|
Pseudovector Meson
In high energy physics, a pseudovector meson or axial vector meson is a meson with total spin 1 and even parity (+) (usually noted as :Compare to a vector meson, which has a total spin 1 and odd parity Charge parity (C) in addition to spatial parity (P) The known pseudovector mesons fall into two different classes, all have even spatial parity ( P = "+" ), but they differ in another kind of parity called ''charge parity'' (C) which can be either even (+) or odd (−). The two types of pseudovector meson are: * those with odd charge parity * those with even charge parity The 1 group has no intrinsic spin excitation , but do gain spin from angular momentum of the orbits of the two constituent quarks around their mutual center. The second group (1) have both intrinsic spin and with and coupling to Pseudovector, or axial vector, mesons in the 1 category are most readily be seen in proton‑antiproton annihilation and pion‑nucleon scattering. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Energy Physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three generations of fermions, but ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that contain an odd number of quarks are called baryons and those that contain an even number are called mesons. Two baryons, the proton and the neutron, make up most of the mass of ordinary matter. Mesons are unstable and the longest-lived last for only a few hundredths of a mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pion
In particle physics, a pion (or a pi meson, denoted with the Greek letter pi: ) is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more generally, the lightest hadrons. They are unstable, with the charged pions and decaying after a mean lifetime of 26.033 nanoseconds ( seconds), and the neutral pion decaying after a much shorter lifetime of 85 attoseconds ( seconds). Charged pions most often decay into muons and muon neutrinos, while neutral pions generally decay into gamma rays. The exchange of virtual pions, along with vector, rho and omega mesons, provides an explanation for the residual strong force between nucleons. Pions are not produced in radioactive decay, but commonly are in high-energy collisions between hadrons. Pions also result from some matter–antimatter annihilation events. All types of pions are also produced in natural processes wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesons
In particle physics, a meson ( or ) is a type of hadronic subatomic particle composed of an equal number of quarks and antiquarks, usually one of each, bound together by the strong interaction. Because mesons are composed of quark subparticles, they have a meaningful physical size, a diameter of roughly one femtometre (10 m), which is about 0.6 times the size of a proton or neutron. All mesons are unstable, with the longest-lived lasting for only a few hundredths of a microsecond. Heavier mesons decay to lighter mesons and ultimately to stable electrons, neutrinos and photons. Outside the nucleus, mesons appear in nature only as short-lived products of very high-energy collisions between particles made of quarks, such as cosmic rays (high-energy protons and neutrons) and baryonic matter. Mesons are routinely produced artificially in cyclotrons or other particle accelerators in the collisions of protons, antiprotons, or other particles. Higher-energy (more massive) mes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudovector Boson
In particle physics, a vector boson is a boson whose spin equals one. The vector bosons that are regarded as elementary particles in the Standard Model are the gauge bosons, the force carriers of fundamental interactions: the photon of electromagnetism, the W and Z bosons of the weak interaction, and the gluons of the strong interaction. Some composite particles are vector bosons, for instance any vector meson (quark and antiquark). During the 1970s and 1980s, intermediate vector bosons (the W and Z bosons, which mediate the weak interaction) drew much attention in particle physics. A pseudovector boson is a vector boson that has even parity, whereas "regular" vector bosons have odd parity. There are no fundamental pseudovector bosons, but there are pseudovector mesons. In relation to the Higgs boson The W and Z particles interact with the Higgs boson as shown in the Feynman diagram. Explanation The name ''vector boson'' arises from quantum field theory. The compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalar Meson
In high energy physics, a scalar meson is a meson with total spin 0 and even parity (usually noted as ''JP''=0+). Compare to ''pseudoscalar meson''. The first known scalar mesons have been observed since the late 1950s, with observations of numerous light states and heavier states proliferating since the 1980s. Scalar mesons are most often observed in proton-antiproton annihilation, radiative decays of vector mesons, and meson-meson scattering. Groups The light (unflavored) scalar mesons may be divided into three groups: * mesons having a mass below 1 GeV/c2 * mesons having a mass between 1 GeV/c2 and 2 GeV/c2 * other radially-excited unflavored scalar mesons above 2 GeV/c2 Lower mass range Since the late 1950s, the lightest scalar mesons were often interpreted within the framework of the linear sigma model, and many theorists still choose this interpretation of the scalar mesons as the chiral partners of the pseudoscalar meson multiplet. With the re-introduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoscalar Meson
In high-energy physics, a pseudoscalar meson is a meson with total spin 0 and odd parity (usually notated as Pseudoscalar mesons are commonly seen in proton-proton scattering and proton-antiproton annihilation, and include the pion (), kaon (), eta (), and eta prime () particles, whose masses are known with great precision. Among all of the mesons known to exist, in some sense, the pseudoscalars are the most well studied and understood. History The pion () was first proposed to exist by Yukawa in the 1930s as the primary force carrying boson of the Yukawa potential in nuclear interactions, and was later observed at nearly the same mass that he originally predicted for it. In the 1950s and 1960s, the pseudoscalar mesons began to proliferate, and were eventually organized into a multiplet according to Murray Gell-Mann's so-called " Eightfold Way". Gell-Mann further predicted the existence of a ninth resonance in the pseudoscalar multiplet, which he originally called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mesons
:''This list is of all known and predicted scalar, pseudoscalar and vector mesons. See list of particles for a more detailed list of particles found in particle physics.'' This article contains a list of mesons, unstable subatomic particles composed of one quark and one antiquark. They are part of the hadron particle family—particles made of quarks. The other members of the hadron family are the baryons—subatomic particles composed of three quarks. The main difference between mesons and baryons is that mesons have integer spin (thus are bosons) while baryons are fermions (half-integer spin). Because mesons are bosons, the Pauli exclusion principle does not apply to them. Because of this, they can act as force mediating particles on short distances, and thus play a part in processes such as the nuclear interaction. Since mesons are composed of quarks, they participate in both the weak and strong interactions. Mesons with net electric charge also participate in the electro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strangeness
In particle physics, strangeness ("''S''") is a property of particles, expressed as a quantum number, for describing decay of particles in strong and electromagnetic interactions which occur in a short period of time. The strangeness of a particle is defined as: S = -(n_\text - n_) where ''n'' represents the number of strange quarks () and ''n'' represents the number of strange antiquarks (). Evaluation of strangeness production has become an important tool in search, discovery, observation and interpretation of quark–gluon plasma (QGP). Strangeness is an excited state of matter and its decay is governed by CKM mixing. The terms ''strange'' and ''strangeness'' predate the discovery of the quark, and were adopted after its discovery in order to preserve the continuity of the phrase: strangeness of particles as −1 and anti-particles as +1, per the original definition. For all the quark flavour quantum numbers (strangeness, charm, topness and bottomness) the convention is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
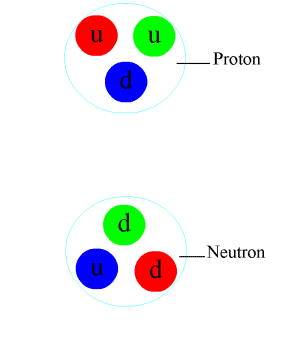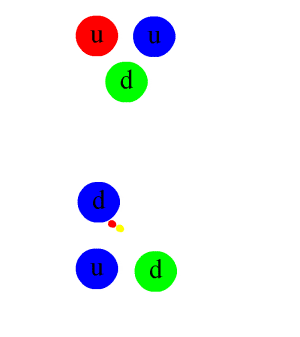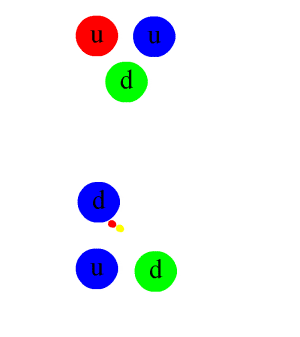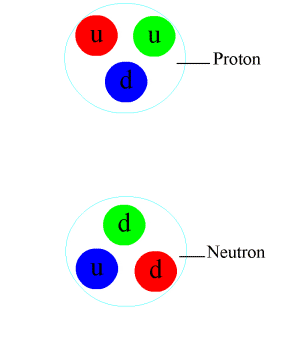
Nucleon
In physics and chemistry, a nucleon is either a proton or a neutron, considered in its role as a component of an atomic nucleus. The number of nucleons in a nucleus defines the atom's mass number (nucleon number). Until the 1960s, nucleons were thought to be elementary particles, not made up of smaller parts. Now they are known to be composite particles, made of three quarks bound together by the strong interaction. The interaction between two or more nucleons is called internucleon interaction or nuclear force, which is also ultimately caused by the strong interaction. (Before the discovery of quarks, the term "strong interaction" referred to just internucleon interactions.) Nucleons sit at the boundary where particle physics and nuclear physics overlap. Particle physics, particularly quantum chromodynamics, provides the fundamental equations that describe the properties of quarks and of the strong interaction. These equations describe quantitatively how quarks can bind toget ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiproton
The antiproton, , (pronounced ''p-bar'') is the antiparticle of the proton. Antiprotons are stable, but they are typically short-lived, since any collision with a proton will cause both particles to be annihilated in a burst of energy. The existence of the antiproton with electric charge of , opposite to the electric charge of of the proton, was predicted by Paul Dirac in his 1933 Nobel Prize lecture. Dirac received the Nobel Prize for his 1928 publication of his Dirac equation that predicted the existence of positive and negative solutions to Einstein's energy equation (E = mc^2) and the existence of the positron, the antimatter analog of the electron, with opposite charge and spin. The antiproton was first experimentally confirmed in 1955 at the Bevatron particle accelerator by University of California, Berkeley physicists Emilio Segrè and Owen Chamberlain, for which they were awarded the 1959 Nobel Prize in Physics. In terms of valence quarks, an antiproton consists of two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meson
In particle physics, a meson ( or ) is a type of hadronic subatomic particle composed of an equal number of quarks and antiquarks, usually one of each, bound together by the strong interaction. Because mesons are composed of quark subparticles, they have a meaningful physical size, a diameter of roughly one femtometre (10 m), which is about 0.6 times the size of a proton or neutron. All mesons are unstable, with the longest-lived lasting for only a few hundredths of a microsecond. Heavier mesons decay to lighter mesons and ultimately to stable electrons, neutrinos and photons. Outside the nucleus, mesons appear in nature only as short-lived products of very high-energy collisions between particles made of quarks, such as cosmic rays (high-energy protons and neutrons) and baryonic matter. Mesons are routinely produced artificially in cyclotrons or other particle accelerators in the collisions of protons, antiprotons, or other particles. Higher-energy (more massive) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with masses of approximately one atomic mass unit, are jointly referred to as "nucleons" (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the nucleus of every atom. They provide the attractive electrostatic central force which binds the atomic electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z''). Since each element has a unique number of protons, each element has its own unique atomic number, which determines the number of atomic electrons and consequently the chemical characteristics of the element. The word ''proton'' is Greek for "first", and this name was given to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |