|
Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Prince Edward Island
The Queen Elizabeth Hospital (QEH) is a 243-bed acute care hospital located in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada, making it the largest hospital in the province. Operated by Health PEI, the hospital opened in 1982, resulting in the closure of the Charlottetown Hospital and the Prince Edward Island Hospital. It is named in honour of Queen Elizabeth II. The QEH is located on a large forested campus originally known as Falconwood Farm in the northeast corner of the city adjoining the neighbourhoods of East Royalty and Sherwood, overlooking the Hillsborough River. The Hillsborough Hospital is a psychiatric hospital located on the same campus. Services The QEH is a full-service health care facility that provides community services to residents of Queens County and is a major referral centre for specialty services for residents across Prince Edward Island. Some of the services that the QEH offers: *Emergency/OPD *Ambulatory care * Surgery/Day surgery * ICU * CCU * Ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlottetown
Charlottetown is the capital and largest city of the Canadian province of Prince Edward Island, and the county seat of Queens County. Named after Queen Charlotte, Charlottetown was an unincorporated town until it was incorporated as a city in 1855. It was the site of the famous Charlottetown Conference in 1864, the first gathering of Canadian and Maritime statesmen to discuss the proposed Maritime Union. This conference led, instead, to the union of British North American colonies in 1867, which was the beginning of the Canadian confederation. PEI, however, did not join Confederation until 1873. From this, the city adopted as its motto ''Cunabula Foederis'', "Birthplace of Confederation". The population of Charlottetown is estimated to be 40,500 (2022); this forms the centre of a census agglomeration of 83,063 (2021), which is roughly half of the province's population (160,302). History Early history (1720–1900) The first European settlers in the area were French; perso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pathological condition such as a disease or injury, to help improve bodily function, appearance, or to repair unwanted ruptured areas. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure, operation, or simply "surgery". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments or surgical nurse. The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person or an animal. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon's assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon's assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
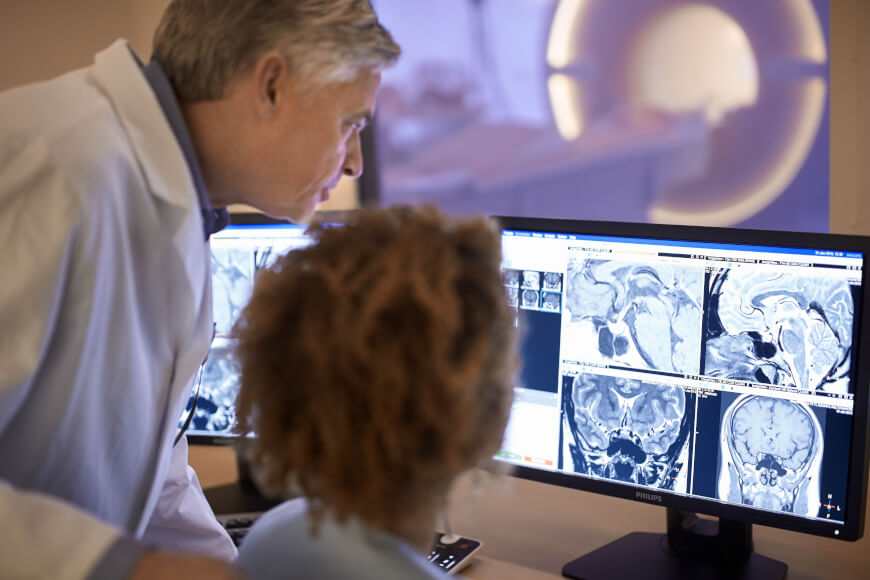
CT Scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry (medical), gantry to measure X-ray Attenuation#Radiography, attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce Tomography, tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is Contraindication, contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiology
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiation), but today it includes all imaging modalities, including those that use no electromagnetic radiation (such as ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging), as well as others that do, such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above. The modern practice of radiology involves several different healthcare professions working as a team. The radiologist is a medical doctor who has completed the appropriate post-graduate training and interprets medical images, communicates these findings to other physicians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physicians' offices, clinics, hospitals, and regional and national referral centers. Overview The organisation and contents of laboratories are determined by the differing requirements of the specialists working within. A physics laboratory might contain a particle accelerator or vacuum chamber, while a metallurgy laboratory could have apparatus for casting or refining metals or for testing their strength. A chemist or biologist might use a wet laboratory, while a psychologist's laboratory might be a room with one-way mirrors and hidden cameras in which to observe behavior. In some laboratories, such as those commonly used by computer scientists, computers (sometimes supercomputers) are used for either simulations or the analysis of data. Scient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue, cell, and body fluid samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be " pathophysiologies"), and the affix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Medicine And Rehabilitation
Physical medicine and rehabilitation, also known as physiatry, is a branch of medicine that aims to enhance and restore functional ability and quality of life to people with physical impairments or disabilities. This can include conditions such as spinal cord injuries, brain injuries, strokes, as well as pain or disability due to muscle, ligament or nerve damage. A physician having completed training in this field may be referred to as a physiatrist. Scope of the field Physical medicine and rehabilitation encompasses a variety of clinical settings and patient populations. In hospital settings, physiatrists commonly treat patients who have had an amputation, spinal cord injury, stroke, traumatic brain injury, and other debilitating injuries or conditions. In treating these patients, physiatrists lead an interdisciplinary team of physical, occupational, recreational and speech therapists, nurses, psychologists, and social workers. In outpatient settings, physiatrists treat pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychiatry
Psychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of mental disorders. These include various maladaptations related to mood, behaviour, cognition, and perceptions. See glossary of psychiatry. Initial psychiatric assessment of a person typically begins with a case history and mental status examination. Physical examinations and psychological tests may be conducted. On occasion, neuroimaging or other neurophysiological techniques are used. Mental disorders are often diagnosed in accordance with clinical concepts listed in diagnostic manuals such as the ''International Classification of Diseases'' (ICD), edited and used by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the widely used '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM), published by the American Psychiatric Association (APA). The fifth edition of the DSM (DSM-5) was published in May 2013 which re-organized the larger categories of various diseases and expanded upon the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediatrics
Pediatrics ( also spelled ''paediatrics'' or ''pædiatrics'') is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, paediatrics covers many of their youth until the age of 18. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends people seek pediatric care through the age of 21, but some pediatric subspecialists continue to care for adults up to 25. Worldwide age limits of pediatrics have been trending upward year after year. A medical doctor who specializes in this area is known as a pediatrician, or paediatrician. The word ''pediatrics'' and its cognates mean "healer of children," derived from the two Greek words: (''pais'' "child") and (''iatros'' "doctor, healer"). Pediatricians work in clinics, research centers, universities, general hospitals and children's hospitals, including those who practice pediatric subspecialties (e.g. neonatology requires resources available in a NICU). History The ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
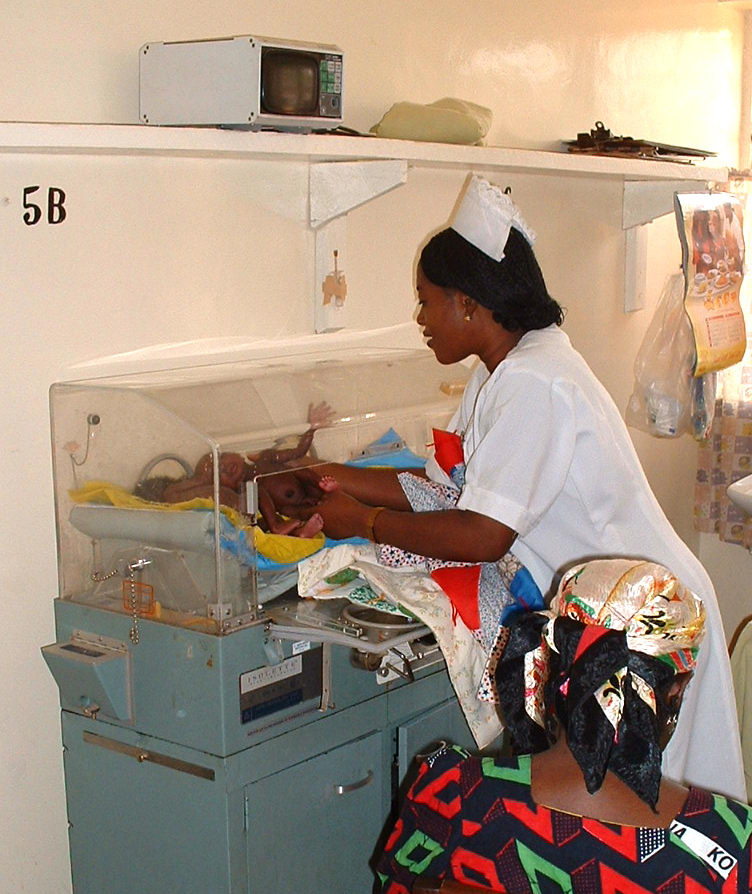
Neonatal ICU
A neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), also known as an intensive care nursery (ICN), is an intensive care unit (ICU) specializing in the care of ill or premature newborn infants. Neonatal refers to the first 28 days of life. Neonatal care, as known as specialized nurseries or intensive care, has been around since the 1960s. The first American newborn intensive care unit, designed by Louis Gluck, was opened in October 1960 at Yale New Haven Hospital. NICU is typically directed by one or more neonatologists and staffed by resident physicians, nurses, nurse practitioners, pharmacists, physician assistants, respiratory therapists, and dietitians. Many other ancillary disciplines and specialists are available at larger units. The term ''neonatal'' comes from ''neo'', "new", and ''natal'', "pertaining to birth or origin". Nursing and neonatal populations Healthcare institutions have varying entry-level requirements for neonatal nurses. Neonatal nurses are registered nurses (RNs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neonatal Nursing
Neonatal nursing is a sub-specialty of nursing care for newborn infants up to 28 days after birth. The term neonatal comes from neo, "new", and natal, "pertaining to birth or origin". Neonatal nursing requires a high degree of skill, dedication and emotional strength as they care for newborn infants with a range of problems. These problems vary between prematurity, birth defects, infection, cardiac malformations and surgical issues. Neonatal nurses are a vital part of the neonatal care team and are required to know basic newborn resuscitation, be able to control the newborn's temperature and know how to initiate cardiopulmonary and pulse oximetry monitoring. Most neonatal nurses care for infants from the time of birth until they are discharged from the hospital. Levels of the Neonatal Nursery There are four different levels of nurseries where a neonatal nurse might work. The updated classification of neonatal levels by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) includes a Level IV. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstetrics
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surgical field. Main areas Prenatal care Prenatal care is important in screening for various complications of pregnancy. This includes routine office visits with physical exams and routine lab tests along with telehealth care for women with low-risk pregnancies: Image:Ultrasound_image_of_a_fetus.jpg, 3D ultrasound of fetus (about 14 weeks gestational age) Image:Sucking his thumb and waving.jpg, Fetus at 17 weeks Image:3dultrasound 20 weeks.jpg, Fetus at 20 weeks First trimester Routine tests in the first trimester of pregnancy generally include: * Complete blood count * Blood type ** Rh-negative antenatal patients should receive RhoGAM at 28 weeks to prevent Rh disease. * Indirect Coombs test (AGT) to assess risk of hemolytic dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.jpg)




