|
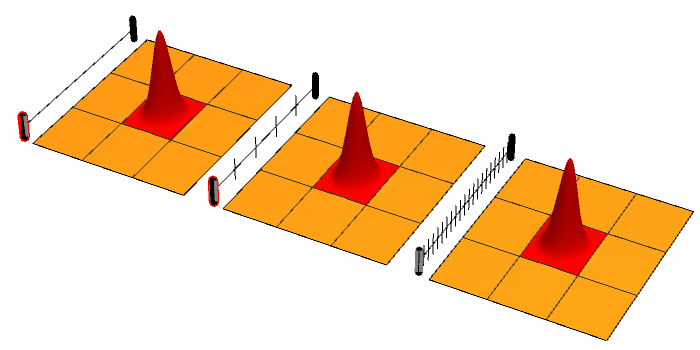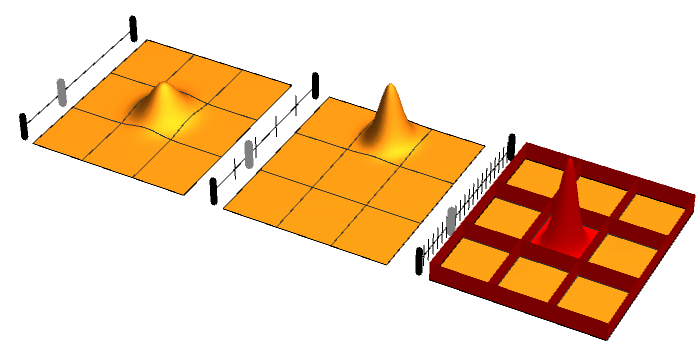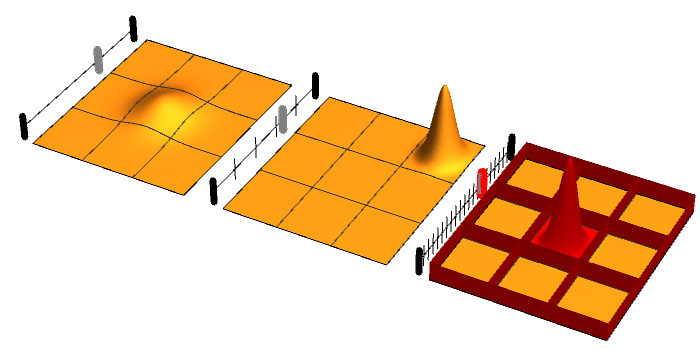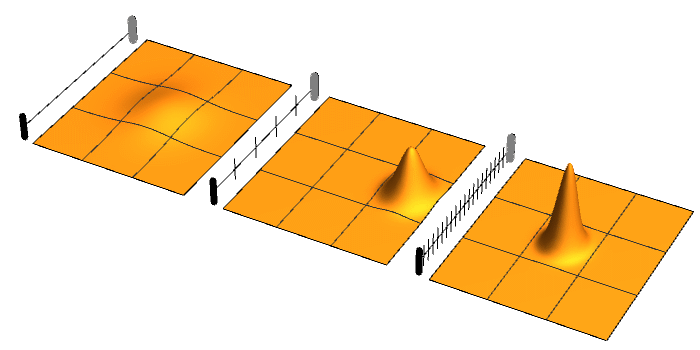
Quantum Zeno Effect
The quantum Zeno effect (also known as the Turing paradox) is a feature of quantum-mechanical systems allowing a particle's time evolution to be slowed down by measuring it frequently enough with respect to some chosen measurement setting. Sometimes this effect is interpreted as "a system cannot change while you are watching it". One can "freeze" the evolution of the system by measuring it frequently enough in its known initial state. The meaning of the term has since expanded, leading to a more technical definition, in which time evolution can be suppressed not only by measurement: the quantum Zeno effect is the suppression of unitary time evolution in quantum systems provided by a variety of sources: measurement, interactions with the environment, stochastic fields, among other factors. As an outgrowth of study of the quantum Zeno effect, it has become clear that applying a series of sufficiently strong and fast pulses with appropriate symmetry can also ''decouple'' a system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Zeno Effect Animation
In physics, a quantum (plural quanta) is the minimum amount of any physical entity (physical property) involved in an interaction. The fundamental notion that a physical property can be "quantized" is referred to as "the hypothesis of quantization". This means that the magnitude of the physical property can take on only discrete values consisting of integer multiples of one quantum. For example, a photon is a single quantum of light (or of any other form of electromagnetic radiation). Similarly, the energy of an electron bound within an atom is quantized and can exist only in certain discrete values. (Atoms and matter in general are stable because electrons can exist only at discrete energy levels within an atom.) Quantization is one of the foundations of the much broader physics of quantum mechanics. Quantization of energy and its influence on how energy and matter interact (quantum electrodynamics) is part of the fundamental framework for understanding and describing nature. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jones & Bartlett Publishers
Jones & Bartlett Learning, a division of Ascend Learning, is a scholarly publisher. The name comes from Donald W. Jones, the company's founder, and Arthur Bartlett, the first editor. History In 1988, the company was named by ''New England Business Magazine'' as one of the 100 fastest-growing companies in New England. In 1989, they opened their first office in London. In 1993, they opened an office in Singapore, and an office in Toronto in 1994. Their corporate headquarters moved to Sudbury, Massachusetts in 1995. In 2011, Jones & Bartlett Learning moved its offices in Sudbury and Maynard, Massachusetts Maynard is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. The town is located 22 miles west of Boston, in the MetroWest and Greater Boston region of Massachusetts and borders Acton, Concord, Stow and Sudbury. The town's populatio ... to Burlington, Massachusetts, sharing a building with other Ascend Learning corporate offices. See also * National Healthcare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Physics B
The ''Journal of Physics B: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by IOP Publishing. It was established in 1968 from the division of the earlier title, '' Proceedings of the Physical Society''. In 2006, the '' Journal of Optics B: Quantum and Semiclassical Optics'' was merged with the ''Journal of Physics B''. The editor-in-chief is Marc Vrakking (Max Born Institute for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy). Scope The journal covers research on atomic, molecular A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ..., and optical physics. Topics include atomic and molecular structure, spectra and collisions, ultracold matter, quantum optics and non linear optics, quantum information, laser physics, intense laser fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Nanoscope
The atomic de Broglie microscope (also atomic nanoscope, neutral beam microscope, or scanning helium microscope when helium is used as the probing atom) is an imaging system which is expected to provide resolution at the nanometer scale. It is sometimes referred to as a "nanoscope." History The resolution of optical microscopes is limited to a few hundred nanometers by the wave properties of the light. The idea of imaging with atoms instead of light is widely discussed in the literature since the past century. Atom optics using neutral atoms instead of light could provide resolution as good as the electron microscope and be completely non-destructive, because short wavelengths on the order of a nanometer can be realized at low energy of the probing particles. "It follows that a helium microscope with nanometer resolution is possible. A helium atom microscope will be unique non-destructive tool for reflection or transmission microscopy." Focusing of neutral atoms Currently, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Mirror
In physics, an atomic mirror is a device which reflects neutral atoms in the similar way as a conventional mirror reflects visible light. Atomic mirrors can be made of electric fields or magnetic fields, electromagnetic waves or just silicon wafer; in the last case, atoms are reflected by the attracting tails of the van der Waals attraction (see quantum reflection). Such reflection is efficient when the normal component of the wavenumber of the atoms is small or comparable to the effective depth of the attraction potential (roughly, the distance at which the potential becomes comparable to the kinetic energy of the atom). To reduce the normal component, most atomic mirrors are blazed at the grazing incidence. At grazing incidence, the efficiency of the quantum reflection can be enhanced by a surface covered with ridges ( ridged mirror). The set of narrow ridges reduces the van der Waals attraction of atoms to the surfaces and enhances the reflection. Each ridge blocks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Mechanics
Classical mechanics is a physical theory describing the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of machinery, and astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. For objects governed by classical mechanics, if the present state is known, it is possible to predict how it will move in the future (determinism), and how it has moved in the past (reversibility). The earliest development of classical mechanics is often referred to as Newtonian mechanics. It consists of the physical concepts based on foundational works of Sir Isaac Newton, and the mathematical methods invented by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Joseph-Louis Lagrange, Leonhard Euler, and other contemporaries, in the 17th century to describe the motion of bodies under the influence of a system of forces. Later, more abstract methods were developed, leading to the reformulations of classical mechanics known as Lagrangian mechanics and Hamiltonian mechanics. These advances, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Reports
''Scientific Reports'' is a peer-reviewed open-access scientific mega journal published by Nature Portfolio, covering all areas of the natural sciences. The journal was established in 2011. The journal states that their aim is to assess solely the scientific validity of a submitted paper, rather than its perceived importance, significance, or impact. In September 2016, the journal became the largest in the world by number of articles, overtaking '' PLOS ONE''. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Chemical Abstracts Service, the Science Citation Index Expanded, and selectively in Index Medicus/MEDLINE/PubMed. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor 4.996. Reviewing policy The ''Guide to Referees'' states that to be published, "a paper must be scientifically valid and technically sound in methodology and analysis", and reviewers have to ensure manuscripts "are not assessed based on their perceived impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 '' Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Physics JETP
The ''Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics'' (''JETP'') [russian: Журнал Экспериментальной и Теоретической Физики, italic=yes (''ЖЭТФ''), or ''Zhurnal Éksperimental'noĭ i Teoreticheskoĭ Fiziki'' (''ZhÉTF'')] is a peer-reviewed Russian bilingual scientific journal covering all areas of experimental and theoretical physics. For example, coverage includes solid state physics, elementary particles, and cosmology. The journal is published simultaneously in both Russian and English languages. The editor-in-chief is Alexander F. Andreev Alexander Fyodorovich Andreev (russian: Александр Фёдорович Андреев, born 1939) is a Russian theoretical physicist best known for explaining the eponymous Andreev reflection. Andreev was educated at the Moscow Institute .... In addition, this journal is a continuation of ''Soviet physics, JETP'' (1931–1992), which began English translation in 1955. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Scientific
World Scientific Publishing is an academic publisher of scientific, technical, and medical books and journals headquartered in Singapore. The company was founded in 1981. It publishes about 600 books annually, along with 135 journals in various fields. In 1995, World Scientific co-founded the London-based Imperial College Press together with the Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine. Company structure The company head office is in Singapore. The Chairman and Editor-in-Chief is Dr Phua Kok Khoo, while the Managing Director is Doreen Liu. The company was co-founded by them in 1981. Imperial College Press In 1995 the company co-founded Imperial College Press, specializing in engineering, medicine and information technology Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information technolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press is a department of the University of Cambridge and is both an academic and educational publisher. It became part of Cambridge University Press & Assessment, following a merger with Cambridge Assessment in 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 Country, countries, it publishes over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publishing includes more than 380 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and university textbooks, and English language teaching and learning publications. It also publishes Bibles, runs a bookshop in Cambridge, sells through Amazon, and has a conference venues business in Cambridge at the Pitt Building and the Sir Geoffrey Cass Spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponential Decay
A quantity is subject to exponential decay if it decreases at a rate proportional to its current value. Symbolically, this process can be expressed by the following differential equation, where is the quantity and (lambda) is a positive rate called the exponential decay constant, disintegration constant, rate constant, or transformation constant: :\frac = -\lambda N. The solution to this equation (see derivation below) is: :N(t) = N_0 e^, where is the quantity at time , is the initial quantity, that is, the quantity at time . Measuring rates of decay Mean lifetime If the decaying quantity, ''N''(''t''), is the number of discrete elements in a certain set, it is possible to compute the average length of time that an element remains in the set. This is called the mean lifetime (or simply the lifetime), where the exponential time constant, \tau, relates to the decay rate constant, λ, in the following way: :\tau = \frac. The mean lifetime can be looked at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |