|
Ptolemy Macron
Ptolemy Macron ( fl. 2nd century BCE) was a general of King Antiochus IV Epiphanes (c. 215 BCE – 164 BCE), head of the Seleucid Empire, a Greek state in Western Asia. His life is covered in parts of the first two Books of the Maccabees, which call him the son of Dorymenes and give him the cognomen "Macron". Biography According to II Macc. x. 12, Ptolemy Macron abandoned Cyprus, which had been entrusted to him by the Egyptian king Ptolemy Philometor. The passage in Polybius and the biography which the Suda gives of Ptolemy Macron refer to his conduct in Cyprus. Ptolemy Macron then went over to Antiochus Epiphanes, and was sent by the chancellor Lysias with the generals Nicanor and Gorgias to defeat the Maccabean Revolt (167 to 160 BCE). In II Macc. viii. 8-11 Ptolemy is called governor of Cœle-Syria and Phenicia, who as such sent Nicanor and Gorgias against the Jews. The Jewish leader Menelaus In Greek mythology, Menelaus (; grc-gre, Μενέλαος , 'wrath of the peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus IV Epiphanes
Antiochus IV Epiphanes (; grc, Ἀντίοχος ὁ Ἐπιφανής, ''Antíochos ho Epiphanḗs'', "God Manifest"; c. 215 BC – November/December 164 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king who ruled the Seleucid Empire from 175 BC until his death in 164 BC. He was a son of King Antiochus III the Great. Originally named Mithradates (alternative form '' Mithridates''), he assumed the name Antiochus after he ascended the throne. Notable events during Antiochus's reign include his near-conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt, his persecution of the Jews of Judea and Samaria, and the rebellion of the Jewish Maccabees. Antiochus's accession to the throne was controversial, and he was seen as a usurper by some. After the death of his brother Seleucus IV Philopator in 175 BC, the "true" heir should have been Seleucus's son Demetrius I. However, Demetrius I was very young and a hostage in Rome at the time, and Antiochus seized the opportunity to declare himself king instead, successfully rall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgias (general)
Gorgias () was a Demographics of Syria, Syrian-Seleucid General of the 2nd century BC, in the service of Antiochus IV Epiphanes, Antiochus Epiphanes (1 Maccabees, 1 Macc 3:38; 2 Maccabees, 2 Macc 8:9). Life After Judas Maccabeus's forces defeated the Seleucid army at the Battle of Beth Horon (166 BC), Battle of Beth Horon, they were determined to send a stronger force against him. According to 1 Maccabees iii. 38, which Josephus follows ("The Antiquities of the Jews" xii. 7, § 3), it was the governor Lysias (Syrian chancellor), Lysias, who had been left as regent during the absence of Antiochus in Persia, who commissioned the generals Nicanor (Seleucid general), Nicanor and Gorgias, sending them with a large army to Judea; but according to 2 Maccabees viii. 8, it was Ptolemy (son of Dorymenes), Ptolemy, governor of Coele-Syria and Phoenicia, who sent them. Nicanor seems to have been the commander-in-chief, although 2 Maccabees viii. 9 describes Gorgias as "a general and a man of exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucid Generals
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire originally founded by Alexander the Great. After receiving the Mesopotamian region of Babylonia in 321 BC, Seleucus I began expanding his dominions to include the Near Eastern territories that encompass modern-day Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Syria, all of which had been under Macedonian control after the fall of the former Persian Achaemenid Empire. At the Seleucid Empire's height, it had consisted of territory that had covered Anatolia, Persia, the Levant, and what are now modern Iraq, Kuwait, Afghanistan, and parts of Turkmenistan. The Seleucid Empire was a major center of Hellenistic culture. Greek customs and language were privileged; the wide variet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopaedia Biblica/Doeg-Ecclesiastes
An encyclopedia (American English) or encyclopædia (British English) is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge either general or special to a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articles or entries that are arranged alphabetically by article name or by thematic categories, or else are hyperlinked and searchable. Encyclopedia entries are longer and more detailed than those in most dictionaries. Generally speaking, encyclopedia articles focus on ''factual information'' concerning the subject named in the article's title; this is unlike dictionary entries, which focus on linguistic information about words, such as their etymology, meaning, pronunciation, use, and grammatical forms.Béjoint, Henri (2000)''Modern Lexicography'', pp. 30–31. Oxford University Press. Encyclopedias have existed for around 2,000 years and have evolved considerably during that time as regards language (written in a major international or a vernacu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menelaus (High Priest)
Menelaus ( he, מנלאוס) was High Priest in Jerusalem from about 172 BC to about 161 BC. He was high priest at the beginning of the Maccabean revolt (167-160). He was the successor of Jason, the brother of Onias III. The sources are divided as to his origin. According to II Maccabees, he belonged to the Tribe of Benjamin and was the brother of the Simeon who had denounced Onias III to Seleucus IV Philopator, and revealed to the Syrians the existence of the treasure of the Temple; according to Flavius Josephus, Menelaus was the brother of Onias III and Jason, his two predecessors as High Priest, and also bore the name Onias. It is possible that Josephus confused Simeon, the brother of Menelaus, with Simeon, the father of Onias and Jason. Hellenizing tendencies Although during the three years of his pontificate Jason had given many proofs of his attachment to the Hellenistic party (by building a gymnasium in Jerusalem and by introducing many Greek customs) the Hellenists of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
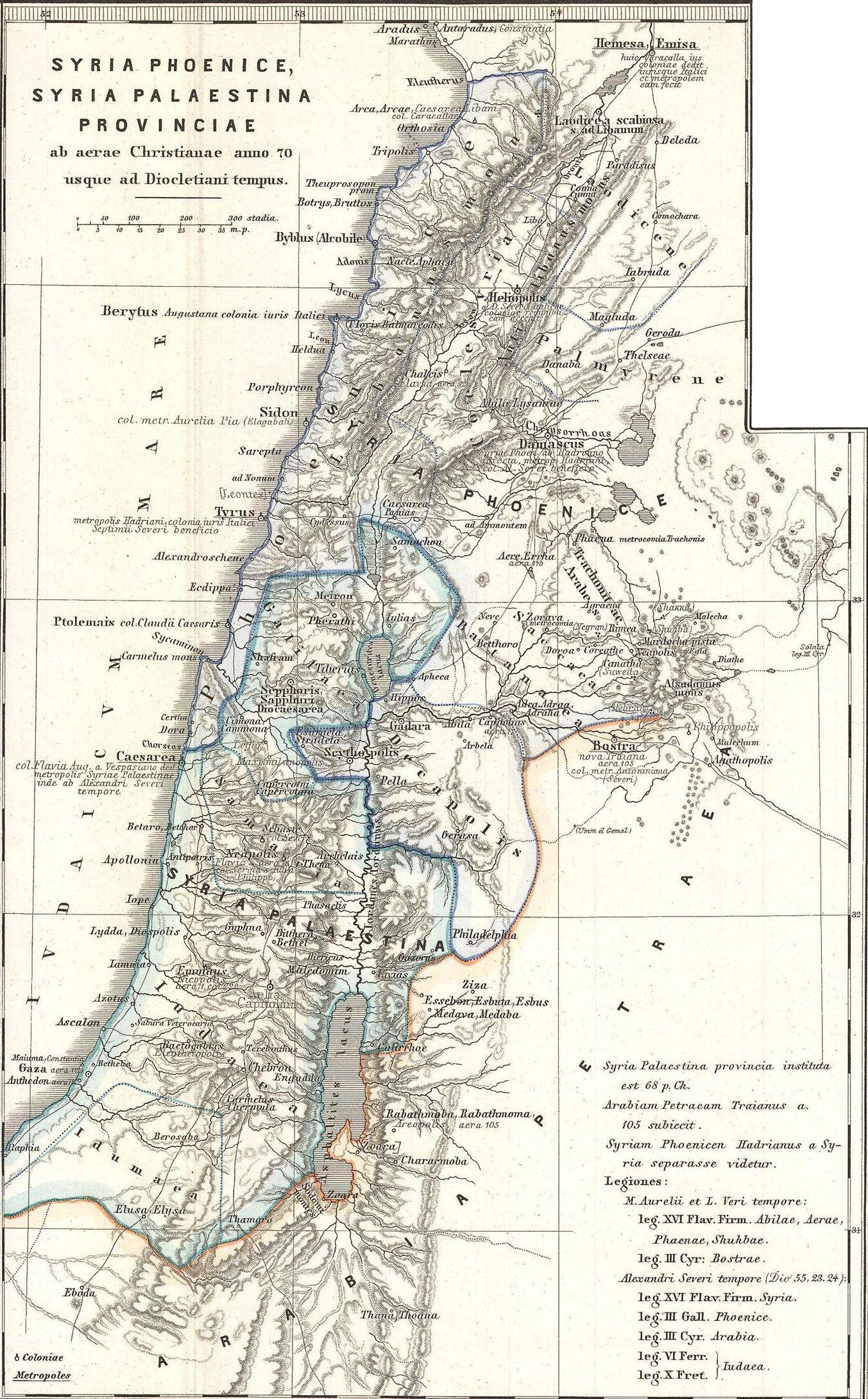
Phenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their history, and they possessed several enclaves such as Arwad and Tell Sukas (modern Syria). The core region in which the Phoenician culture developed and thrived stretched from Tripoli and Byblos in northern Lebanon to Mount Carmel in modern Israel. At their height, the Phoenician possessions in the Eastern Mediterranean stretched from the Orontes River mouth to Ashkelon. Beyond its homeland, the Phoenician civilization extended to the Mediterranean from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula. The Phoenicians were a Semitic-speaking people of somewhat unknown origin who emerged in the Levant around 3000 BC. The term ''Phoenicia'' is an ancient Greek exonym that most likely described one of their most famous exports, a dye also known as Tyrian purple; it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cœle-Syria
Coele-Syria (, also spelt Coele Syria, Coelesyria, Celesyria) alternatively Coelo-Syria or Coelosyria (; grc-gre, Κοίλη Συρία, ''Koílē Syría'', 'Hollow Syria'; lat, Cœlē Syria or ), was a region of Syria in classical antiquity. It probably derived from the Aramaic word for all of the region of Syria, but it was most often applied to the Beqaa Valley between the Lebanon and the Anti-Lebanon mountain ranges. The area is now part of the modern-day Syria and Lebanon. Name It is widely accepted that the term Coele is a transcription of Aramaic ''kul'', meaning "all, the entire", such that the term originally identified ''all'' of Syria.A History of the Jews and Judaism in the Second Temple Period, Volume 2, Lester L. Grab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maccabean Revolt
The Maccabean Revolt ( he, מרד החשמונאים) was a Jewish rebellion led by the Maccabees against the Seleucid Empire and against Hellenistic influence on Jewish life. The main phase of the revolt lasted from 167–160 BCE and ended with the Seleucids in control of Judea, but conflict between the Maccabees, Hellenized Jews, and the Seleucids continued until 134 BCE, with the Maccabees eventually attaining independence. Seleucid King Antiochus IV Epiphanes launched a massive campaign of repression against the Jewish religion in 168 BCE. The reason he did so is not entirely clear, but it seems to have been related to the King mistaking an internal conflict among the Jewish priesthood as a full-scale rebellion. Jewish practices were banned, Jerusalem was placed under direct Seleucid control, and the Second Temple in Jerusalem was made the site of a syncretic Pagan-Jewish cult. This repression triggered exactly the revolt that Antiochus IV had feared, with a group o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicanor (Seleucid General)
Nicanor (; el, Nικάνωρ ''Nīkā́nōr''; died 161 BC) was a Syrian-Seleucid General under the kings Antiochus Epiphanes and Demetrius Soter. Early military career The son of Patroclus and one of the king's "chief friends" ( 2 Macc 8:9), After the defeat of Seron by Judas Maccabeus at the Battle of Beth Horon, Epiphanes entrusted his chancellor Lysias with the destruction of Judea ( 1 Macc 3:34). Nicanor was one of the three generals commissioned by Lysias; the others being Ptolemy, son of Dorymenes, and Gorgias (1 Macc 3:38). The campaign began in 166 BC; the Syrians were defeated at Emmaus (1 Macc 3:57), while Gorgias at a later stage gained a victory at Jamnia over a group of Jews who disobeyed Judas Maccabeus (1 Macc 5:58). The account given in 2 Maccabees differs considerably, both in omissions and in additions (2 Macc 8:9). There Nicanor, not Gorgias, is the chief in command. The battle of Emmaus is not mentioned, but "the thrice-accursed Nicanor," having in overwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire originally founded by Alexander the Great. After receiving the Mesopotamian region of Babylonia in 321 BC, Seleucus I began expanding his dominions to include the Near Eastern territories that encompass modern-day Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Syria, all of which had been under Macedonian control after the fall of the former Persian Achaemenid Empire. At the Seleucid Empire's height, it had consisted of territory that had covered Anatolia, Persia, the Levant, and what are now modern Iraq, Kuwait, Afghanistan, and parts of Turkmenistan. The Seleucid Empire was a major center of Hellenistic culture. Greek customs and language were privileged; the wide varie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysias (Syrian Chancellor)
Lysias (; el, Λυσίας; he, ליזיאש; died 162 BCE) was a 2nd-century BCE general and governor of Syria under the Seleucid Empire. Biography He was described as, "A noble man, and one of the blood royal". The Seleucid Empire of the era was huge; it possessed two heartlands, the capital at Antioch and Syria, and a secondary capital in Babylon and Mesopotamia. Seleucid rulers had to aggressively remind their client rulers of their loyalty lest the client rulers drift towards independence, as happened with various subkingdoms over time. King Antiochus IV Epiphanes left Antioch circa 166 or 165 BCE on an expedition to the eastern satrapies; he would see to affairs in Babylonia, dismiss corrupt or overly independent officials, and attempt to exercise control over the drifting Persian provinces to what would become the Parthian Empire. Antiochus IV left Lysias in charge of the government of the Western half of the empire as regent. Lysias also took guardianship of Antiochu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suda
The ''Suda'' or ''Souda'' (; grc-x-medieval, Σοῦδα, Soûda; la, Suidae Lexicon) is a large 10th-century Byzantine encyclopedia of the ancient Mediterranean world, formerly attributed to an author called Soudas (Σούδας) or Souidas (Σουίδας). It is an encyclopedic lexicon, written in Greek, with 30,000 entries, many drawing from ancient sources that have since been lost, and often derived from medieval Christian compilers. Title The derivation is probably from the Byzantine Greek word ''souda'', meaning "fortress" or "stronghold", with the alternate name, ''Suidas'', stemming from an error made by Eustathius, who mistook the title for the author's name. Paul Maas once ironized by suggesting that the title may be connected to the Latin verb ''suda'', the second-person singular imperative of ''sudāre'', meaning "to sweat", but Franz Dölger traced its origins back to Byzantine military lexicon (σοῦδα, "ditch, trench", then "fortress"). Silvio Giuse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |