|
Pu, Shanxi
Pu County (), also known by its Chinese name Puxian, is a county in the southwest of Shanxi province, China. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Linfen; bordering county-level divisions are Yaodu District (the urban area of Linfen) to the southeast, Ji County to the southwest, Daning County to the west, Xi County to the north, Fenxi County to the northeast, and Hongtong County to the east. Pu County spans an area of , and had a population of 107,339 according to the 2010 Chinese Census. Toponymy Pu County is named after the fabled Puzi Mountain () in the area. History Spring and Autumn period During the Spring and Autumn period of Chinese history, the city of Pu and its hinterland were the appendage of the Jin prince Ji Chong'er before the Rong beauty Li Ji successfully schemed to drive him from the country in 655BC and to place her own son into succession for the duchy. Pu would have also been a home to the famous courtiers like Jie Zhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postal Code Of China
Postal codes in the People's Republic of China () are postal codes used by China Post for the delivery of letters and goods within mainland China. China Post uses a six-digit all-numerical system with four tiers: the first tier, composed of the first two digits, show the province, province-equivalent municipality, or autonomous region; the second tier, composed of the third digit, shows the postal zone within the province, municipality or autonomous region; the fourth digit serves as the third tier, which shows the postal office within prefectures or prefecture-level cities; the last two digits are the fourth tier, which indicates the specific mailing area for delivery. The range 000000–009999 was originally marked for Taiwan (The Republic of China) but is not used because it not under the control of the People's Republic of China. Mail to ROC is treated as international mail, and uses postal codes set forth by Chunghwa Post. Codes starting from 999 are the internal codes use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xi County, Shanxi
Xi County or Xixian () is a county in the southwest of Shanxi province, China. It is located in the northwest of the administrative area of the prefecture-level city of Linfen. The county spans an area of , and according to the 2010 Chinese Census, Xi County had a population of 103,617. Toponymy The county was named after a definition in the Erya which stated "that which is wet shall be called ''xi''" (), in reference to the county's wet period during the spring. History During the Han dynasty, the area was organized as Puzi County (). Under the Northern Wei, the northern portion of present-day Xi County was organized as part of , and the southern portion was part of Pingchang County (). In 579 CE, the Northern Zhou established Changshou County () in the area, under the jurisdiction of . In 585 CE, the area was reorganized as , which existed on and off until the area was reorganized as Xichuan County () in the mid 14th century. In 1912, the area was reorganized as Xi Count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jie Zhitui
Jie Zhitui (centuryBC), also known as Jie Zitui, was a Han aristocrat who served the Jin prince Chong'er during the Spring and Autumn Period of Chinese history. Chinese legend holds that when Chong'er finally ascended to power as the duke of Jin ("Duke Wen"), Jie either refused or was passed over for any reward, despite his great loyalty during the prince's times of hardship. Jie then retired to the forests of Jin in what is now central Shanxi with his mother. Supposedly, the duke so desired to repay Jie's years of loyalty that, when Jie declined to present himself at court, he ordered a forest fire to compel the recluse out of hiding. Instead, Jie and his mother were killed by the fire on . By the Han, Jie was being revered in central Shanxi as a Taoist immortal. He was annually commemorated with a ritual avoidance of fire that, despite many official bans, eventually became China's Cold Food and Qingming Festivals. Names Jie Zhitui or Jiezhi Tui is the name given to him i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiqi
Xiqi (, 665–651 BC) was briefly the ruler of the Jin (Chinese state), State of Jin during the Spring and Autumn period of ancient China. He was the son of Duke Xian of Jin and his favored concubine Li Ji (concubine), Li Ji, and later replaced his older half-brother Shensheng as crown prince. After the death of Duke Xian, he ascended the throne for about a month before being killed by Li Ke. Biography In 665 BC, the twelfth year of the reign of Duke Xian of Jin, Li Ji gave birth to Xiqi. Since Li Ji wanted her son to be the crown prince, she bribed two of Duke Xian's most trusted officials, Liang Wu (梁五) and Dongguan Biwu (東關嬖五). The two officials persuaded Duke Xian of Jin to let princes Shensheng, Duke Wen of Jin, Chong'er and Duke Hui of Jin, Yiwu leave the capital, Jiang (絳). The officials told the duke that the northern Rong tribes (戎族) and Di tribes (狄族) frequently attacked Jin such that the princes were needed to defend their territory. Duke Xia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Ji Unrest
The Li Ji Unrest or Rebellion (657–651 BCE) was a series of events that took place in the State of Jin during the Spring and Autumn period of ancient China, caused by Li Ji, the concubine of Duke Xian of Jin, in order to put her son Xiqi onto the throne of Jin. Background Duke Xian of Jin married six wives who gave birth to five sons. The first was Jia Jun (賈君) from the State of Jia (賈國). Qi Jiang (齊姜) gave birth to Prince Shensheng. Hu Ji (狐姬) was the mother of Prince Chong'er while her younger sister Xiao Rongzi (小戎子) gave birth to Prince Yiwu. Li Ji was the mother of Xiqi while her dowry younger sister Shao Ji (少姬) gave birth to Zhuozi. Duke Xian marries Li Ji At the time Duke Xian considered taking his concubine Li Ji as his first wife. Before doing so he asked the gods through divination whether or not it was wise to do this. The answer he received was that the outcome would not be good. He asked a second time and on receiving a positive respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Ji (concubine)
Li Ji (; died 651 BCE) was a concubine and later wife of Duke Xian of Jin, ruler of the State of Jin between 676 and 651 BC during the Spring and Autumn period of ancient China. Li Ji is best known for starting the Li Ji Unrest which led to the suicide of Prince Shensheng. She also placed her own son Xiqi on the Jin throne after the death of Duke Xian. She was nicknamed as the "Witch of the Age" () because of her devious acts. Biography Li Ji was originally a native of Li Rong (驪戎), one of the northern Rong tribes. In 672 BC, the fifth year of his reign, Duke Xian obtained two daughters of leader of the Li Rong tribe: Li Ji and her younger sister, Shao Ji (少姬). Because of her beauty, Li Ji gained the favor of Duke Xian, therefore he had a desire to make Li Ji his main wife. Before doing so he asked the gods through divination whether or not it was wise to do this. The answer he received was that the outcome would not be good. He asked a second time and on receiving a posit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xirong
Xirong () or Rong were various people who lived primarily in and around the western extremities of ancient China (in modern Gansu and Qinghai). They were known as early as the Shang dynasty (1765–1122 BCE), as one of the Four Barbarians that frequently (and often violently) interacted with the sinitic Huaxia civilization. They typically resided to the west of Guanzhong Plains from the Zhou Dynasty (1046–221 BCE) onwards. They were mentioned in some ancient Chinese texts as perhaps genetically and linguistically related to the people of the Chinese civilization. Etymology The historian Li Feng says that during the Western Zhou period, since the term ''Rong'' "warlike foreigners" was "often used in bronze inscriptions to mean 'warfare', it is likely that when a people was called 'Rong', the Zhou considered them as political and military adversaries rather than as cultural and ethnic 'others'." Paul R. Goldin also proposes that ''Rong'' was a "pseudo-ethnonym" meaning "belli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ji Chong'er
Duke Wen of Jin (697–628BC), born Chong'er (literally "Double Ears"), was a scion of the royal house of Jin during the Spring and Autumn Period of Chinese history. He famously endured a long period of exile from his realm before finally being restored to power (r.636–628BC) and rapidly leading Jin to hegemony over the other Chinese states of his time. He is a figure in numerous Chinese legends, including those about his loyal courtier Jie Zhitui, whose death is said to have inspired China's Cold Food and Qingming Festivals. Names "Duke Wen of Jin" is a posthumous name bestowed on him as part of his family's ancestral veneration. It literally means the "Cultured Duke of Jin". Duke Wen's given name was Chong'er. His clan name was Ji. Life Early life Prince Chong'er was born to Duke Xian of Jin in 697 BC. The '' Zuo Zhuan'' notes that "his ribs were all grown together," a sign of strength and leadership. Chong'er's half-brothers included Shensheng and Xiqi. While Shens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jin (Chinese State)
Jin (, Old Chinese: ''*''), originally known as Tang (唐), was a major state during the middle part of the Zhou dynasty, based near the centre of what was then China, on the lands attributed to the legendary Xia dynasty: the southern part of modern Shanxi. Although it grew in power during the Spring and Autumn period, its aristocratic structure saw it break apart when the duke lost power to his nobles. In 403BC, Jin was split into three successor states: Han, Zhao and Wei. The Partition of Jin marks the end of the Spring and Autumn Period and the beginning of the Warring States period. Geography Jin was located in the lower Fen River drainage basin on the Shanxi plateau. To the north were the Xirong and Beidi peoples. To the west were the Lüliang Mountains and then the Loess Plateau of northern Shaanxi. To the southwest the Fen River turns west to join the south-flowing part of the Yellow River which soon leads to the Guanzhong, an area of the Wei River Valley that wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appendage
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part, or natural prolongation, that protrudes from an organism's body. In arthropods, an appendage refers to any of the homologous body parts that may extend from a body segment, including antennae, mouthparts (including mandibles, maxillae and maxillipeds), gills, locomotor legs ( pereiopods for walking, and pleopods for swimming), sexual organs (gonopods), and parts of the tail (uropods). Typically, each body segment carries one pair of appendages. An appendage which is modified to assist in feeding is known as a maxilliped or gnathopod. In vertebrates, an appendage can refer to a locomotor part such as a tail, fins on a fish, limbs (legs, flippers or wings) on a tetrapod; exposed sex organ; defensive parts such as horns and antlers; or sensory organs such as auricles, proboscis ( trunk and snout) and barbels. Appendages may become ''uniramous'', as in insects and centipedes, where each appendage comprises a single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese History
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the ''Book of Documents'' (early chapters, 11th century BC), the ''Bamboo Annals'' (c. 296 BC) and the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' (c. 91 BC) describe a Xia dynasty before the Shang, but no writing is known from the period, and Shang writings do not indicate the existence of the Xia. The Shang ruled in the Yellow River valley, which is commonly held to be the cradle of Chinese civilization. However, Neolithic civilizations originated at various cultural centers along both the Yellow River and Yangtze River. These Yellow River and Yangtze civilizations arose millennia before the Shang. With thousands of years of continuous history, China is among the world's oldest civilizations and is regarded as one of the cradles of civilization. The Zhou dynasty (1046–256 BC) suppl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
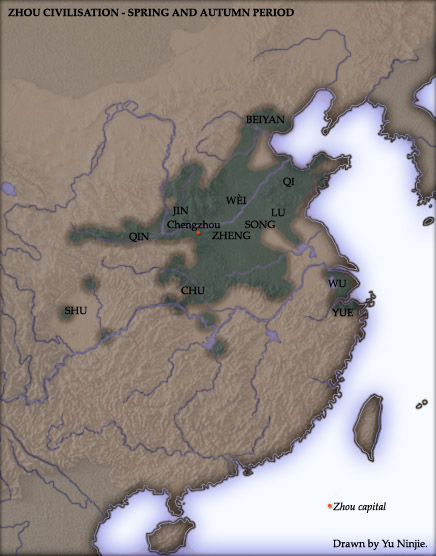
Spring And Autumn Period
The Spring and Autumn period was a period in Chinese history from approximately 770 to 476 BC (or according to some authorities until 403 BC) which corresponds roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou period. The period's name derives from the ''Spring and Autumn Annals'', a chronicle of the state of Lu between 722 and 479 BCE, which tradition associates with Confucius (551–479 BCE). During this period, the Zhou royal authority over the various feudal states eroded as more and more dukes and marquesses obtained ''de facto'' regional autonomy, defying the king's court in Luoyi and waging wars amongst themselves. The gradual Partition of Jin, one of the most powerful states, marked the end of the Spring and Autumn period and the beginning of the Warring States period. Background In 771 BCE, a Quanrong invasion in coalition with the states of Zeng and Shen — the latter polity being the fief of the grandfather of the disinherited crown prince Yijiu — destroyed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)