|
Puerto Miranda
Puerto Miranda is an oil port situated on the east side of Lake Maracaibo in Venezuela opposite the city of Maracaibo and is operated by the Venezuelan State Oil Company (PDVSA PETROLEO, S.A.) It is the largest crude oil export port in South America. History Shell, together with the Esso and Gulf subsidiaries Creole and Mene Grande, decided to construct a deepwater port inside Lake Maracaibo from which to export their crude oils, together with a tank farm to store crude oils that were later sent to the refineries in Amuay and Cardon on the Paraguaná peninsula. Construction of the port started at the end of the 1950s and was completed in 1961. Facilities Puerto Miranda has two jetties, each long enough to take two tankers, so that four tankers can be serviced at one time. Jetty No. 2 (North) provides two berths, Berth No. 1 and No. 2; Jetty No. 3 (South) provides Berths No. 5 and 6. All cargo is loaded through chiksans at a maximum rate of about 5,500 Tonnes per hour. Product ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Of The World
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, 2 United Nations General Assembly observers#Present non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (2 states, both in associated state, free association with New Zealand). Compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amuay
Amuay () is a fishing town located in the Paraguana Peninsula, in Falcón state, Venezuela. It is a natural bay, also has a fishing port and the bigger part of the Paraguana Refinery Complex ''(one of the largest oil refineries in the world - )'' is located there. This natural bay was extended to supply oil tankers. Despite the presence of the Oil Refinery, beaches near the bay are healthy and the water is crystalline. The nearest cities to Amuay are Judibana and Punto Fijo. History Amuay appears for first time in a map by the year 1800. Its first inhabitants belonged to the native tribe "Amuayes", who populated the Paraguana Peninsula with the "Moruyes" tribe members. They used to exchange products by barter. Amuay means "caquetío" in their native language: ''Place where water and winds meet''. Until 1947 it was only barely populated as a fishing village; after that year, the Creole Petroleum Corporation built the refinery and this changed the way of life of the villagers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Displacement (ship)
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into weight. Traditionally, various measurement rules have been in use, giving various measures in long tons. Today, tonnes are more commonly used. Ship displacement varies by a vessel's degree of load, from its empty weight as designed (known as "lightweight tonnage") to its maximum load. Numerous specific terms are used to describe varying levels of load and trim, detailed below. Ship displacement should not be confused with measurements of volume or capacity typically used for commercial vessels and measured by tonnage: net tonnage and gross tonnage. Calculation The process of determining a vessel's displacement begins with measuring its draft.George, 2005. p.5. This is accomplished by means of its "draft marks" (or "load lines"). A mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam (nautical)
The beam of a ship is its width at its widest point. The maximum beam (BMAX) is the distance between planes passing through the outer extremities of the ship, beam of the hull (BH) only includes permanently fixed parts of the hull, and beam at waterline (BWL) is the maximum width where the hull intersects the surface of the water. Generally speaking, the wider the beam of a ship (or boat), the more initial stability it has, at the expense of secondary stability in the event of a capsize, where more energy is required to right the vessel from its inverted position. A ship that heels on her ''beam ends'' has her deck beams nearly vertical. Typical values Typical length-to-beam ratios ( aspect ratios) for small sailboats are from 2:1 (dinghies to trailerable sailboats around ) to 5:1 (racing sailboats over ). Large ships have widely varying beam ratios, some as large as 20:1. Rowing shells designed for flatwater racing may have length to beam ratios as high as 30:1, while a cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Length Overall
__NOTOC__ Length overall (LOA, o/a, o.a. or oa) is the maximum length of a vessel's hull measured parallel to the waterline. This length is important while docking the ship. It is the most commonly used way of expressing the size of a ship, and is also used for calculating the cost of a marina berth (for example, £2.50 per metre LOA). LOA is usually measured on the hull alone. For sailing ships, this may ''exclude'' the bowsprit and other fittings added to the hull. This is how some racing boats and tall ships use the term LOA. However, other sources may include bowsprits in LOA. Confusingly, LOA has different meanings. "Sparred length", "Total length including bowsprit", "Mooring length" and "LOA including bowsprit" are other expressions that might indicate the full length of a sailing ship. LOD Often used to distinguish between the length of a vessel including projections (e.g. bow sprits, etc.) from the length of the hull itself, the Length on Deck or LOD is often repor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draft (hull)
The draft or draught of a ship's hull is the vertical distance between the waterline and the bottom of the hull (keel). The draught of the vessel is the maximum depth of any part of the vessel, including appendages such as rudders, propellers and drop keels if deployed. Draft determines the minimum depth of water a ship or boat can safely navigate. The related term air draft is the maximum height of any part of the vessel above the water. The more heavily a vessel is loaded, the deeper it sinks into the water, and the greater its draft. After construction, the shipyard creates a table showing how much water the vessel displaces based on its draft and the density of the water (salt or fresh). The draft can also be used to determine the weight of cargo on board by calculating the total displacement of water, accounting for the content of the ship's bunkers, and using Archimedes' principle. The closely related term "trim" is defined as the difference between the forward and aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
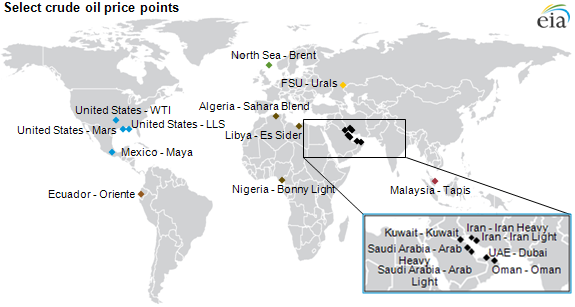
List Of Crude Oil Products
In the international petroleum industry, crude oil products are traded on various oil bourses based on established chemical profiles, delivery locations, and financial terms. The chemical profiles, or crude oil assays, specify important properties such as the oil's API gravity. The delivery locations are usually sea ports close to the oil fields from which the crude was obtained (and new fields are constantly being explored), and the pricing is usually quoted based on FOB (''free on board'', without consideration of final delivery costs). Benchmarks The three most quoted oil products are North America's West Texas Intermediate crude (WTI), North Sea Brent Crude, and the UAE Dubai Crude, and their pricing is used as a barometer for the entire petroleum industry, although, in total, there are 46 key oil exporting countries. Brent Crude is typically priced at about $2 over the WTI Spot price, which is typically priced $5 to $6 above the EIA's Imported Refiner Acquisition Cost ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Oil
Fuel oil is any of various fractions obtained from the distillation of petroleum (crude oil). Such oils include distillates (the lighter fractions) and residues (the heavier fractions). Fuel oils include heavy fuel oil, marine fuel oil (MFO), bunker fuel, furnace oil (FO), gas oil (gasoil), heating oils (such as home heating oil), diesel fuel and others. The term ''fuel oil'' generally includes any liquid fuel that is burned in a furnace or boiler to generate heat ( heating oils), or used in an engine to generate power (as motor fuels). However, it does not usually include other liquid oils, such as those with a flash point of approximately , or oils burned in cotton- or wool-wick burners. In a stricter sense, ''fuel oil'' refers only to the heaviest commercial fuels that crude oil can yield, that is, those fuels heavier than gasoline (petrol) and naphtha. Fuel oil consists of long-chain hydrocarbons, particularly alkanes, cycloalkanes, and aromatics. Small molecules, such as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United States customary units), and the long ton ( British imperial units). It is equivalent to approximately 2204.6 pounds, 1.102 short tons, and 0.984 long tons. The official SI unit is the megagram (symbol: Mg), a less common way to express the same mass. Symbol and abbreviations The BIPM symbol for the tonne is t, adopted at the same time as the unit in 1879.Table 6 . BIPM. Retrieved on 2011-07-10. Its use is also official for the metric ton in the United States, having been adopted by the United States |
Chiksan
A marine loading arm, also known as a mechanical loading arm, loading arm, or MLA is a mechanical arm consisting of articulated steel pipes that connect a tankship such as an oil tanker or chemical tanker to a cargo terminal. Genericized trademarks such as Chiksan (often misspelled Chicksan) are often used to refer to marine loading arms.Huber, 2001, p.83.Hayler and Keever, 2001, p. G-7. Operation and design A marine loading arm is an alternative to direct hose hookups that is particularly useful for larger vessels and transfers at higher loading rates and pressures. Controlled manually or hydraulically, a loading arm employs swivel joints and can, to some extent, follow the movement of a moored vessel.Hayler and Keever, 2001, p. 14-10 to 14-11. Many loading arm systems feature quick-connect fittings. Gasket or o-ring arrangements are required to make a secure seal to the ship's manifold flange. A loading arm must be drained or closed off before the connection is broken off.Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraguaná Peninsula
The Paraguaná Peninsula () is a peninsula in Venezuela, situated in the north of Falcón State, and comprises the municipalities of Carirubana, Los Taques and Falcón. The island of Aruba lies to the north. Bonaire and Curaçao are slightly further away. The Paraguaná Peninsula is connected to the rest of the state by a natural isthmus of Médanos. The Peninsula contains two oil refineries, in the West city of Punto Fijo. The output of these refineries is shipped internationally through the ports of Amuay and Cardón. The Paraguaná Peninsula lies in the Caribbean Sea. The peninsula lies in the Paraguana xeric scrub ecoregion. Because it is almost completely surrounded by water, the peninsula is sometimes called an island, and is sometimes considered as part of the Leeward Antilles. It was in fact an island earlier in the Holocene, before a tombolo formed joining Paraguaná to the mainland. The Solar eclipse of February 26, 1998 was visible from the peninsula. The ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Depot
An oil terminal (also called a tank farm, tankfarm, oil installation or oil depot) is an industrial facility for the storage of oil, petroleum and petrochemical products, and from which these products are transported to end users or other storage facilities. An oil terminal typically has a variety of above or below ground tankage; facilities for inter-tank transfer; pumping facilities; loading gantries for filling road tankers or barges; ship loading/unloading equipment at marine terminals; and pipeline connections. History Originally, open pits and cubic reservoirs were used for industrial oil storage. The structure was pioneered by Russian engineer Vladimir Shukhov during his work for Branobel oil company. He published an article "Mechanical structures in oil industry" ("") in 1883, mathematically proving that cylindrical shape would require the least amount of steel, modelling structural stresses specific to oil storage. Shukhov also developed construction methods, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)