|
Pseudomonas Poae
''Pseudomonas poae'' is a fluorescent, Gram-negative bacterium isolated from the phyllosphere of grass Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns an ...es. The type strain is DSM 14936. References Further reading * External linksType strain of ''Pseudomonas poae'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase Pseudomonadales Bacteria described in 2003 {{Pseudomonadales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescent
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, than the absorbed radiation. A perceptible example of fluorescence occurs when the absorbed radiation is in the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum (invisible to the human eye), while the emitted light is in the visible region; this gives the fluorescent substance a distinct color that can only be seen when the substance has been exposed to UV light. Fluorescent materials cease to glow nearly immediately when the radiation source stops, unlike phosphorescent materials, which continue to emit light for some time after. Fluorescence has many practical applications, including mineralogy, gemology, medicine, chemical sensors (fluorescence spectroscopy), fluorescent labelling, dyes, biological detectors, cosmic-ray detection, vacuu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane. Gram-negative bacteria are found in virtually all environments on Earth that support life. The gram-negative bacteria include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', as well as many pathogenic bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', ''Chlamydia trachomatis'', and ''Yersinia pestis''. They are a significant medical challenge as their outer membrane protects them from many antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and lysozyme, an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. Additionally, the outer leaflet of this membrane comprises a complex lipo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
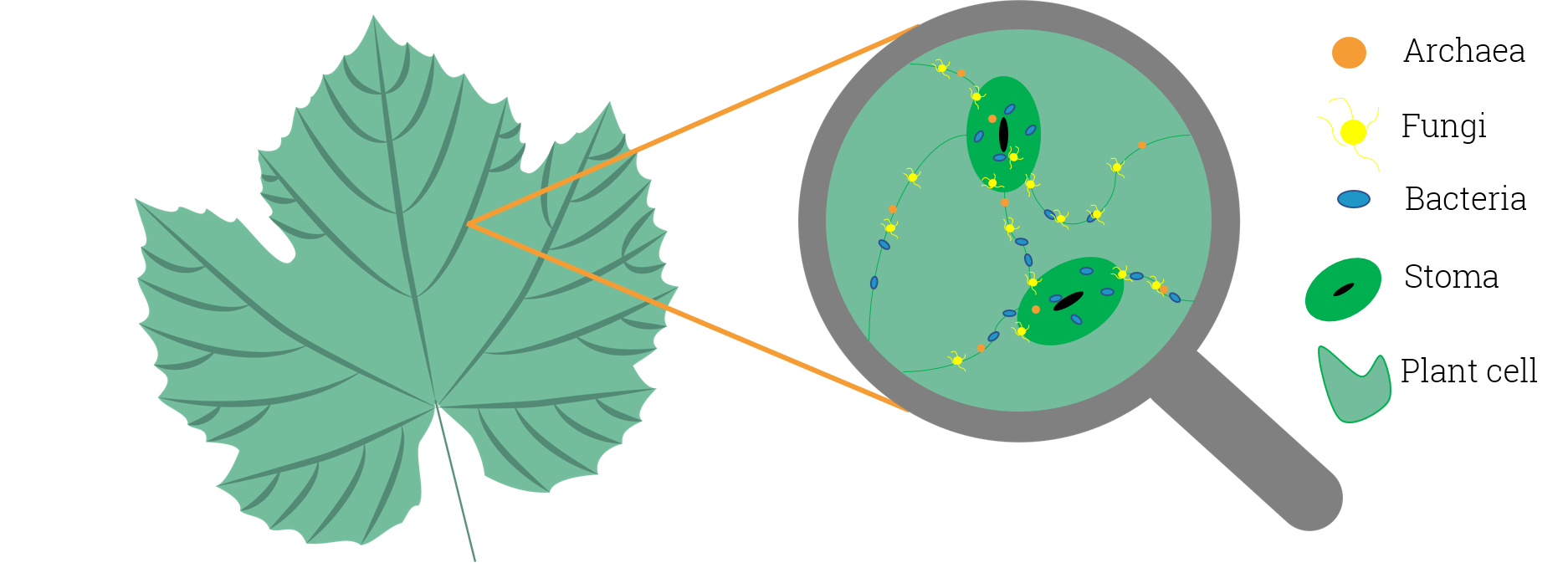
Phyllosphere
In microbiology, the phyllosphere is the total above-ground surface of a plant when viewed as a habitat for microorganisms. The phyllosphere can be further subdivided into the caulosphere (stems), phylloplane (leaves), anthosphere (flowers), and carposphere (fruits). The below-ground microbial habitats (i.e. the thin-volume of soil surrounding root or subterranean stem surfaces) are referred to as the rhizosphere and laimosphere. Most plants host diverse communities of microorganisms including bacteria, fungi, archaea, and protists . Some are beneficial to the plant, others function as plant pathogens and may damage the host plant or even kill it. The phyllosphere microbiome The leaf surface, or phyllosphere, harbours a microbiome comprising diverse communities of bacteria, archaea, fungi, algae and viruses. Microbial colonizers are subjected to diurnal and seasonal fluctuations of heat, moisture, and radiation. In addition, these environmental elements affect plant physiolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grass
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and pasture. The latter are commonly referred to collectively as grass. With around 780 genera and around 12,000 species, the Poaceae is the fifth-largest plant family, following the Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. The Poaceae are the most economically important plant family, providing staple foods from domesticated cereal crops such as maize, wheat, rice, barley, and millet as well as feed for meat-producing animals. They provide, through direct human consumption, just over one-half (51%) of all dietary energy; rice provides 20%, wheat supplies 20%, maize (corn) 5.5%, and other grains 6%. Some members of the Poaceae are used as building materials (bamboo, thatch, and straw); others can provide a source of biofuel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonadales
The Pseudomonadales are an order of Pseudomonadota. A few members are pathogens, such as species of ''Pseudomonas'', ''Moraxella'', and ''Acinetobacter'', which may cause disease in humans, animals and plants. ''Pseudomonas'' The bacterial genus ''Pseudomonas'' includes the opportunistic human pathogen ''P. aeruginosa'', plant pathogenic bacteria, plant beneficial bacteria, ubiquitous soil bacteria with bioremediation capabilities and other species that cause spoilage of milk and dairy products. ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' can cause chronic opportunistic infections that have become increasingly apparent in immunocompromised patients and the ageing population of industrialised societies. The genome sequences of several pseudomonads have become available in recent years and researchers are beginning to use the data to make new discoveries about this bacterium. ''Acinetobacter'' The genus ''Acinetobacter'' is a group of Gram-negative, nonmotile and nonfermentative bacteria belongin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |