|
Pulse (signal Processing)
A pulse in signal processing is a rapid, transient change in the amplitude of a Signalling (telecommunication), signal from a baseline value to a higher or lower value, followed by a rapid return to the baseline value. Pulse shapes Pulse shapes can arise out of a process called Pulse shaping, pulse-shaping. Optimum pulse shape depends on the application. Rectangular pulse These can be found in pulse waves, square waves, boxcar functions, and rectangular functions. In digital signals the up and down transitions between high and low levels are called the rising signal edge, edge and the falling edge. In digital systems the detection of these sides or action taken in response is termed edge-triggered, rising or falling depending on which side of rectangular pulse. A digital timing diagram is an example of a well-ordered collection of rectangular pulses. Nyquist pulse A Nyquist pulse is one which meets the Nyquist ISI criterion and is important in data transmission. An example of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse Examples
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the neck (carotid artery), wrist (radial artery), at the groin (femoral artery), behind the knee (popliteal artery), near the ankle joint (posterior tibial artery), and on foot (dorsalis pedis artery). Pulse (or the count of arterial pulse per minute) is equivalent to measuring the heart rate. The heart rate can also be measured by listening to the heart beat by auscultation, traditionally using a stethoscope and counting it for a minute. The radial pulse is commonly measured using three fingers. This has a reason: the finger closest to the heart is used to occlude the pulse pressure, the middle finger is used get a crude estimate of the blood pressure, and the finger most distal to the heart (usually the ring finger) is used to nullify the effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinc Function
In mathematics, physics and engineering, the sinc function, denoted by , has two forms, normalized and unnormalized.. In mathematics, the historical unnormalized sinc function is defined for by \operatornamex = \frac. Alternatively, the unnormalized sinc function is often called the sampling function, indicated as Sa(''x''). In digital signal processing and information theory, the normalized sinc function is commonly defined for by \operatornamex = \frac. In either case, the value at is defined to be the limiting value \operatorname0 := \lim_\frac = 1 for all real . The normalization causes the definite integral of the function over the real numbers to equal 1 (whereas the same integral of the unnormalized sinc function has a value of ). As a further useful property, the zeros of the normalized sinc function are the nonzero integer values of . The normalized sinc function is the Fourier transform of the rectangular function with no scaling. It is used in the concep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Delay
In signal processing, group delay and phase delay are delay times experienced by a signal's various frequency components when the signal passes through a system that is linear time-invariant (LTI), such as a microphone, coaxial cable, amplifier, loudspeaker, telecommunications system or ethernet cable. These delays are generally frequency dependent. This means that different frequency components experience different delays, which cause distortion of the signal's waveform as it passes through the system. This distortion can cause problems such as poor fidelity in analog video and analog audio, or a high bit-error rate in a digital bit stream. For a modulation signal (passband signal), the information carried by the signal is carried exclusively in the wave envelope. Group delay therefore operates only with the frequency components derived from the envelope. Introduction The group delay and phase delay properties of a linear time-invariant (LTI) system are functions of frequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaussian Filter
In electronics and signal processing mainly in digital signal processing, a Gaussian filter is a filter whose impulse response is a Gaussian function (or an approximation to it, since a true Gaussian response would have infinite impulse response). Gaussian filters have the properties of having no overshoot to a step function input while minimizing the rise and fall time. This behavior is closely connected to the fact that the Gaussian filter has the minimum possible group delay. A Gaussian filter will have the best combination of suppression of high frequencies while also minimizing spatial spread, being the critical point of the uncertainty principle. These properties are important in areas such as oscilloscopes and digital telecommunication systems. Mathematically, a Gaussian filter modifies the input signal by convolution with a Gaussian function; this transformation is also known as the Weierstrass transform. Definition The one-dimensional Gaussian filter has an im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
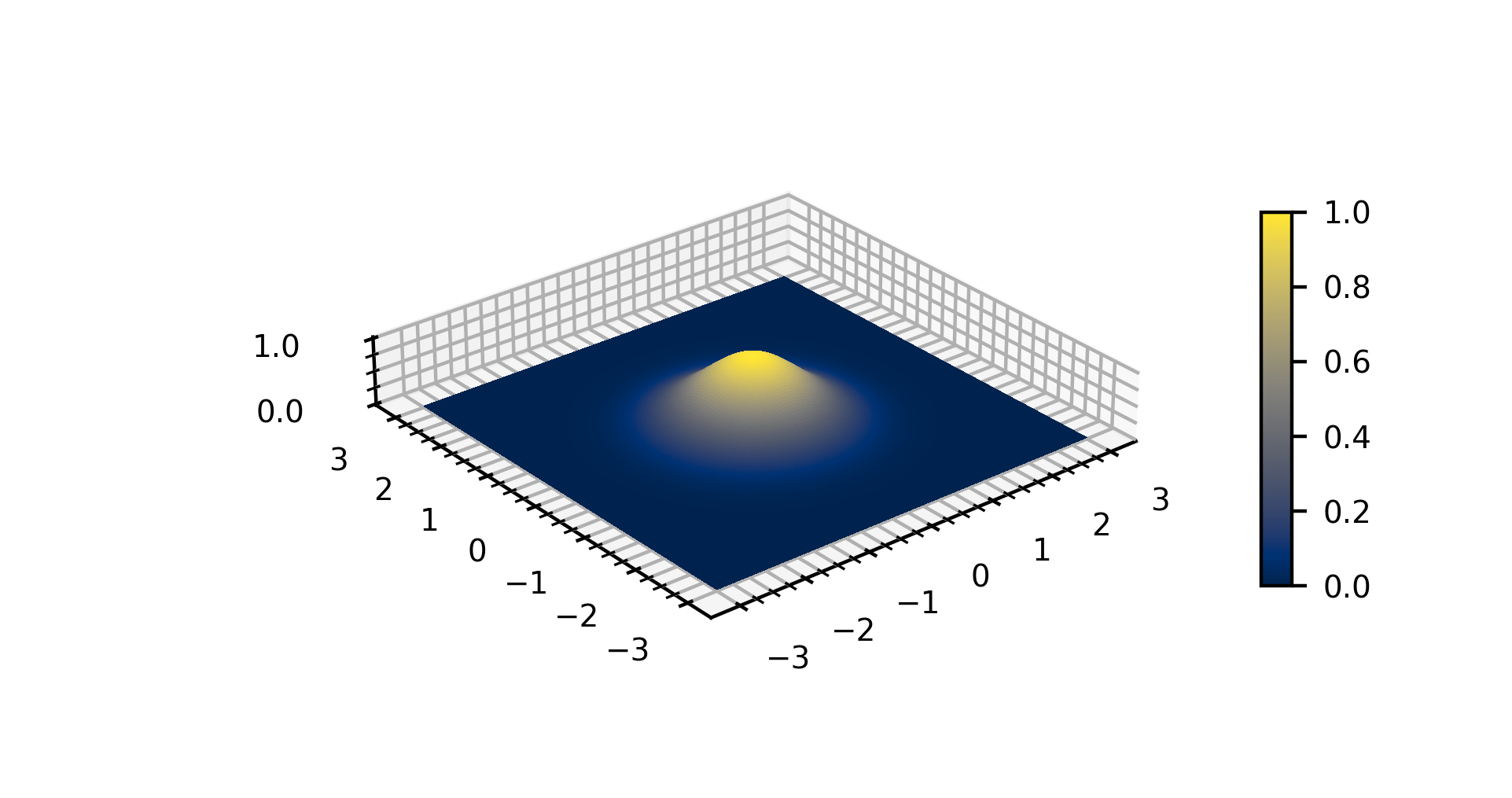
Gaussian Function
In mathematics, a Gaussian function, often simply referred to as a Gaussian, is a function of the base form f(x) = \exp (-x^2) and with parametric extension f(x) = a \exp\left( -\frac \right) for arbitrary real constants , and non-zero . It is named after the mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss. The graph of a Gaussian is a characteristic symmetric " bell curve" shape. The parameter is the height of the curve's peak, is the position of the center of the peak, and (the standard deviation, sometimes called the Gaussian RMS width) controls the width of the "bell". Gaussian functions are often used to represent the probability density function of a normally distributed random variable with expected value and variance . In this case, the Gaussian is of the form g(x) = \frac \exp\left( -\frac \frac \right). Gaussian functions are widely used in statistics to describe the normal distributions, in signal processing to define Gaussian filters, in image processing where two-dimen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filter (signal Processing)
In signal processing, a filter is a device or process that removes some unwanted components or features from a signal. Filtering is a class of signal processing, the defining feature of filters being the complete or partial suppression of some aspect of the signal. Most often, this means removing some frequencies or frequency bands. However, filters do not exclusively act in the frequency domain; especially in the field of image processing many other targets for filtering exist. Correlations can be removed for certain frequency components and not for others without having to act in the frequency domain. Filters are widely used in electronics and telecommunication, in radio, television, audio recording, radar, control systems, music synthesis, image processing, and computer graphics. There are many different bases of classifying filters and these overlap in many different ways; there is no simple hierarchical classification. Filters may be: * non-linear or linear * time-vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impulse Response
In signal processing and control theory, the impulse response, or impulse response function (IRF), of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse (). More generally, an impulse response is the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change. In both cases, the impulse response describes the reaction of the system as a function of time (or possibly as a function of some other independent variable that parameterizes the dynamic behavior of the system). In all these cases, the dynamic system and its impulse response may be actual physical objects, or may be mathematical systems of equations describing such objects. Since the impulse function contains all frequencies (see the Fourier transform of the Dirac delta function, showing infinite frequency bandwidth that the Dirac delta function has), the impulse response defines the response of a linear time-invariant system for all frequencies. Mathematical consideratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heaviside Step Function
The Heaviside step function, or the unit step function, usually denoted by or (but sometimes , or ), is a step function, named after Oliver Heaviside (1850–1925), the value of which is zero for negative arguments and one for positive arguments. It is an example of the general class of step functions, all of which can be represented as linear combinations of translations of this one. The function was originally developed in operational calculus for the solution of differential equations, where it represents a signal that switches on at a specified time and stays switched on indefinitely. Oliver Heaviside, who developed the operational calculus as a tool in the analysis of telegraphic communications, represented the function as . The Heaviside function may be defined as: * a piecewise function: H(x) := \begin 1, & x > 0 \\ 0, & x \le 0 \end * using the Iverson bracket notation: H(x) := 0.html" ;"title=">0">>0/math> * an indicator function: H(x) := \mathbf_=\mathbf 1_(x ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirac Delta Function
In mathematics, the Dirac delta distribution ( distribution), also known as the unit impulse, is a generalized function or distribution over the real numbers, whose value is zero everywhere except at zero, and whose integral over the entire real line is equal to one. The current understanding of the unit impulse is as a linear functional that maps every continuous function (e.g., f(x)) to its value at zero of its domain (f(0)), or as the weak limit of a sequence of bump functions (e.g., \delta(x) = \lim_ \frace^), which are zero over most of the real line, with a tall spike at the origin. Bump functions are thus sometimes called "approximate" or "nascent" delta distributions. The delta function was introduced by physicist Paul Dirac as a tool for the normalization of state vectors. It also has uses in probability theory and signal processing. Its validity was disputed until Laurent Schwartz developed the theory of distributions where it is defined as a linear form actin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyquist ISI Criterion
In communications, the Nyquist ISI criterion describes the conditions which, when satisfied by a communication channel (including responses of transmit and receive filters), result in no intersymbol interference or ISI. It provides a method for constructing band-limited functions to overcome the effects of intersymbol interference. When consecutive symbols are transmitted over a channel by a linear modulation (such as ASK, QAM, etc.), the impulse response (or equivalently the frequency response) of the channel causes a transmitted symbol to be spread in the time domain. This causes intersymbol interference because the previously transmitted symbols affect the currently received symbol, thus reducing tolerance for noise. The Nyquist theorem relates this time-domain condition to an equivalent frequency-domain condition. The Nyquist criterion is closely related to the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem, with only a differing point of view. Nyquist criterion If we denote the chann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing '' signals'', such as sound, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, digital storage efficiency, correcting distorted signals, subjective video quality and to also detect or pinpoint components of interest in a measured signal. History According to Alan V. Oppenheim and Ronald W. Schafer, the principles of signal processing can be found in the classical numerical analysis techniques of the 17th century. They further state that the digital refinement of these techniques can be found in the digital control systems of the 1940s and 1950s. In 1948, Claude Shannon wrote the influential paper " A Mathematical Theory of Communication" which was published in the Bell System Technical Journal. The paper laid the groundwork for later development of information communication systems and the processing of sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Timing Diagram
A digital timing diagram represents a set of signals in the time domain. A timing diagram can contain many rows, usually one of them being the clock. It is a tool commonly used in digital electronics, hardware debugging, and digital communications. Besides providing an overall description of the timing relationships, the digital timing diagram can help find and diagnose digital logic hazards. Diagram convention Most timing diagrams use the following conventions: * Higher value is a logic one * Lower value is a logic zero * A slot showing a high and low is an either-or (such as on a data line) * A Z indicates high impedance * A greyed out slot is a don't-care or indeterminate. Example: SPI bus timing The timing diagram example on the right describes the Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Bus. Most SPI master nodes can set the clock polarity (CPOL) and clock phase (CPHA) with respect to the data. This timing diagram shows the clock for both values of CPOL and the values for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |