|
Puivert
Puivert (; Languedocien: ''Puègverd'') is a commune in the Aude department in the Occitanie region in southern France. History In the 12th century a castle (Château de Puivert) stood on this site which had strong links to both Cathars and troubadours. A meeting of troubadours took place here in 1170, and in 1185 festivities attended by the Viscount of Carcassonne and Loba, Lady of Cabaret. At the time of the Wars against the Cathars its seigneur was Bernard de Congost. His wife Alpaïs had become a Cathar ''Parfaite'' before her death in 1208. In November 1210 the Castle was besieged by Simon de Montfort, and fell after three days. The Congost family continued the fight against the invaders. Bernard died after receiving the Cathar Consolamentum at Montségur in 1232. His son continued the fight, participating in the events of Avignonet in 1242 and helping defend Montsegùr in 1243–4. In 1213 the seigneurie, now in French hands, was conferred by Simon de Montfort on one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Château De Puivert
The Château de Puivert (Languedocien: ''Castèl de Puègverd'') is a so-called Cathar castle situated in the ''commune'' of Puivert, in the Aude ''département'' of France. The castle has been classified as a ''monument historique'' by the French Ministry of Culture since 1902. This building, on top of a hill overhanging the village and its lake, reaches an elevation of 605 m. The site is in the Quercob region, south of Carcassonne and east of Foix. History The first castle The construction of the present castle dates from the 12th century. The first mention is in 1170; it belonged to the Congost family before the Albigensian Crusade. These lords practised Catharism and were accused as heretics. Then, in November 1210, the castle was subjected for three days to a siege by the army of Thomas Pons de Bruyère, lieutenant of Simon de Montfort. The castle subsequently became the property of the northern barons. All that is left of this older castle is a few sections of wall to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aude
Aude (; ) is a Departments of France, department in Southern France, located in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region and named after the river Aude (river), Aude. The departmental council also calls it "Catharism, Cathar Country" (French language, French: ''Pays cathare'') after a group of religious dissidents active in the 12th to 14th centuries. Its Prefectures in France, prefecture is Carcassonne and its Subprefectures in France, subprefectures are Limoux and Narbonne. As of 2019, it had a population of 374,070.Populations légales 2019: 11 Aude INSEE Aude is a frequent feminine French given name in Francophone countries, deriving initially from Aude or Oda, a wife of Bertrand, Duke of Aquitaine, and mother of Eudo, brother of Saint Hubertus. Aude was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of The Aude Department
The following is a list of the 433 communes of the Aude department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):BANATIC Périmètre des EPCI à fiscalité propre. Accessed 3 July 2020. * *Communauté d'agglomération Le * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troubadour
A troubadour (, ; oc, trobador ) was a composer and performer of Old Occitan lyric poetry during the High Middle Ages (1100–1350). Since the word ''troubadour'' is etymologically masculine, a female troubadour is usually called a ''trobairitz''. The troubadour school or tradition began in the late 11th century in Occitania, but it subsequently spread to the Italian and Iberian Peninsulas. Under the influence of the troubadours, related movements sprang up throughout Europe: the Minnesang in Germany, ''trovadorismo'' in Galicia and Portugal, and that of the trouvères in northern France. Dante Alighieri in his ''De vulgari eloquentia'' defined the troubadour lyric as ''fictio rethorica musicaque poita'': rhetorical, musical, and poetical fiction. After the "classical" period around the turn of the 13th century and a mid-century resurgence, the art of the troubadours declined in the 14th century and around the time of the Black Death (1348) it died out. The texts of troubadou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kate Mosse
Katharine Mosse (born 20 October 1961) is a British novelist, non-fiction and short story writer and broadcaster. She is best known for her 2005 novel ''Labyrinth'', which has been translated into more than 37 languages. Early life and career Mosse was born in Chichester, and raised in Fishbourne, West Sussex, the eldest of three sisters born to a solicitor, Richard (1920–2011) and Barbara (1931–2014). Mosse's aunt was involved in the campaign for the ordination of women and her grandfather was a vicar. She was educated at Chichester High School For Girls and New College, Oxford and graduated in 1984 with a BA (Hons) in English. After leaving university, she spent seven years working in publishing in London for Hodder & Stoughton, then Century, and finally as an editorial director at Hutchinson, part of the Random House Group. She was a member of the National Union of Journalists (NUJ) and Women in Publishing. She left publishing in 1992, for a writing career beginn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montségur
Montségur (; Languedocien: ''Montsegur'') is a commune in the Ariège department in southwestern France. It is famous for its fortification, the Château de Montségur, that was built on the "pog" (mountain) on the ruins of one of the last strongholds of the Cathars. The present fortress on the site, though described as one of the " Cathar castles," is from a later period. It has been listed as a historic site by the French Ministry of Culture since 1862. According to the book, ''Holy Blood, Holy Grail'', Montségur was the location of a mythical treasure related to the Holy Grail, which was promptly smuggled away before the Cathar surrender. History The earliest signs of settlement in the area date back to the time of the Neanderthals, tens of thousands of years ago. Evidence of Roman occupation such as Roman currency and tools have also been found in and around the site. The name "Montségur" comes from Latin ''mons securus'' ("safe hill") which evolved into ''mont s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consolamentum
''Consolamentum'' (called heretication by its Catholic opponents) was the unique sacrament of the Cathars. Cathars believed in original sin, and – like Gnostics – believed temporal pleasure to be sinful or unwise. The process of living thus inevitably incurred "regret" that required "consolation" to move nearer to God or to approach heaven. It occurred only twice in a lifetime: upon confirmation in the faith and upon impending death. It was available to both men and women who made a commitment to the faith. Following the ceremony the consoled individual became a "Cathar Perfect" or "Parfait". According to the Albigenses and other Cathars, the ''consolamentum'' was an immersion (or baptism) in the Holy Spirit. It implied reception of all spiritual gifts including absolution from sin, spiritual regeneration, the power to preach, and elevation to a higher plane of perfection. The ritual Reference to the trinity was systematically replaced with the name of Christ since the doc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon De Montfort, 5th Earl Of Leicester
{{Infobox noble , name = Simon de Montfort , title = 5th Earl of Leicester , image = File:Simon4demontfort.gif , caption = Seal of Simon de Montfort, depicting him riding a horse and blowing a hunting horn with a hound alongside, inscribed with his Latinised name: ''SIGILL MSIMONIS DE MONTE FORTI ("seal of Simon from the strong mountain") , alt = , CoA = , more = no , succession = , reign = , reign-type = , predecessor = , successor = , suc-type = , spouse = Alix de Montmorency , spouse-type = , issue = Amaury de MontfortSimon de Montfort, 6th Earl of LeicesterGuy de Montfort, Count of Bigorre Amicie de MontfortPetronilla , issue-link = , issue-pipe = , full name = , native_name = , styles = , other_titles = , noble family = Mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathars
Catharism (; from the grc, καθαροί, katharoi, "the pure ones") was a Christian dualist or Gnostic movement between the 12th and 14th centuries which thrived in Southern Europe, particularly in northern Italy and southern France. Followers were described as Cathars and referred to themselves as Good Christians; in modern times, they are mainly remembered for a prolonged period of religious persecution by the Catholic Church, which did not recognize their unorthodox Christianity. Catharism emerged in Western Europe in the Languedoc region of southern France in the 11th century. Adherents were sometimes referred to as Albigensians, after the French city Albi where the movement first took hold. Catharism was initially taught by ascetic leaders who set few guidelines, leading some Catharist practices and beliefs to vary by region and over time. The movement was greatly influenced by the Bogomils of the First Bulgarian Empire, and may have originated in the Byzantine E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
The () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal arrondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathar
Catharism (; from the grc, καθαροί, katharoi, "the pure ones") was a Christian dualist or Gnostic movement between the 12th and 14th centuries which thrived in Southern Europe, particularly in northern Italy and southern France. Followers were described as Cathars and referred to themselves as Good Christians; in modern times, they are mainly remembered for a prolonged period of religious persecution by the Catholic Church, which did not recognize their unorthodox Christianity. Catharism emerged in Western Europe in the Languedoc region of southern France in the 11th century. Adherents were sometimes referred to as Albigensians, after the French city Albi where the movement first took hold. Catharism was initially taught by ascetic leaders who set few guidelines, leading some Catharist practices and beliefs to vary by region and over time. The movement was greatly influenced by the Bogomils of the First Bulgarian Empire, and may have originated in the Byzantine Empire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
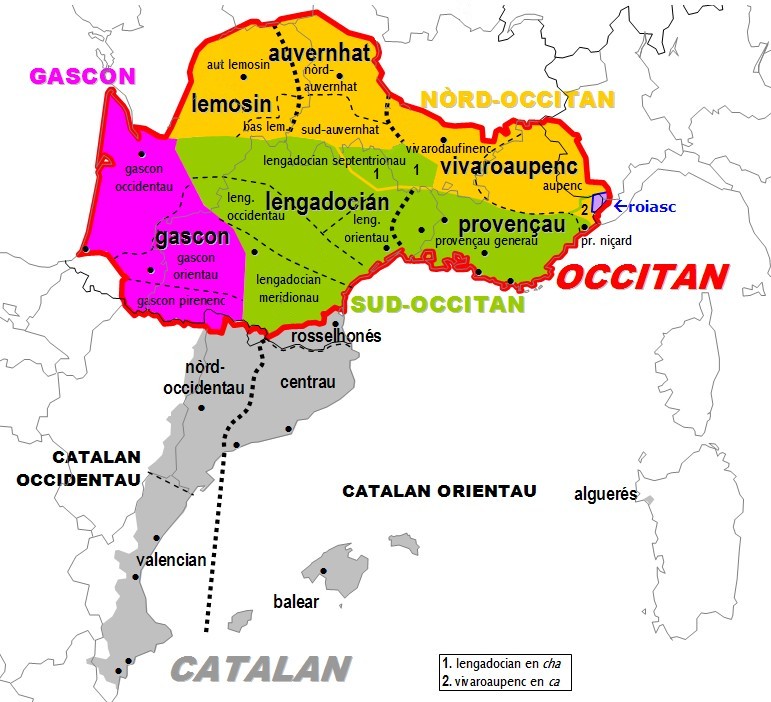
Languedocien Dialect
Languedocien (French name, ), Languedocian or Lengadocian (), is an Occitan dialect spoken in rural parts of southern France such as Languedoc, Rouergue, Quercy, Agenais and Southern Périgord. It is sometimes also called Languedocien-Guyennais. Due to its central position among the dialects of Occitan, it is often used as a basis for a Standard Occitan. About 10% of the population of Languedoc are fluent in the language (about 300,000), and another 20% (600,000) "have some understanding" of the language. All speak French as their first or second language. Geographic distribution Languedocien is spoken in certain parts of three French regions. * Occitanie: Aveyron, Lot, Tarn, Tarn-et-Garonne except Lomagne, Ariège (except a western part), Haute-Garonne (except the districts of Saint-Gaudens and Muret), Aude, Hérault, Lozère, western and northern parts of Gard and Fenouillèdes. * Nouvelle-Aquitaine: south of the Dordogne, east of the Gironde, north-eastern two-thirds of L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)