|
Ptc Heating Element
A positive temperature coefficient heating element (PTC heating element) or self-regulating heater is an electrical resistance heater whose resistance increases significantly with temperature. The name self-regulating heater comes from the tendency of such heating elements to maintain a constant temperature. PTC heating elements are a type of thermistor. Properties PTC heating elements have a large positive temperature coefficient of resistance, which means if a constant voltage is applied, the element produces a large amount of heat when its temperature is low, and a smaller amount of heat when its temperature is high. In comparison, most electrical heating elements also have a positive temperature coefficient, but that coefficient is so small, they produce approximately the same amount of heat regardless of temperature. Self-regulating Some PTC heating elements are designed to have a sharp change in resistance at a particular temperature. These elements are called self-r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistive Heating
Joule heating, also known as resistive, resistance, or Ohmic heating, is the process by which the passage of an electric current through a conductor (material), conductor produces heat. Joule's first law (also just Joule's law), also known in countries of former Soviet Union, USSR as the Joule–Lenz law, Assuming the element behaves as a perfect resistor and that the power is completely converted into heat, the formula can be re-written by substituting Ohm's law, V = I R , into the generalized power equation: P = IV = I^2R = V^2/R where ''R'' is the electrical resistance and conductance, resistance. Alternating current When current varies, as it does in AC circuits, P(t) = U(t) I(t) where ''t'' is time and ''P'' is the instantaneous power being converted from electrical energy to heat. Far more often, the ''average'' power is of more interest than the instantaneous power: P_ = U_\text I_\text = I_\text^2 R = U_\text^2 / R where "avg" denotes Arithmetic mean, average (mean) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermistor
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance is strongly dependent on temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word thermistor is a portmanteau of ''thermal'' and ''resistor''. Thermistors are divided based on their conduction model. Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) thermistors have ''less'' resistance at ''higher'' temperatures, while Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) thermistors have ''more'' resistance at ''higher'' temperatures. Hence, a PTC thermistor's resistance is directly proportional to temperature. NTC thermistor are widely used as inrush current limiters, temperature sensors, while PTC thermistors are used as self-resetting overcurrent protectors, and self-regulating heating elements. An operational temperature range of a thermistor is dependent on the probe type and is typically between −100 °C and 300 °C (−148 °F and 572 °F). Types Depending on materials used, thermistors are classified into two types: *With ''NTC'' the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature Coefficient
A temperature coefficient describes the relative change of a physical property that is associated with a given change in temperature. For a property ''R'' that changes when the temperature changes by ''dT'', the temperature coefficient α is defined by the following equation: :\frac = \alpha\,dT Here α has the dimension of an inverse temperature and can be expressed e.g. in 1/K or K−1. If the temperature coefficient itself does not vary too much with temperature and \alpha\Delta T \ll 1, a linear approximation will be useful in estimating the value ''R'' of a property at a temperature ''T'', given its value ''R''0 at a reference temperature ''T''0: :R(T) = R(T_0)(1 + \alpha\Delta T), where Δ''T'' is the difference between ''T'' and ''T''0. For strongly temperature-dependent α, this approximation is only useful for small temperature differences Δ''T''. Temperature coefficients are specified for various applications, including electric and magnetic properties of materials a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heating Element
A heating element converts electrical energy into heat through the process of Joule heating. Electric current through the element encounters resistance, resulting in heating of the element. Unlike the Peltier effect, this process is independent of the direction of current. Heating elements types Metal Resistance wire: Metallic resistance heating elements may be wire or ribbon, straight or coiled. They are used in common heating devices like toasters and hair dryers, furnaces for industrial heating, floor heating, roof heating, pathway heating to melt snow, dryers, etc. The most common classes of materials used include: * Nichrome: Most resistance wire heating elements usually use nichrome 80/20 (80% Nickel, 20% Chromium) wire, ribbon, or strip. Nichrome 80/20 is an ideal material, because it has relatively high resistance and forms an adherent layer of chromium oxide when it is heated for the first time. Material beneath this layer will not oxidize, preventing the wire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermostat
A thermostat is a regulating device component which senses the temperature of a physical system and performs actions so that the system's temperature is maintained near a desired setpoint. Thermostats are used in any device or system that heats or cools to a setpoint temperature. Examples include building heating, central heating, air conditioners, HVAC systems, water heaters, as well as kitchen equipment including ovens and refrigerators and medical and scientific incubators. In scientific literature, these devices are often broadly classified as thermostatically controlled loads (TCLs). Thermostatically controlled loads comprise roughly 50% of the overall electricity demand in the United States. A thermostat operates as a "closed loop" control device, as it seeks to reduce the error between the desired and measured temperatures. Sometimes a thermostat combines both the sensing and control action elements of a controlled system, such as in an automotive thermostat. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Heater
A space heater is a device used to heat a single, small to medium sized area. Operation Electric space heaters fall into four main categories: fan heaters, ceramic, infrared, and oil-filled. * Fan heaters are the cheapest, but are often the least efficient and versatile. Nonetheless, they can be useful for heating small spaces, such as a small room or office cubicle. * Ceramic heaters push air across a piece of heated ceramic material. They can adequately heat a typical bedroom. * Infrared heaters provide more heat than ceramic models, and are also smaller and quieter. They do not oscillate like ceramic heaters, but consist of a heating chamber deep within the unit that prevent accidental fires, and allows for greater accumulation of heat before it is emitted by the unit. By the mid-2010s, many were outfitted with touch-screen controls and energy-saving settings, and were styled in such a way to complement the user's furniture. They grew in popularity in the 2010s. * Oi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Hogging
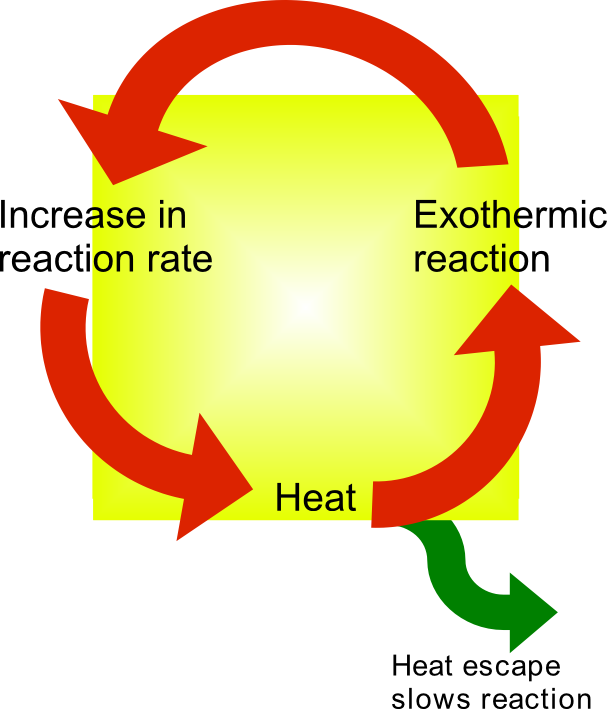
Thermal runaway describes a process that is accelerated by increased temperature, in turn releasing energy that further increases temperature. Thermal runaway occurs in situations where an increase in temperature changes the conditions in a way that causes a further increase in temperature, often leading to a destructive result. It is a kind of uncontrolled positive feedback. In chemistry (and chemical engineering), thermal runaway is associated with strongly exothermic reactions that are accelerated by temperature rise. In electrical engineering, thermal runaway is typically associated with increased current flow and power dissipation. Thermal runaway can occur in civil engineering, notably when the heat released by large amounts of curing concrete is not controlled. In astrophysics, runaway nuclear fusion reactions in stars can lead to nova and several types of supernova explosions, and also occur as a less dramatic event in the normal evolution of solar-mass stars, the " he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PTC Rubber
PTC rubberUS patent 8,367,986 is a silicone rubber which conducts electricity with a resistivity that increases exponentially with increasing temperature for all temperatures up to a temperature where the resistivity grows to infinity. Above this temperature the PTC rubber is an electrical insulator. PTC rubber is made from polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) loaded with carbon nanoparticles. PTC stands for Positive temperature coefficient. Properties If the electric field strength inside the material is large enough (typically larger than 30 V/mm), the carbon nanoparticles trigger a quantum mechanical tunneling effect current to flow through the material. The contribution from a large number of small tunneling effect currents can add up to macroscopic currents in the range of amperes. The quantum mechanical tunneling effect inside the material is highly temperature dependent. The current decreases exponentially with increasing temperature. This means that the resistivity of the material g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doping (semiconductor)
In semiconductor production, doping is the intentional introduction of impurities into an intrinsic semiconductor for the purpose of modulating its electrical, optical and structural properties. The doped material is referred to as an extrinsic semiconductor. Small numbers of dopant atoms can change the ability of a semiconductor to conduct electricity. When on the order of one dopant atom is added per 100 million atoms, the doping is said to be ''low'' or ''light''. When many more dopant atoms are added, on the order of one per ten thousand atoms, the doping is referred to as ''high'' or ''heavy''. This is often shown as ''n+'' for n-type doping or ''p+'' for p-type doping. (''See the article on semiconductors for a more detailed description of the doping mechanism.'') A semiconductor doped to such high levels that it acts more like a conductor than a semiconductor is referred to as a degenerate semiconductor. A semiconductor can be considered i-type semiconductor if it has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curie Temperature
In physics and materials science, the Curie temperature (''T''C), or Curie point, is the temperature above which certain materials lose their permanent magnetic properties, which can (in most cases) be replaced by induced magnetism. The Curie temperature is named after Pierre Curie, who showed that magnetism was lost at a critical temperature. The force of magnetism is determined by the magnetic moment, a dipole moment within an atom which originates from the angular momentum and spin of electrons. Materials have different structures of intrinsic magnetic moments that depend on temperature; the Curie temperature is the critical point at which a material's intrinsic magnetic moments change direction. Permanent magnetism is caused by the alignment of magnetic moments and induced magnetism is created when disordered magnetic moments are forced to align in an applied magnetic field. For example, the ordered magnetic moments (ferromagnetic, Figure 1) change and become disorder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermistor
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance is strongly dependent on temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word thermistor is a portmanteau of ''thermal'' and ''resistor''. Thermistors are divided based on their conduction model. Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) thermistors have ''less'' resistance at ''higher'' temperatures, while Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) thermistors have ''more'' resistance at ''higher'' temperatures. Hence, a PTC thermistor's resistance is directly proportional to temperature. NTC thermistor are widely used as inrush current limiters, temperature sensors, while PTC thermistors are used as self-resetting overcurrent protectors, and self-regulating heating elements. An operational temperature range of a thermistor is dependent on the probe type and is typically between −100 °C and 300 °C (−148 °F and 572 °F). Types Depending on materials used, thermistors are classified into two types: *With ''NTC'' the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |