|
Pulse-chase Experiments
In biochemistry and molecular biology, a pulse-chase analysis is a method for examining a cellular process occurring over time by successively exposing the cells to a labeled compound (pulse) and then to the same compound in an unlabeled form (chase). Mechanism A selected cell or a group of cells is first exposed to a labeled compound (the pulse) that is to be incorporated into a molecule or system that is studied (also see pulse labeling). The compound then goes through the metabolic pathways and is used in the synthesis of the product studied. For example, a radioactively labeled form of leucine (3H-leucine) can be supplied to a group of pancreatic beta cells, which then uses this amino acid in insulin synthesis. Shortly after introduction of the labeled compound (usually about 5 minutes, but the actual time needed is dependent on the object studied), excess of the same, but unlabeled, substance (the chase) is introduced into the environment. Following the previous example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse Labelling
Pulse labelling is a biochemistry technique of identifying the presence of a target molecule by labeling a sample with a radioactive compound. This is mainly done to identify the stage at which the messenger RNA is being produced in a cell Cell most often refers to: * Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life Cell may also refer to: Locations * Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery .... References Biochemistry detection methods {{Biochemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leucine
Leucine (symbol Leu or L) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Leucine is an α-amino acid, meaning it contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α- carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain isobutyl group, making it a non-polar aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Human dietary sources are foods that contain protein, such as meats, dairy products, soy products, and beans and other legumes. It is encoded by the codons UUA, UUG, CUU, CUC, CUA, and CUG. Like valine and isoleucine, leucine is a branched-chain amino acid. The primary metabolic end products of leucine metabolism are acetyl-CoA and acetoacetate; consequently, it is one of the two exclusively ketogenic amino acids, with lysine being the other. It is the most imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
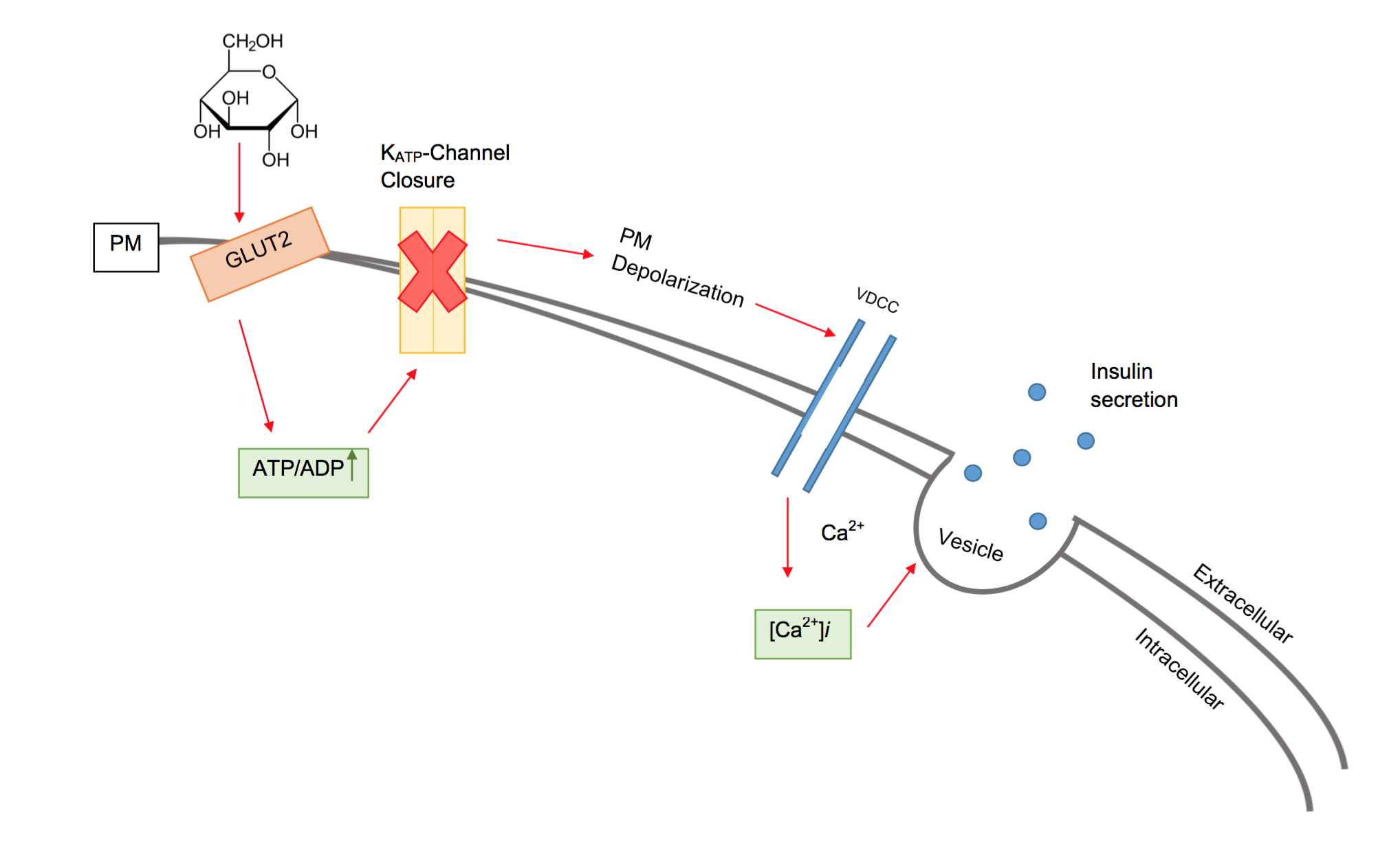
Beta Cell
Beta cells (β-cells) are a type of cell found in pancreatic islets that synthesize and secrete insulin and amylin. Beta cells make up 50–70% of the cells in human islets. In patients with Type 1 diabetes, beta-cell mass and function are diminished, leading to insufficient insulin secretion and hyperglycemia. Function The primary function of a beta cell is to produce and release insulin and amylin. Both are hormones which reduce blood glucose levels by different mechanisms. Beta cells can respond quickly to spikes in blood glucose concentrations by secreting some of their stored insulin and amylin while simultaneously producing more. Primary cilia on beta cells regulate their function and energy metabolism. Cilia deletion can lead to islet dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. Insulin synthesis Beta cells are the only site of insulin synthesis in mammals. As glucose stimulates insulin secretion, it simultaneously increases proinsulin biosynthesis, mainly through translational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into liver, fat and skeletal muscle cells. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen via glycogenesis or fats ( triglycerides) via lipogenesis, or, in the case of the liver, into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver is strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is therefore an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large molecules inside the cells. Low insulin levels in the blood have the opposite effect by promoting widespread catabolism, espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Kinase C
In cell biology, Protein kinase C, commonly abbreviated to PKC (EC 2.7.11.13), is a family of protein kinase enzymes that are involved in controlling the function of other proteins through the phosphorylation of hydroxyl groups of serine and threonine amino acid residues on these proteins, or a member of this family. PKC enzymes in turn are activated by signals such as increases in the concentration of diacylglycerol (DAG) or calcium ions (Ca2+). Hence PKC enzymes play important roles in several signal transduction cascades. In biochemistry, the PKC family consists of fifteen isozymes in humans. They are divided into three subfamilies, based on their second messenger requirements: conventional (or classical), novel, and atypical. Conventional (c)PKCs contain the isoforms α, βI, βII, and γ. These require Ca2+, DAG, and a phospholipid such as phosphatidylserine for activation. Novel (n)PKCs include the δ, ε, η, and θ isoforms, and require DAG, but do not require Ca2+ f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Four genes in the human genome code for ubiquitin: UBB, UBC, UBA52 and RPS27A. The addition of ubiquitin to a substrate protein is called ubiquitylation (or, alternatively, ubiquitination or ubiquitinylation). Ubiquitylation affects proteins in many ways: it can mark them for degradation via the proteasome, alter their cellular location, affect their activity, and promote or prevent protein interactions. Ubiquitylation involves three main steps: activation, conjugation, and ligation, performed by ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s), ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s), and ubiquitin ligases (E3s), respectively. The result of this sequential cascade is to bind ubiquitin to lysine residues on the protein substrate via an isopeptide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okazaki Fragments
Okazaki fragments are short sequences of DNA nucleotides (approximately 150 to 200 base pairs long in eukaryotes) which are synthesized discontinuously and later linked together by the enzyme DNA ligase to create the lagging strand during DNA replication. They were discovered in the 1960s by the Japanese molecular biologists Reiji and Tsuneko Okazaki, along with the help of some of their colleagues. During DNA replication, the double helix is unwound and the complementary strands are separated by the enzyme DNA helicase, creating what is known as the DNA replication fork. Following this fork, DNA primase and DNA polymerase begin to act in order to create a new complementary strand. Because these enzymes can only work in the 5’ to 3’ direction, the two unwound template strands are replicated in different ways. One strand, the leading strand, undergoes a continuous replication process since its template strand has 3’ to 5’ directionality, allowing the polymerase assem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Palade
George Emil Palade (; November 19, 1912 – October 7, 2008) was a Romanian cell biologist. Described as "the most influential cell biologist ever",Archived ( copy) in 1974 he was awarded the along with and |
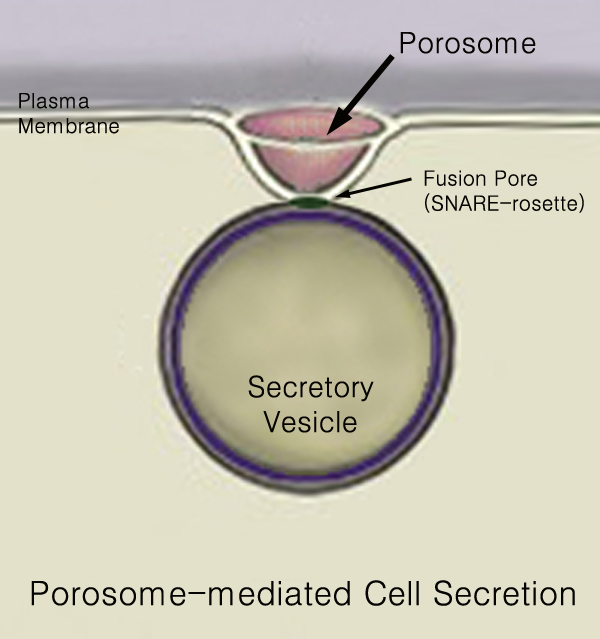
Secretory Pathway
440px Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. Secretion in bacterial species means the transport or translocation of effector molecules for example: proteins, enzymes or toxins (such as cholera toxin in pathogenic bacteria e.g. '' Vibrio cholerae'') from across the interior (cytoplasm or cytosol) of a bacterial cell to its exterior. Secretion is a very important mechanism in bacterial functioning and operation in their natural surrounding environment for adaptation and survival. In eukaryotic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |