|
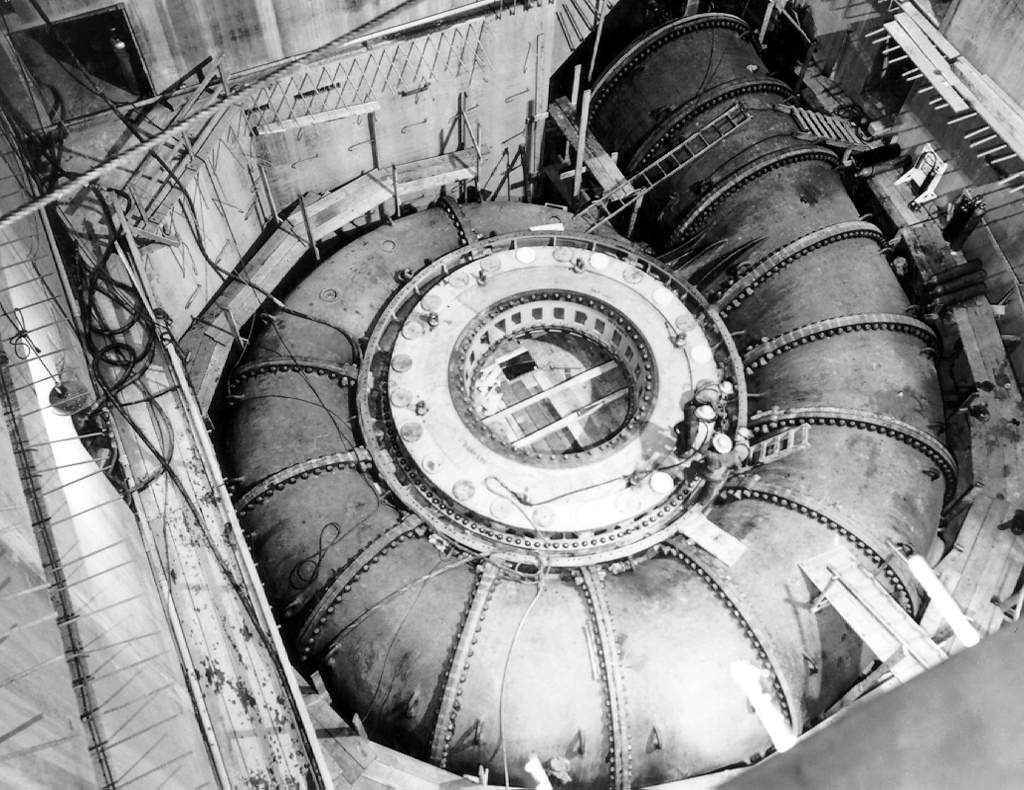
Pātea Dam
The Pātea Dam is a high compacted earth fill–type hydroelectric dam in Taranaki, New Zealand, constructed between 1980 and 1984. The dam is high, and is the fourth highest in New Zealand. It was the first dam constructed using tertiary sandstone and siltstone as fill materials. The dam impounds Lake Rotorangi, which is the longest man-made lake in New Zealand (). Pātea Hydro Electric Scheme The Pātea Hydro Electric Scheme was commissioned in May 1984 and was built for the South Taranaki District Council. After construction difficulties, wetter than normal conditions had caused a six-month delay. Since 1999 it is owned and operated by TrustPower. With three vertical Francis turbine The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The proces ... generator sets and a auxiliary generator, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectric Dam
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) because they are the most resistant minerals to weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be any color due to impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Since sandstone beds often form highly visible cliffs and other topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have been strongly identified with certain regions. Rock formations that are primarily composed of sandstone usually allow the percolation of water and other fluids and are porous enough to store large quantities, making them valuable aquifers and petroleum reservoirs. Quartz-bearing sandstone can be changed into quartzite through metamorphism, usually related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siltstone
Siltstone, also known as aleurolite, is a clastic sedimentary rock that is composed mostly of silt. It is a form of mudrock with a low clay mineral content, which can be distinguished from shale by its lack of fissility.Blatt ''et al.'' 1980, pp.381-382 Although its permeability and porosity is relatively low, siltstone is sometimes a tight gas reservoir rock, an unconventional reservoir for natural gas that requires hydraulic fracturing for economic gas production. Siltstone was prized in ancient Egypt for manufacturing statuary and cosmetic palettes. The siltstone quarried at Wadi Hammamat was a hard, fine-grained siltstone that resisted flaking and was almost ideal for such uses. Description There is not complete agreement on the definition of siltstone. One definition is that siltstone is mudrock ( clastic sedimentary rock containing at least 50% clay and silt) in which at least 2/3 of the clay and silt fraction is composed of silt-sized particles. Silt is defined a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Rotorangi
Lake Rotorangi is the largest lake in the New Zealand region of Taranaki. The reservoir was created in 1984 by the damming of the Pātea River. History Lake Rotorangi was formed in 1984 as a reservoir for hydroelectric power. The lake was formed by building an 80-metre high earth wall dam near the end of Ball Road in South Taranaki District. The dam created then filled the Patea River valley for a distance of about 46 kilometres to make the longest reservoir of its type in New Zealand New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count .... The Pātea Dam is owned by Manawa Energy (formerly Trust Power) and rated at 33 MW output (115 GWh per annum). Pātea is operated as a peaking station. With around one week's storage capacity, the station generates electricity over periods when el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TrustPower
Manawa Energy Limited, formerly Trustpower, is a New Zealand electricity generation company that offers bespoke electricity products to commercial and industrial customers across New Zealand. Manawa Energy has 26 hydro-electricity schemes, with a total of 47 power stations and is New Zealand's fifth largest electricity generator (in MW capacity, GWh output and revenue). The company is listed on the New Zealand stock exchange, but its ownership structure is dominated by its two major shareholders: Infratil which owns 51.0% and the Tauranga Energy Consumer Trust (TECT) which owns 26.8%. The remaining 22.2% is widely held. The company changed its name to Manawa Energy following the 2022 sale of its mass market retail business, retail customer base and the Trustpower brand to Mercury Energy. History Tauranga city In 1913, the Tauranga Borough Council applied to the Department of Lands to have the Omanawa Falls vested in their body corporate for the purposes of water power generat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine for d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dams Completed In 1984
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aquaculture, and navigability. Hydropower is often used in conjunction with dams to generate electricity. A dam can also be used to collect or store water which can be evenly distributed between locations. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees (also known as dikes) are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions. The earliest known dam is the Jawa Dam in Jordan, dating to 3,000 BC. The word ''dam'' can be traced back to Middle English, and before that, from Middle Dutch, as seen in the names of many old cities, such as Amsterdam and Rotterdam. History Ancient dams Early dam building took place in Mesopotamia and the Middle East. Dams were used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dams In New Zealand
Many of the largest dams and reservoirs in New Zealand have been developed principally to produce hydroelectricity. Other uses include irrigation and municipal water supply. Hydro-electric dams The main river systems comprising a series of dams and powerhouses are situated on the following rivers: :The Waikato River :The Waitaki River :The Clutha River Other schemes are standalone developments associated with specific sites. Tongariro Power Scheme The Tongariro Power Scheme (1,400 GWh) diverts water from the south side of Mount Ruapehu and the west and north sides of Tongariro into Lake Taupō, and thus eventually into the Waikato River. *Rangipo (cavern) (120 MW) *Tokaanu (240 MW) * Moawhango Dam The Waikato The hydro stations, starting from Lake Taupō, are (capacity in MW and nominal annual energy output in GWh): * Aratiatia (84 MW) (331 GWh) * Ohakuri (112 MW) (400 GWh) * Atiamuri (84 MW) (305 GWh) *Whakamaru (100 MW) (486 GWh) *Maraetai (360 MW) (855 GWh) *Waipapa (51 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Taranaki
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, monument, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the :Human habitats, human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Taranaki District
South Taranaki is a territorial authority on the west coast of New Zealand's North Island that contains the towns of Hāwera (the seat of the district), Manaia, Ōpunake, Patea, Eltham, and Waverley. The District has a land area of 3,575.46 km2 (1,380.49 sq mi) and a population of It is part of the greater Taranaki Region. The district straddles the boundary separating the Wellington and Taranaki provinces, resulting in the town of Waverley celebrating Wellington Anniversary Day in January, and the town of Patea 15 kilometres away celebrating Taranaki Anniversary Day in March. Council facilities include the South Taranaki LibraryPlus, Mania, Kaponga, Patea, Eltham, Opunake, Hāwera and Waverley libraries. History The South Taranaki District was established as part of the 1989 local government reforms, merging Egmont, Eltham, Hawera, Patea and Waimate West counties. Demographics South Taranaki District covers and had an estimated population of as of with a populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

Saunders_Quarry-1.jpg)