|
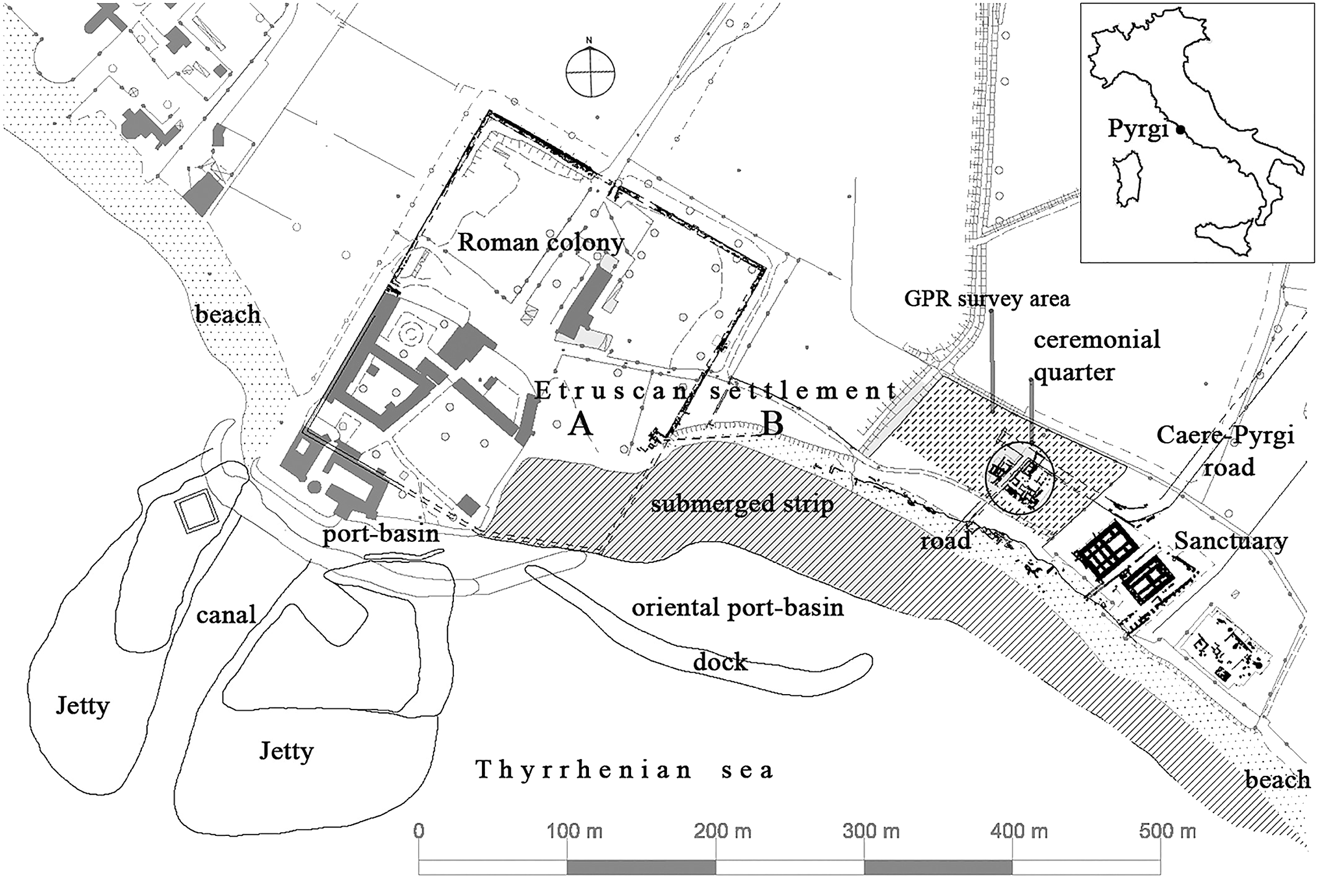
Pyrgi
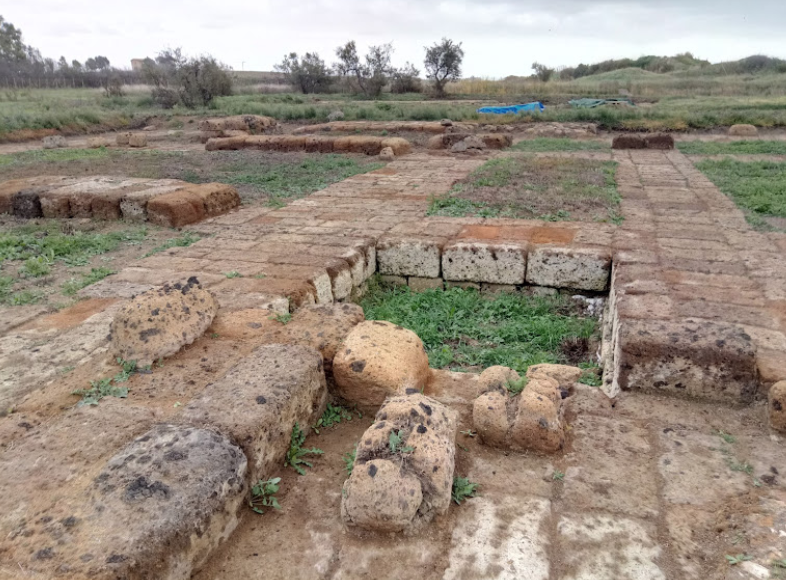
Pyrgi (''Pyrgus'' in Etruscan) was originally an ancient Etruscan town and port in Latium, central Italy, to the north-west of Caere. Its location is now occupied by the borough of Santa Severa. It is notable for the discovery here of the gold tablets, an exceptional epigraphic document with rare texts in Phoenician and Etruscan languages, and also the exceptional terracotta pediment statues from the temple. Excavations Excavations by Sapienza University of Rome since 1957 have focussed on the large sacred district, including the Monumental Sanctuary of Uni (Phoenician Astarte) and a Demetriac cult area, the most ancient so far known in Etruria, dedicated to the pair of deities Sur/Suri and Cavatha. In 2009 a block of ceremonial buildings north of Temple A was found. History The foundation of the settlement was ascribed to the Pelasgi and dates from the end of the 7th century BC. The connection between the great Etruscan city of Caere and the coast was ensured by the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrgi Walls
Pyrgi (''Pyrgus'' in Etruscan) was originally an ancient Etruscan town and port in Latium, central Italy, to the north-west of Caere. Its location is now occupied by the borough of Santa Severa. It is notable for the discovery here of the gold tablets, an exceptional epigraphic document with rare texts in Phoenician and Etruscan languages, and also the exceptional terracotta pediment statues from the temple. Excavations Excavations by Sapienza University of Rome since 1957 have focussed on the large sacred district, including the Monumental Sanctuary of Uni (Phoenician Astarte) and a Demetriac cult area, the most ancient so far known in Etruria, dedicated to the pair of deities Sur/Suri and Cavatha. In 2009 a block of ceremonial buildings north of Temple A was found. History The foundation of the settlement was ascribed to the Pelasgi and dates from the end of the 7th century BC. The connection between the great Etruscan city of Caere and the coast was ensured by the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrgi Sanctuary
Pyrgi (''Pyrgus'' in Etruscan) was originally an ancient Etruscan town and port in Latium, central Italy, to the north-west of Caere. Its location is now occupied by the borough of Santa Severa. It is notable for the discovery here of the gold tablets, an exceptional epigraphic document with rare texts in Phoenician and Etruscan languages, and also the exceptional terracotta pediment statues from the temple. Excavations Excavations by Sapienza University of Rome since 1957 have focussed on the large sacred district, including the Monumental Sanctuary of Uni (Phoenician Astarte) and a Demetriac cult area, the most ancient so far known in Etruria, dedicated to the pair of deities Sur/Suri and Cavatha. In 2009 a block of ceremonial buildings north of Temple A was found. History The foundation of the settlement was ascribed to the Pelasgi and dates from the end of the 7th century BC. The connection between the great Etruscan city of Caere and the coast was ensured by the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrgi
Pyrgi (''Pyrgus'' in Etruscan) was originally an ancient Etruscan town and port in Latium, central Italy, to the north-west of Caere. Its location is now occupied by the borough of Santa Severa. It is notable for the discovery here of the gold tablets, an exceptional epigraphic document with rare texts in Phoenician and Etruscan languages, and also the exceptional terracotta pediment statues from the temple. Excavations Excavations by Sapienza University of Rome since 1957 have focussed on the large sacred district, including the Monumental Sanctuary of Uni (Phoenician Astarte) and a Demetriac cult area, the most ancient so far known in Etruria, dedicated to the pair of deities Sur/Suri and Cavatha. In 2009 a block of ceremonial buildings north of Temple A was found. History The foundation of the settlement was ascribed to the Pelasgi and dates from the end of the 7th century BC. The connection between the great Etruscan city of Caere and the coast was ensured by the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uni (mythology)
Uni is the ancient goddess of marriage, fertility, family, and women in Etruscan religion and myth, and was the patron goddess of Perugia. She is identified as the Etruscan equivalent of Juno in Roman mythology, and Hera in Greek mythology. As the supreme goddess of the Etruscan pantheon, she is part of the Etruscan trinity, an original precursor to the Capitoline Triad, made up of her husband Tinia, the god of the sky, and daughter Menrva, the goddess of wisdom. She is often depicted with a goatskin cloak and sandals whilst holding a shield, similarly to Juno, wearing a bridal veil, or completely nude.Nancy Thomson de Grummond, ''Etruscan Myth, Sacred History, and Legend'' (University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology, 2006). Livy states (Book V, ''Ab Urbe Condita'') that Juno was an Etruscan goddess of the Veientes, who was adopted ceremonially into the Roman pantheon when Veii was sacked in 396 BC. This seems to refer to Uni. She also appears on the Liver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catha (mythology)
Catha (Cavatha, Cavtha, Cath, Cautha, and Kavtha) is a female Etruscan lunar or solar deity, who may also be connected to childbirth, and has a connection to the underworld. Catha is also the goddess of the south sanctuary at Pyrgi, Italy. She is known as Leucothea in ancient Greek. She is often seen with the Etruscan god Śuri with whom she shares a cult. Catha is also frequently paired with the Etruscan god Fufluns, who is the counterpart to the Greek god Dionysus, and Pacha, the counterpart to the Roman god Bacchus. Additionally, at Pyrgi, Catha is linked with the god Aplu, the counterpart to the Greek god Apollo. Aplu may have even taken some of the characteristics of Catha when he was brought into the Etruscan religion. Giovanni Colonna has suggested that Catha is linked to the Greek Persephone since he links Catha's consort, Suri, to Dis Pater in Roman mythology. Inscriptions The bulk of information regarding Catha comes mostly from inscriptions on Etruscan artifacts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caere
: Caere (also Caisra and Cisra) is the Latin name given by the Romans to one of the larger cities of southern Etruria, the modern Cerveteri, approximately 50–60 kilometres north-northwest of Rome. To the Etruscans it was known as Cisra, to the Greeks as Agylla and to the Phoenicians as Kyšryʼ. Caere was one of the most important and populous Etruscan city-states, in area 15 times larger than today's town, and only Tarquinia was equal in power at its height around 600 BC. Caere was also one of the cities of the Etruscan League. Its sea port and monumental sanctuary at Pyrgi was important for overseas trade. Today, the area of Cerveteri is best known for its Etruscan necropolis and archaeological treasures. Geography The ancient city was situated on a hill about 7 km from the sea, a location which made it a wealthy trading town derived originally from the iron ore mines in the Tolfa hills. It had three sea ports including Pyrgi and Punicum. It was bounded by the two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Marinella
Santa Marinella is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Rome Capital, Metropolitan City of Rome in the Italy, Italian region Lazio, located about northwest of Rome. It includes the beach resort of Santa Severa (the ancient Pyrgi), and a medieval castle. History In antiquity, Santa Marinella was the site of Punicum, the Etruscan port which served the city of Caere. Punicum was identified in the Peutinger Table, in which it is on the Via Aurelia 9km N of Pyrgi. The area had several scattered settlements in Etruscan times. It was also later known as Aquae Caeretanae, a Roman resort and site of many opulent villas under the Empire. There was a Sanctuary of Minerva overlooking the Punto della Vipera north of S. Marinella, finds f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alsium
Alsium ( el, ; modern: Palo) was an ancient city on the coast of Etruria, between Pyrgi and Fregenae, on the Via Aurelia, by which it is about 35 km from Rome near the modern Ladispoli. It was one of the oldest towns of Etruria, but does not appear in history until the Roman colonisation of 247 BC. It was never of great importance, except as a resort of wealthy Romans, many of whom (including Pompey and the Antonine emperors) had villas there. History It is mentioned by Dionysius among the cities which were founded by the Pelasgians in connection with the aborigines, and afterwards wrested from them by the Tyrrhenians (Etruscans). But no mention of it occurs in history as an Etruscan city, or during the wars of that people with Rome. In 247 BC a Roman ''colonia maritima'' was established there and which gave them exemption from all military service, which was, however, overruled during the exigencies of the Second Punic War. It is mentioned by Strabo, Pliny, and Ptolemy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astarte
Astarte (; , ) is the Hellenized form of the Ancient Near Eastern goddess Ashtart or Athtart (Northwest Semitic), a deity closely related to Ishtar (East Semitic), who was worshipped from the Bronze Age through classical antiquity. The name is particularly associated with her worship in the ancient Levant among the Canaanites and Phoenicians, though she was originally associated with Amorite cities like Ugarit and Emar, as well as Mari and Ebla. She was also celebrated in Egypt, especially during the reign of the Ramessides, following the importation of foreign cults there. Phoenicians introduced her cult in their colonies on the Iberian Peninsula. Name Astarte was a goddess of both the Canaanite and the Phoenician pantheon, derived from an earlier Syrian deity. She is recorded in Akkadian as (), the feminine form of Ishtar.K. van der Toorn, Bob Becking, Pieter Willem van der Horst, Dictionary of Deities and Demons in the Bible', p. 109-10. The name appears in Ugaritic as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Severa
Santa Severa is a ''frazione'' of the ''comune'' of Santa Marinella, in the province of Rome, Lazio, Italy. It is a small sea resort on the Via Aurelia, c. south of Santa Marinella and north of Rome. It takes its name from the 2nd-century Christian martyr. The village includes a small medieval town with a 9th-century castle facing the sea, where the ancient Etruscan port of Pyrgi was once located. The Pyrgi Tablets were found here in 1964. Filmography * Medici: Masters of Florence TV series (S1E01). * Three Steps Over Heaven. * Salvo D'Acquisto Salvo D'Acquisto (15 October 1920 in Naples – 23 September 1943 in Fiumicino) was a member of the Italian ''Carabinieri'' during the Second World War. After Italy switched sides in September 1943, joining the Allies, the Germans occupied the n ....http://www.davinotti.com/index.php?forum=50008868 References External links Medieval castle of Santa SeveraArcheologia con fantasmi Frazioni of the Province of Rome Coastal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelasgi
The name Pelasgians ( grc, Πελασγοί, ''Pelasgoí'', singular: Πελασγός, ''Pelasgós'') was used by Classical Greece, classical Greek writers to refer either to the predecessors of the Greeks, or to all the inhabitants of Greece before the emergence or arrival of the Greeks#Origins, Greeks. In general, "Pelasgian" has come to mean more broadly all the Indigenous peoples, indigenous inhabitants of the Aegean Sea region and their cultures, "a hold-all term for any ancient, primitive and presumably indigenous people in the Greek world". During the Classical Greece, classical period, enclaves under that name survived in several locations of mainland Greece, Crete, and other regions of the Aegean Sea, Aegean. Populations identified as "Pelasgian" spoke a language or languages that at the time Greeks identified as "barbarians, barbarian", though some ancient writers nonetheless described the Pelasgians as Greeks. A tradition also survived that large parts of Greece had o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutilius Namatianus
Rutilius Claudius Namatianus (fl. 5th century) was a Roman Imperial poet, best known for his Latin poem, ''De reditu suo'', in elegiac metre, describing a coastal voyage from Rome to Gaul in 416. The poem was in two books; the exordium of the first and the greater part of the second have been lost. What remains consists of about seven hundred lines. Whether Rutilius had converted to Christianity (the state church of the Roman Empire during his time) has been a matter of scholarly debate, but in the early 21st century, editors of his work concluded that he had not. Alan Cameron, a leading scholar of Late Antiquity, agrees that he "probably" remained unconverted from Rome's traditional religious practices, but that his hostility was not to Christianity as it was practiced by the vast majority of citizens of the Empire, but rather against the total renunciation of public life advocated by the ascetics. Life Origins Rutilius was a native of southern Gaul (Toulouse or perhaps Poit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |