|
Psychoactive Fungi
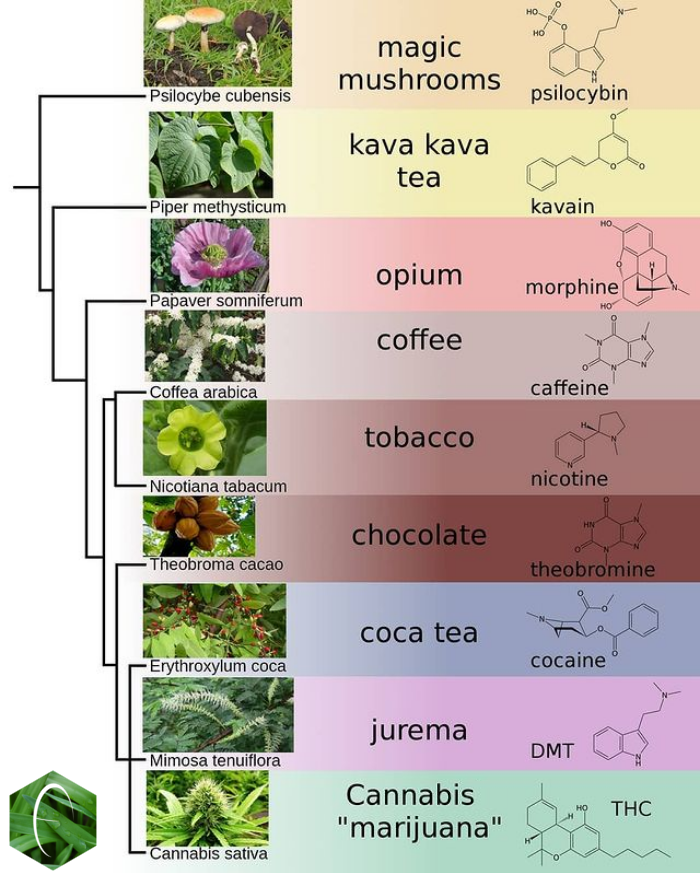
This is a list of psychoactive plants, fungi, and animals. Plants Psychoactive plants include, but are not limited to, the following examples: * ''Cannabis'': cannabinoids * Tobacco: nicotine and beta-carboline alkaloids * Coca: cocaine * Opium Poppy: morphine, codeine, thebaine, papaverine, noscapine, and narceine * '' Salvia divinorum'': salvinorin A * Khat: cathine and cathinone * Kava: kavalactones * Nutmeg: myristicin * Nightshade (''Solanaceae'') plants containing hyoscyamine, atropine, and scopolamine: ** ''Datura'' ** Deadly nightshade (''Atropa belladonna'') ** Henbane (''Hyoscyamus niger'') ** Mandrake (''Mandragora officinarum'') ** Other ''Solanaceae'' * Psychoactive cacti, which contain mainly mescaline: ** Peyote ** Other ''Lophophora'' ** Peruvian Torch cactus ** San Pedro cactus ** Other ''Echinopsis'' * Minimally psychoactive plants that contain mainly caffeine and theobromine: ** Coffee ** Tea (also contains theanine) ** Guarana ** Yerba Mate ** Coc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychoactive Plants
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior. These substances may be used medically, recreationally or spiritually to a. Purposefully improve one’s perceived performance b. Alter one's consciousness (such as with entheogens for ritual, spiritual or shamanic purposes) or c. For research. Some categories of psychoactive drugs - which are believed, by some, to have therapeutic value - may be prescribed by some physicians and other healthcare practitioners. Examples of medication categories that may contain potentially beneficial psychoactive drugs include, but are not limited to: # Anesthetics # Analgesics # Anticonvulsants # Anti-Parkinson’s medications # Medications used to treat Neuropsychiatric Disorders a. Antidepressants b. Anxiolytics c. Antipsychotics d. Sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salvia Divinorum
''Salvia divinorum'' (Latin: "sage of the diviners"; also called ska maría pastora, seer's sage, yerba de la pastora, magic mint or simply salvia) is a plant species with transient psychoactive properties when its leaves are consumed by chewing, smoking, or as a tea. The leaves contain opioid-like compounds that induce hallucinations. Because the plant has not been well-studied in high-quality clinical research, little is known about its toxicology, adverse effects, or safety over long-term consumption. Its native habitat is cloud forest in the isolated Sierra Mazateca of Oaxaca, Mexico, where it grows in shady, moist locations. Valdes 1987, p. 106. The plant grows to over a meter high, has hollow square stems like others in the mint family Lamiaceae, large leaves, and occasional white flowers with violet calyxes. Botanists have not determined whether ''Salvia divinorum'' is a cultigen or a hybrid because native plants reproduce vegetatively and rarely produce viable seed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Datura
''Datura'' is a genus of nine species of highly poisonous, vespertine-flowering plants belonging to the nightshade family Solanaceae. They are commonly known as thornapples or jimsonweeds, but are also known as devil's trumpets (not to be confused with angel's trumpets, which are placed in the closely related genus ''Brugmansia''). Other English common names include moonflower, devil's weed, and hell's bells. All species of ''Datura'' are extremely poisonous and potentially psychoactive, especially their seeds and flowers, which can cause respiratory depression, arrhythmias, fever, delirium, hallucinations, anticholinergic syndrome, psychosis, and even death if taken internally. Due to their effects and symptoms, they have occasionally been used not only as poisons, but also as hallucinogens by various groups throughout history. Traditionally, psychoactive administration of ''Datura'' species has often been associated with witchcraft and sorcery or similar practices in man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scopolamine
Scopolamine, also known as hyoscine, or Devil's Breath, is a natural or synthetically produced tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic drug that is formally used as a medication for treating motion sickness and postoperative nausea and vomiting. It is also sometimes used before surgery to decrease saliva. When used by injection, effects begin after about 20 minutes and last for up to 8 hours. It may also be used orally and as a transdermal patch since it has been long known to have transdermal bioavailability Scopolamine is in the antimuscarinic family of drugs and works by blocking some of the effects of acetylcholine within the nervous system. Scopolamine was first written about in 1881 and started to be used for anesthesia around 1900. Scopolamine is also the main active component produced by certain plants of the nightshade family, which historically have been used as psychoactive drugs (known as ''deliriants'') due to their antimuscarinic-induced hallucinogenic eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atropine
Atropine is a tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically given intravenously or by injection into a muscle. Eye drops are also available which are used to treat uveitis and early amblyopia. The intravenous solution usually begins working within a minute and lasts half an hour to an hour. Large doses may be required to treat some poisonings. Common side effects include a dry mouth, large pupils, urinary retention, constipation, and a fast heart rate. It should generally not be used in people with angle closure glaucoma. While there is no evidence that its use during pregnancy causes birth defects, that has not been well studied. It is likely safe during breastfeeding. It is an antimuscarinic (a type of anticholinergic) that works by inhibiting the parasympathetic nervous system. Atropine occurs n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyoscyamine
Hyoscyamine (also known as daturine or duboisine) is a naturally occurring tropane alkaloid and plant toxin. It is a secondary metabolite found in certain plants of the family Solanaceae, including henbane, mandrake, angel's trumpets, jimsonweed, tomato, the sorcerers' tree, and deadly nightshade. It is the levorotary isomer of atropine (third of the three major nightshade alkaloids) and thus sometimes known as levo-atropine. Brand names for hyoscyamine include Symax, HyoMax, Anaspaz, Egazil, Buwecon, Cystospaz, Levsin, Levbid, Levsinex, Donnamar, NuLev, Spacol T/S, and Neoquess. Uses Hyoscyamine is used to provide symptomatic relief of spasms caused by various lower abdominal and bladder disorders including peptic ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome, diverticulitis, pancreatitis, colic, and interstitial cystitis. It has also been used to relieve some heart problems, control some of the symptoms of Parkinson's disease, as well as for control of abnormal respiratory symptoms and " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solanaceae
The Solanaceae , or nightshades, are a family of flowering plants that ranges from annual and perennial herbs to vines, lianas, epiphytes, shrubs, and trees, and includes a number of agricultural crops, medicinal plants, spices, weeds, and ornamentals. Many members of the family contain potent alkaloids, and some are highly toxic, but many—including tomatoes, potatoes, eggplant, bell and chili peppers—are used as food. The family belongs to the order Solanales, in the asterid group and class Magnoliopsida ( dicotyledons). The Solanaceae consists of about 98 genera and some 2,700 species, with a great diversity of habitats, morphology and ecology. The name Solanaceae derives from the genus ''Solanum''. The etymology of the Latin word is unclear. The name may come from a perceived resemblance of certain solanaceous flowers to the sun and its rays. At least one species of ''Solanum'' is known as the "sunberry". Alternatively, the name could originate from the Latin verb ''sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myristicin
Myristicin is a naturally occurring compound found in common herbs and spices, the most well known being nutmeg. It is an insecticide, and has been shown to enhance the effectiveness of other insecticides in combination. Myristicin is also a precursor for substituted amphetamine derivative compounds structurally related to MMDA and MDMA; it was believed to be metabolized in the liver into MMDA, but unlikely since no MMDA was found in urine, in the body it produces hallucinogenic effects, and can be converted to MMDMA in controlled chemical synthesis. It interacts with many enzymes and signaling pathways in the body, is cytotoxic to living cells, and may also have chemoprotective properties. Uses Isolated myristicin has proven an effective insecticide against many agricultural pests, including ''Aedes aegypti'' mosquito larvae, '' Spilosoma obliqua'' (hairy caterpillars), ''Epilachna varivestis'' (Mexican bean beetles), ''Acyrthosiphon pisum'' (pea aphids), mites, and ''Dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutmeg
Nutmeg is the seed or ground spice of several species of the genus ''Myristica''. ''Myristica fragrans'' (fragrant nutmeg or true nutmeg) is a dark-leaved evergreen tree cultivated for two spices derived from its fruit: nutmeg, from its seed, and mace, from the seed covering. It is also a commercial source of an essential oil and nutmeg butter. Conifers of the genus ''Torreya'', commonly known as the nutmeg yews, have edible seeds of similar appearance, but are not closely related to ''Myristica fragrans'', and are not used as a spice. Indonesia is the main producer of nutmeg and mace. If consumed in amounts exceeding its typical use as a spice, nutmeg powder may produce allergic reactions, cause contact dermatitis, or have psychoactive effects. Although used in traditional medicine for treating various disorders, nutmeg has no scientifically confirmed medicinal value. Common nutmeg Nutmeg is the spice made by grinding the seed of the fragrant nutmeg tree (''Myristica fragra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kavalactones
Kavalactones are a class of lactone compounds found in kava roots and Alpinia zerumbet (Shell ginger). Kavalactones are under research for potential to have various psychotropic effects, including anxiolytic and sedative/hypnotic activities. Enzyme inhibition Kava extract has been shown in vitro to potentially inhibit a wide range of hepatic enzymes, suggesting a possible potential for interactions with many pharmaceuticals and herbal medications. In human volunteers in vivo inhibition is currently limited to CYP1A2, and CYP2E1 through use of probe drugs to measure inhibition. Research Several preliminary studies are assessing potential effects of kava, including its anxiolytic actions and hepatotoxicity, but the role specifically of kavalactones among many other kava compounds for these effects remains under study. Kavalactone type compounds may help protect against high glucose induced cell damage. Toxicity Several kavalactones (e.g. methysticin and yangonin) affect a group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kava
Kava or kava kava (''Piper methysticum'': Latin 'pepper' and Latinized Greek 'intoxicating') is a crop of the Pacific Islands. The name ''kava'' is from Tongan and Marquesan, meaning 'bitter'; other names for kava include ''ʻawa'' (Hawaiʻi), ''ʻava'' (Samoa), ''yaqona'' or ''yagona'' (Fiji), ''sakau'' (Pohnpei), ''seka'' (Kosrae), and ''malok'' or ''malogu'' (parts of Vanuatu). Kava is consumed for its sedating effects throughout the Pacific Ocean cultures of Polynesia, including Hawaii and Vanuatu, Melanesia, some parts of Micronesia, such as Pohnpei and Kosrae, and the Philippines. The root of the plant is used to produce a drink with sedative, anesthetic, and euphoriant properties. Its active ingredients are called kavalactones. A systematic review done by the British nonprofit Cochrane concluded it was likely to be more effective than placebo at treating short-term anxiety. Moderate consumption of kava in its traditional form, i.e., as a water-based suspension of kav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathinone
Cathinone (also known as benzoylethanamine, or β-keto-amphetamine) is a monoamine alkaloid found in the shrub '' Catha edulis'' (khat) and is chemically similar to ephedrine, cathine, methcathinone and other amphetamines. It is probably the main contributor to the stimulant effect of ''Catha edulis'', also known as khat. Cathinone differs from many other amphetamines in that it has a ketone functional group. Other phenethylamines that share this structure include the stimulants methcathinone, MDPV, mephedrone and the antidepressant bupropion. History Discovery Khat has been cultivated in the Horn of Africa and Arabian Peninsula region of the world for thousands of years. It is most commonly chewed for the euphoric effect it produces. The active ingredient was first proposed in 1930, when cathine was identified as a predominant alkaloid in the plant. Cathine was thought to be the main active ingredient in khat until the 1960s, when it was found that the amount of cathine in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |