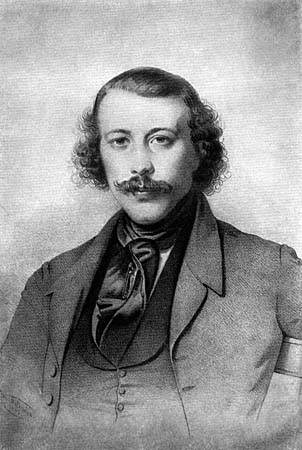|
Pyotr Lavrov
Pyotr Lavrovich Lavrov (russian: Пётр Ла́врович Лавро́в; alias Mirtov (); (June 14 O.S.">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="une 2 Old Style and New Style dates">O.S. 1823 – February 6 [January 6 O.S.], 1900) was a prominent Russians, Russian theorist of narodism, philosopher, publicist, revolutionary, and sociologist. Biography Lavrov was born in to a military family of hereditary nobles. He entered a military academy and graduated in 1842 as an army officer. He became well-versed in natural science, history, logic, philosophy, and psychology. He also taught mathematics for two decades. Lavrov joined the revolutionary movement as a radical in 1862. His actions led to his being exiled to the Ural Mountains in 1868; he soon escaped and fled abroad. In France, he lived mostly in Paris, where he became a member of the Anthropological Society. Lavrov had been attracted to European socialist ideas early on, though at first he did not know how they applie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Philosophy
Russian philosophy is a collective name for the philosophical heritage of Russian thinkers. Historiography In historiography, there is no consensus regarding the origins of Russian philosophy, its periodization and its cultural significance. The historical boundaries of Russian philosophy directly depend on the philosophical content that a specific researcher sees in Russian intellectual history. Traditionally, since the 19th century, the "pre–Petrine" or "Old Russian" and "post–Petrine" or "Enlightenment" stages of the development of Russian philosophy have been distinguished. In modern historiography, a third, "Soviet" period is also distinguished. Starting from religious thought, Archimandrite Gabriel, the first historian of Russian philosophy, saw its origins in the didactic "Teachings" of Vladimir Monomakh, thereby directly elevating Russian philosophy to traditional ancient Russian scribes. A number of major historians of Russian philosophy, however, tend to view philoso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coup D'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, military, or a dictator. Many scholars consider a coup successful when the usurpers seize and hold power for at least seven days. Etymology The term comes from French ''coup d'État'', literally meaning a 'stroke of state' or 'blow of state'. In French, the word ''État'' () is capitalized when it denotes a sovereign political entity. Although the concept of a coup d'état has featured in politics since antiquity, the phrase is of relatively recent coinage.Julius Caesar's civil war, 5 January 49 BC. It did not appear within an English text before the 19th century except when used in the translation of a French source, there being no simple phrase in English to convey the contextualized idea of a 'knockout blow to the existing administratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyotr Tkachev
Pyotr Nikitich Tkachev (Russian: Пётр Ники́тич Ткачёв; 29 June 1844 – 4 January 1886) was a Russian writer, critic and revolutionary theorist who formulated many of the revolutionary principles that were later developed and put into action by Vladimir Lenin. Although Tkachev is sometimes described as "the First Bolshevik", he did not figure prominently in the mythology of the Soviet Union. Biography Early life Tkachev was born in 1844 to a minor gentry family.Figes, p. 137. He was born in the village of Sivistov, at the time located in the Pskov Governorate. His sister Alexandra Nikitichna Annenskaya was a writer for young adults. Tkachev began attending St. Petersburg University in 1861 and took part in a series of violent student protests that year. Arrested by police during a riot on 11 October 1861, he likely came into contact with radical Russian political philosophy through other inmates during the months he was incarcerated at a Kronstadt prison. Af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Bakunin
Mikhail Alexandrovich Bakunin (; 1814–1876) was a Russian revolutionary anarchist, socialist and founder of collectivist anarchism. He is considered among the most influential figures of anarchism and a major founder of the revolutionary socialist and social anarchist tradition. Bakunin's prestige as a revolutionary also made him one of the most famous ideologues in Europe, gaining substantial influence among radicals throughout Russia and Europe. Bakunin grew up in Pryamukhino, a family estate in Tver Governorate. From 1840, he studied in Moscow, then in Berlin hoping to enter academia. Later in Paris, he met Karl Marx and Pierre-Joseph Proudhon, who deeply influenced him. Bakunin's increasing radicalism ended hopes of a professorial career. He was expelled from France for opposing The Russian Empire's occupation of Poland. In 1849, he was arrested in Dresden for his participation in the Czech rebellion of 1848 and deported to Russian Empire, where he was imprisoned fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |