by the Elf (Middle-earth), Elf Fëanor in Valinor, and used first to write the Elven tongues Quenya and Telerin. According to J. R. R. Tolkien's ''The War of the Jewels'', at the time Fëanor created his script, he introduced a change in terminology. He called a letter, a written representation of a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Finnish Influences On Tolkien
Finnish influences on Tolkien include both the Finnish language, which he especially liked, and the ''Kalevala'', Elias Lönnrot's 19th century compilation of Finnish mythology, which Tolkien stated had powerfully affected him. He further stated that his invented Elvish language of Quenya was influenced by the phonology and structure of Finnish. Scholars have identified both multiple surface-level parallels between elements and characters in the ''Kalevala'' and Tolkien's legendarium, and deeper resemblances. These began with his unfinished 1914 '' The Story of Kullervo'', his adaptation of a section of the ''Kalevala''. The story already displays numerous features characteristic of his Middle-earth writings. Another work from this period, "The Voyage of Éarendel the Evening Star", resembles the ''Kalevala's'' closing scene. Among the specific parallels between the ''Kalevala'' and Tolkien's writings is a magical object of great power, the Sampo, reflected in Tolkien's Silmaril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Namárië
"Namárië" () is a poem by J. R. R. Tolkien written in one of his constructed languages, Quenya, and published in ''The Lord of the Rings''., Book 2, ch. 8 "Farewell to Lórien" It is subtitled "Galadriel's Lament in Lórien", which in Quenya is ''Altariello nainië Lóriendessë''. The poem appears, too, in a book of musical settings by Donald Swann of songs from Middle-earth, ''The Road Goes Ever On''; the Gregorian plainsong-like melody was hummed to Swann by Tolkien. The poem is the longest Quenya text in ''The Lord of the Rings'' and also one of the longest continuous texts in Quenya that Tolkien ever wrote. An English translation is provided in the book. "Namárië" has been set to music by The Tolkien Ensemble, by the Finnish composer for a theatre production, and by the Spanish band . Part of the poem is sung by a female chorus in a scene of Peter Jackson's ''The Fellowship of the Ring'' to music by Howard Shore. Poem The poem names Valimar, the residence of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sundering Of The Elves
In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the Elves or Quendi are a sundered (divided) people. They awoke at Cuiviénen on the continent of Middle-earth, where they were divided into three tribes: Minyar (the Firsts), Tatyar (the Seconds) and Nelyar (the Thirds). After some time, they were summoned by Oromë to live with the Valar in Valinor, on Aman. That summoning and the Great Journey that followed split the Elves into two main groups (and many minor ones), which were never fully reunited. Tolkien stated that the stories were made to create a world for his elvish languages, not the reverse. The Tolkien scholar Tom Shippey writes that ''The Silmarillion'' derived from the linguistic relationship between the two languages, Quenya and Sindarin, of the divided Elves. The Tolkien scholar Verlyn Flieger states that Tolkien used the Indo-European type of proto-language as his model. In her view, the sundering of the Elves reflects the progressive decline and fall in Middle-earth from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sarati
Sarati is an artificial script, one of several scripts created by J. R. R. Tolkien. According to Tolkien's mythology, the Sarati alphabet was invented by the Elf Rúmil of Tirion. External history As Tolkien strove to create a world that would feel authentic, he realized that for that to be possible, he must invent accompanying scripts for his languages. And, being a perfectionist, he acknowledged that a fully-fledged writing system could not have just appeared out of nowhere. Therefore, he set out to create a series of scripts for the elves as well as for the humans and dwarves that would indicate a certain degree of evolution and development. The first script for the elves was the Sarati which eventually developed into Tengwar by Fëanor.Smith, Ross ''Inside Language'', p. 107 Known as the first writing system of Arda, Sarati was in the fiction invented by the Ñoldorin chronicler Rúmil of Valinor in the Valian Year 1169 of the First Age. It was he "who first achiev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Númenor
Númenor, also called Elenna-nórë or Westernesse, is a fictional place in J. R. R. Tolkien's writings. It was the kingdom occupying a large island to the west of Middle-earth, the main setting of Tolkien's writings, and was the greatest civilization of Men. However, after centuries of prosperity, many of its inhabitants ceased to worship the One God, Eru Ilúvatar, and they rebelled against the Valar. They invaded Valinor in an erroneous search for immortality, resulting in the destruction of the island and the death of most of its people. Tolkien intended Númenor to allude to the legendary Atlantis. Commentators have noted that the destruction of Númenor echoes the Biblical stories of the fall of man and the destruction of Sodom and Gomorrah, and John Milton's ''Paradise Lost''. The tale forms part of the theme of decline and fall in Middle-earth that runs throughout Tolkien's legendarium, ancient Númenor representing a now-mythical age of greatness. Scholars, and Tolkie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Noldor
In the works of J. R. R. Tolkien, the Noldor (also spelled Ñoldor, meaning ''those with knowledge'' in his constructed language Quenya) are a kindred of Elves who migrate west to the blessed realm of Valinor from the continent of Middle-earth, splitting from other groups of Elves as they went. They then settle in the coastal region of Eldamar. The Dark Lord Morgoth murders their first leader, Finwë. The majority of the Noldor, led by Finwë's eldest son Fëanor, then return to Beleriand in the northwest of Middle-earth. This makes them the only group to return and then play a major role in Middle-earth's history; much of ''The Silmarillion'' is about their actions. They are the second clan of the Elves in both order and size, the other clans being the Vanyar and the Teleri. Among Elves, the Noldor show the greatest talents for intellectual pursuits, technical skills and physical strength, yet are prone to unchecked ambition and pride in their ability to create. Scholar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Elf (Middle-earth)
In J. R. R. Tolkien's writings, Elves are the first fictional race to appear in Middle-earth. Unlike Men and Dwarves, Elves do not die of disease or old age. Should they die in battle or of grief, their souls go to the Halls of Mandos in Aman. After a long life in Middle-earth, Elves yearn for the Earthly Paradise of Valinor, and can sail there from the Grey Havens. They feature in '' The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of the Rings''. Their history is described in detail in '' The Silmarillion''. Tolkien derived Elves from mentions in the ancient poetry and languages of Northern Europe, especially Old English. These suggested to him that Elves were large, dangerous, beautiful, lived in wild natural places, and practised archery. He invented languages for the Elves, including Sindarin and Quenya. Tolkien-style Elves have become a staple of fantasy literature. They have appeared, too, in film and role-playing game adaptations of Tolkien's works. Origins Icelandic folklo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |