|
Quench Polish Quench
Quench polish quench (QPQ) is a specialized type of nitrocarburizing case hardening that increases corrosion resistance. It is sometimes known by the brand name of Tufftride, Tenifer or Melonite. Three steps are involved: nitrocarburize ("quench"), polish, and post-oxidize ("quench"). This process is often used when two or more of the following properties are required in a workpiece: * wear resistance * corrosion resistance * lubricity * fatigue strength Common applications of the process are for piston rods of shock absorbers, cylinders and rods for hydraulic systems, pumps, axles, spindle (tool), spindles, firearm slides and barrels and valves. Process The process starts with a standard salt bath nitrocarburizing cycle, which produces a layer of ε iron nitride. Next, the workpiece is mechanically polished; typical polishing processes include vibratory finishing, lapping, and centerless grinding. Finally, the workpiece is re-immersed into the salt quench bath for 20 to 30 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrocarburizing
Ferritic nitrocarburizing or FNC, also known by the proprietary names Tenifer, Tufftride and Melonite as well as ARCOR,Other trade names include Tuffride/ Tuffrider, QPQ, Sulfinuz, Sursulf, Meli 1, and Nitride, among others is a range of proprietary case hardening processes that diffuse nitrogen and carbon into ferrous metals at sub-critical temperatures during a salt bath. Other methods of ferric nitrocarburizing include gaseous process such as Nitrotec and ion (plasma) ones. The processing temperature ranges from to , but usually occurs at . At this temperature steels and other ferrous alloys remain in the Allotropes_of_iron#Alpha_iron_(α-Fe), ferritic phase region. This allows for better control of the dimensional stability that would not be present in case hardening processes that occur when the alloy is transitioned into the austenitic phase.. There are four main classes of ferritic nitrocarburizing: ''gaseous'', ''salt bath'', ''ion'' or ''plasma'', and ''fluidized-bed''.. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lapping
Lapping is a machining process in which two surfaces are rubbed together with an abrasive between them, by hand movement or using a machine. Lapping often follows other subtractive processes with more aggressive material removal as a first step, such as milling and/or grinding. Lapping can take two forms. The first type of lapping (traditionally often called grinding), involves rubbing a brittle material such as glass against a surface such as iron or glass itself (also known as the "lap" or grinding tool) with an abrasive such as aluminum oxide, jeweller's rouge, optician's rouge, emery, silicon carbide, diamond, etc., between them. This produces microscopic conchoidal fractures as the abrasive rolls about between the two surfaces and removes material from both. The other form of lapping involves a softer material such as pitch or a ceramic for the lap, which is "charged" with the abrasive. The lap is then used to cut a harder material—the workpiece. The abrasive emb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Spray Test
The salt spray test (or salt fog test) is a standardized and popular corrosion test method, used to check corrosion resistance of materials and surface coatings. Usually, the materials to be tested are metallic (although stone, ceramics, and polymers may also be tested) and finished with a surface coating which is intended to provide a degree of corrosion protection to the underlying metal. Salt spray testing is an accelerated corrosion test that produces a corrosive attack to coated samples in order to evaluate (mostly comparatively) the suitability of the coating for use as a protective finish. The appearance of corrosion products (rust or other oxides) is evaluated after a pre-determined period of time. Test duration depends on the corrosion resistance of the coating; generally, the more corrosion resistant the coating is, the longer the period of testing before the appearance of corrosion or rust. The salt spray test is one of the most widespread and long-established corrosion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%–6% by weight) in water for consumer use, and in higher concentrations for industrial use. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, or " high-test peroxide", decomposes explosively when heated and has been used as a propellant in rocketry. Hydrogen peroxide is a reactive oxygen species and the simplest peroxide, a compound having an oxygen–oxygen single bond. It decomposes slowly when exposed to light, and rapidly in the presence of organic or reactive compounds. It is typically stored with a stabilizer in a weakly acidic solution in a dark bottle to block light. Hydrogen peroxide is found in biological systems including the human body. Enzymes that use or decompose hydrogen peroxide are classified as peroxidases. Properties The boiling poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Litre
The litre (international spelling) or liter (American English spelling) (SI symbols L and l, other symbol used: ℓ) is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metre (m3). A cubic decimetre (or litre) occupies a volume of (see figure) and is thus equal to one-thousandth of a cubic metre. The original French metric system used the litre as a base unit. The word ''litre'' is derived from an older French unit, the '' litron'', whose name came from Byzantine Greek—where it was a unit of weight, not volume—via Late Medieval Latin, and which equalled approximately 0.831 litres. The litre was also used in several subsequent versions of the metric system and is accepted for use with the SI,Bureau International des Poids et M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram
The gram (originally gramme; SI unit symbol g) is a Physical unit, unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one one thousandth of a kilogram. Originally defined as of 1795 as "the absolute weight of a volume of pure water equal to Cube (algebra), the cube of the hundredth part of a metre [1 Cubic centimetre, cm3], and at Melting point of water, the temperature of Melting point, melting ice", the defining temperature (~0 °C) was later changed to 4 °C, the temperature of maximum density of water. However, by the late 19th century, there was an effort to make the Base unit (measurement), base unit the kilogram and the gram a derived unit. In 1960, the new International System of Units defined a ''gram'' as one one-thousandth of a kilogram (i.e., one gram is Scientific notation, 1×10−3 kg). The kilogram, 2019 redefinition of the SI base units, as of 2019, is defined by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures from the fixed numeric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35.45 g/mol respectively, 100 g of NaCl contains 39.34 g Na and 60.66 g Cl. Sodium chloride is the salt most responsible for the salinity of seawater and of the extracellular fluid of many multicellular organisms. In its edible form, salt (also known as ''table salt'') is commonly used as a condiment and food preservative. Large quantities of sodium chloride are used in many industrial processes, and it is a major source of sodium and chlorine compounds used as feedstocks for further chemical syntheses. Another major application of sodium chloride is de-icing of roadways in sub-freezing weather. Uses In addition to the familiar domestic uses of salt, more dominant applications of the approximately 250 million tonnes per year production (2008 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QPQ ASTM B117 Comparison Chart (QPQ), a process for hardening steel
{{disambiguation ...
QPQ may refer to: * Quid pro quo, Latin phrase meaning something for something * Quench polish quench Quench polish quench (QPQ) is a specialized type of nitrocarburizing case hardening that increases corrosion resistance. It is sometimes known by the brand name of Tufftride, Tenifer or Melonite. Three steps are involved: nitrocarburize ("quench"), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QPQ Field Immersion Comparison Chart (QPQ), a process for hardening steel
{{disambiguation ...
QPQ may refer to: * Quid pro quo, Latin phrase meaning something for something * Quench polish quench Quench polish quench (QPQ) is a specialized type of nitrocarburizing case hardening that increases corrosion resistance. It is sometimes known by the brand name of Tufftride, Tenifer or Melonite. Three steps are involved: nitrocarburize ("quench"), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmonton, Alberta
Edmonton ( ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city anchors the north end of what Statistics Canada defines as the "Calgary–Edmonton Corridor". As of 2021, Edmonton had a city population of 1,010,899 and a metropolitan population of 1,418,118, making it the fifth-largest city and sixth-largest metropolitan area (CMA) in Canada. Edmonton is North America's List of northernmost settlements, northernmost large city and metropolitan area comprising over one million people each. A resident of Edmonton is known as an ''Edmontonian''. Edmonton's historic growth has been facilitated through the absorption of five adjacent urban municipalities (Strathcona, Alberta, Strathcona, North Edmonton, Alberta, North Edmonton, West Edmonton, Alberta, West Edmonton, Beverly, Alberta, Beverly and Jasper Place) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
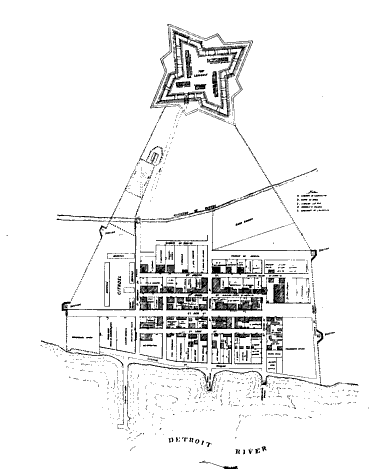
Detroit, Michigan
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at the 2020 census, making it the 27th-most populous city in the United States. The metropolitan area, known as Metro Detroit, is home to 4.3 million people, making it the second-largest in the Midwest after the Chicago metropolitan area, and the 14th-largest in the United States. Regarded as a major cultural center, Detroit is known for its contributions to music, art, architecture and design, in addition to its historical automotive background. ''Time'' named Detroit as one of the fifty World's Greatest Places of 2022 to explore. Detroit is a major port on the Detroit River, one of the four major straits that connect the Great Lakes system to the Saint Lawrence Seaway. The City of Detroit anchors the second-largest regional econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kennebunk, Maine
Kennebunk is a town in York County, Maine, United States. The population was 11,536 at the 2020 census (The population does not include Kennebunkport, a separate town). Kennebunk is home to several beaches, the Rachel Carson National Wildlife Refuge, the 1799 Kennebunk Inn, many historic shipbuilders' homes, the Brick Store Museum and the Nature Conservancy Kennebunk Plains (known locally as the Blueberry Plains), with 1,500 acres (6 km) of nature trails and blueberry fields. The municipality includes the constituent villages of Kennebunk Village (Town), the Lower Village (Lower Kennebunk), Kennebunk Landing (the Landing), Bartlett Mills, West Kennebunk, Kennebunk Beach, Lords Point, Coopers Corner Crossing, Sea Roads Crossing, Webahennet Grove, and Vinegarhill, Cheshire Commons, Kennebunk Meadows, and various newer neighborhoods. History First settled in 1621, the town developed as a trading and, later, shipbuilding and shipping center with light manufacturing. It was pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)