|
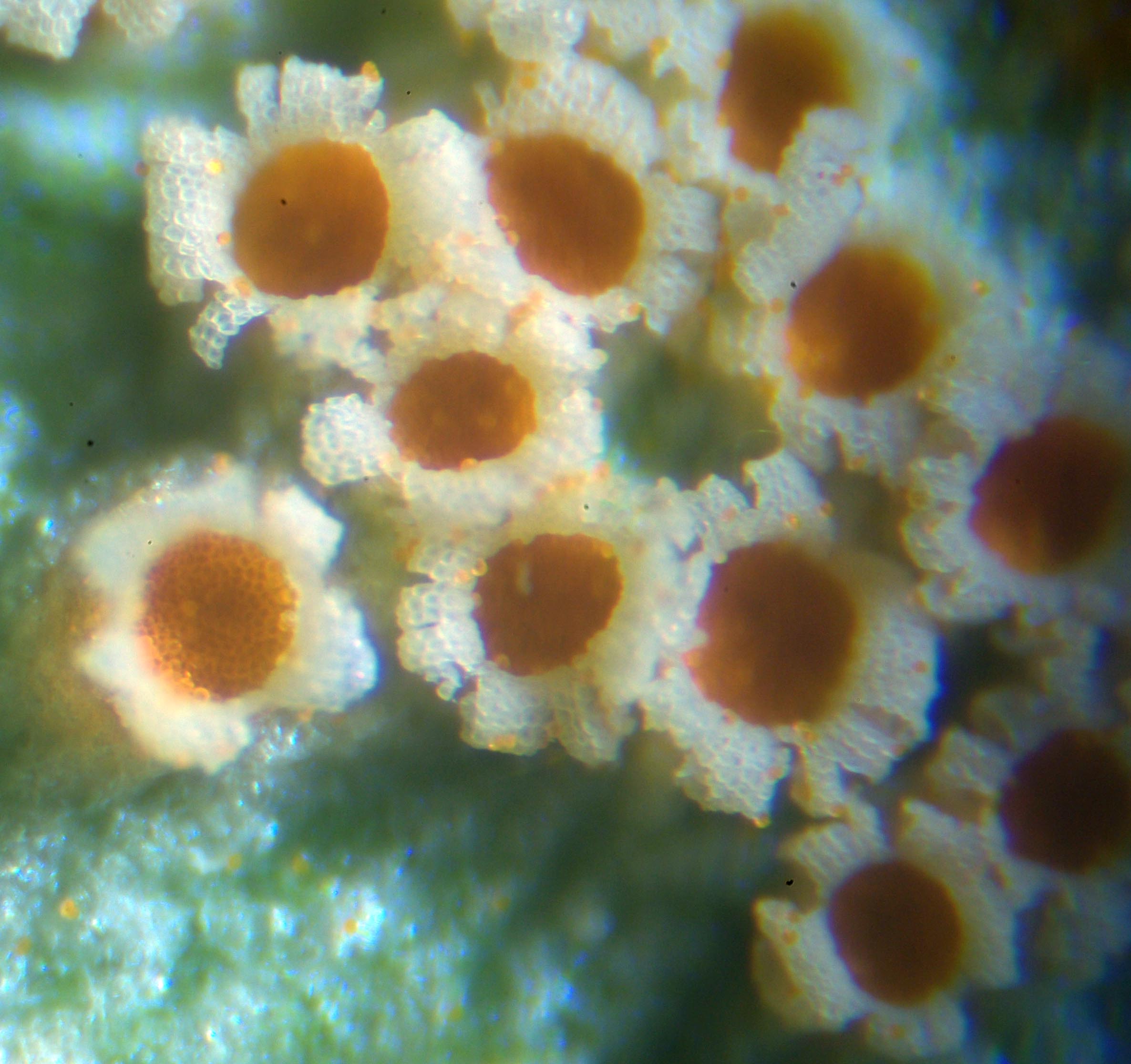
Puccinia Poarum
''Puccinia poarum'', the coltsfoot gall rust or meadow grass rust, is a plant pathogen. This fungal parasite forms a yellow to orange gall, 1–2 cm in diameter, on the underside of leaves of coltsfoot (''Tussilago farfara''). It also infects, but does not gall grasses of the family Poaceae. ''P. poarum'' is a genetically diverse species that has been reported on at least seventy plant hosts. Characteristics On ''Tussilago farfara'' (coltsfoot), infection by ''P. poarum'' results in large, circular, yellow or orange-red spots that protrude from the undersides of the leaves,.Hancy, Page 106 The spots often have a purple marginStubbs, Page 70 and sometimes a central hole. On the lower leaf surface, 20-30 cup-shaped aecia of the fungus form on each gall. On the upper surface of the leaf, infection results in a yellow circle with no swelling. Spermogonia) may also be present.Redfern, Page 260 On ''T. farfara'' the rust is necrotrophic, obtaining nutrients from dead cells and tiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tussilago Farfara
''Tussilago farfara'', commonly known as coltsfoot, is a plant in the tribe Senecioneae in the family Asteraceae, native to Europe and parts of western and central Asia. The name "tussilago" is derived from the Latin ''tussis'', meaning cough, and ''ago'', meaning to cast or to act on. It has had uses in traditional medicine, but the discovery of toxic pyrrolizidine alkaloids in the plant has resulted in liver health concerns. ''Tussilago farfara'' is the only accepted species in the genus ''Tussilago'', although more than two dozen other species have at one time or another been considered part of this group. Most of them are now regarded as members of other genera ''(Chaptalia, Chevreulia, Farfugium, Homogyne, Leibnitzia, Petasites, Senecio).''Flann, C (ed) 2009+ Global Compositae Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poaceae
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and pasture. The latter are commonly referred to collectively as grass. With around 780 genera and around 12,000 species, the Poaceae is the fifth-largest plant family, following the Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. The Poaceae are the most economically important plant family, providing staple foods from domesticated cereal crops such as maize, wheat, rice, barley, and millet as well as feed for meat-producing animals. They provide, through direct human consumption, just over one-half (51%) of all dietary energy; rice provides 20%, wheat supplies 20%, maize (corn) 5.5%, and other grains 6%. Some members of the Poaceae are used as building materials (bamboo, thatch, and straw); others can provide a source of biofuel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aecia
An aecium (plural aecia) is a specialised reproductive structure found in some plant pathogenic rust fungi that produce aeciospores. Aecia may also be referred to as "cluster cups". The term aecidium (plural aecidia) is used interchangeably but is not preferred. In some rust fungi such as ''Phragmidium'', aecia lack an outer wall structure (a peridium The peridium is the protective layer that encloses a mass of spores in fungi. This outer covering is a distinctive feature of gasteroid fungi. Description Depending on the species, the peridium may vary from being paper-thin to thick and rubber ...) but instead produce a diffuse aecium called a caeoma.''Fungi''. Lilian E Hawker, 1966, Hutchinson University Library In some species of rust fungi with a life cycle including two different host plants, the binucleate spores produced in the aecia cannot infect the current plant host, but must infect a different plant species. References Fungal morphology and anatomy Reproduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermogonia
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrotrophic
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puccinia Poarum On Coltsfoot Leaf
''Puccinia'' is a genus of fungi. All species in this genus are obligate plant pathogens and are known as rusts. The genus contains about 4000 species. The genus name of ''Puccinia'' is in honour of Tommaso Puccini (died 1735), who was an Italian doctor and botanist who taught Anatomy at Hospital of Santa Maria Nuova in Florence. The genus was circumscribed by Pier Antonio Micheli in Nov. Pl. Gen. on page 213 in 1729. Taxonomy Examples of ''Puccinia'' rusts and the diseases they cause: * ''Puccinia asparagi'' - Asparagus rust * ''Puccinia graminis'' - Stem rust, also known as black rust * '' Puccinia horiana'' - Chrysanthemum white rust * ''Puccinia mariae-wilsoniae'' - Spring beauty rust * ''Puccinia poarum'' - Coltsfoot rust gall * ''Puccinia psidii'' - Guava rust or eucalyptus rust * ''Puccinia recondita'' - Brown rust * ''Puccinia sessilis'' - Arum rust and Ransoms rust * ''Puccinia striiformis'' - Stripe rust, also known as yellow rust * ''Puccinia triticina'' - Wheat l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coleosporium Tussilaginis
''Coleosporium tussilaginis'' is a species of rust fungus in the family Coleosporiaceae. It is a plant pathogen. It is known to infect ''Campanula rotundifolia'', on which it produces urediniospores and teliospores. References Fungal plant pathogens and diseases Pucciniales Fungi described in 1801 Taxa named by Christiaan Hendrik Persoon {{plant-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uredinia
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telium
Telium, plural telia, are structures produced by rust fungi as part of the reproductive cycle. They are typically yellow or orange drying to brown or black and are exclusively a mechanism for the release of teliospores which are released by wind or water to infect the alternate host in the rust life-cycle. The telial stage provides an overwintering strategy in the life cycle of a parasitic heteroecious fungus by producing teliospores; this occurs on cedar trees. A primary aecial stage is spent parasitizing a separate host plant which is a precursor in the life cycle of heteroecious fungi. Teliospores are released from the telia in the spring. The spores can spread many kilometers through the air, however most are spread near the host plant. Host plants There are a number of plants that can be infected by the telial stage. Therefore, the telial stage is considered a pathogen to those plants. A few specific plant pathogenic species are listed here with their hosts. # ''Puccinia grami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puccinia Striiformis
''Puccinia striiformis'' var. ''striiformis'' is a plant pathogen. It causes stripe rust on wheat, but has other hosts as well. The species is common in Europe and in more recent years has become a problem in Australia. Infection can cause losses of up to 40%, and the fungus will infect both winter wheat and spring wheat. The taxonomy of ''Puccinia striiformis'' was revised in 2010. The commonly called stripe rusts on wheat and grasses were separated into four species based on molecular and morphological studies: ''Puccinia striiformis'' sensu stricto (on ''Aegilops'', ''Elymus'', ''Hordeum'' and ''Triticum'' spp.), ''Puccinia pseudostriiformis'' (on ''Poa'' spp.), ''Puccinia striiformoides'' (on ''Dactylis'' spp.) and ''Puccinia gansensis'' (on ''Achnatherum'' spp.) The stripe rust, ''Puccinia striiformis'', can greatly decrease wheat yield in northern Punjab and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (NWFP). See also * Wheat yellow rust Wheat yellow rust (''Puccinia striiformis'' f.sp. '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Nielsen (botanist)
Peter Nielsen (28 July 1829 – 30 September 1897) was a Danish botanist and plant pathologist. He was born at a farm in Vonsbæk parish in the Duchy of Schleswig. He graduated in 1857 from Jelling Statsseminarium in Vejle. He was employed at Flakkebjerg Institute from 1857-1859. In 1859 he became a school teacher at Ørslev in Zealand, where he studied the local flora. He was particularly interested in plants useful to agriculture and in plant pathogens. He was a prolific writer on these topics. He undertook meticulous studies of rust fungi. He was the first to describe the host alternation of Puccinia poarum between grasses and ''Tussilago farfara ''Tussilago farfara'', commonly known as coltsfoot, is a plant in the tribe Senecioneae in the family Asteraceae, native to Europe and parts of western and central Asia. The name "tussilago" is derived from the Latin ''tussis'', meaning cough, an ...''. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Nielsen, Peter 1829 births 1897 deaths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |