|
Pseudocertainty Effect
In prospect theory, the pseudocertainty effect is the tendency for people to perceive an outcome as certain while it is actually uncertain in multi-stage decision making. The evaluation of the certainty of the outcome in a previous stage of decisions is disregarded when selecting an option in subsequent stages. Not to be confused with certainty effect, the pseudocertainty effect was discovered from an attempt at providing a normative use of decision theory for the certainty effect by relaxing the cancellation rule. Background The pseudocertainty effect was illustrated by Daniel Kahneman, who received the Nobel Prize in economics for his work on decision making and decision theory, in collaboration with Amos Tversky. The studies that they researched used real and hypothetical monetary gambles and were often used in undergraduate classrooms and laboratories. Kahneman and Tversky illustrated the pseudocertainty effect by the following examples. Problem 1 Consider the following two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
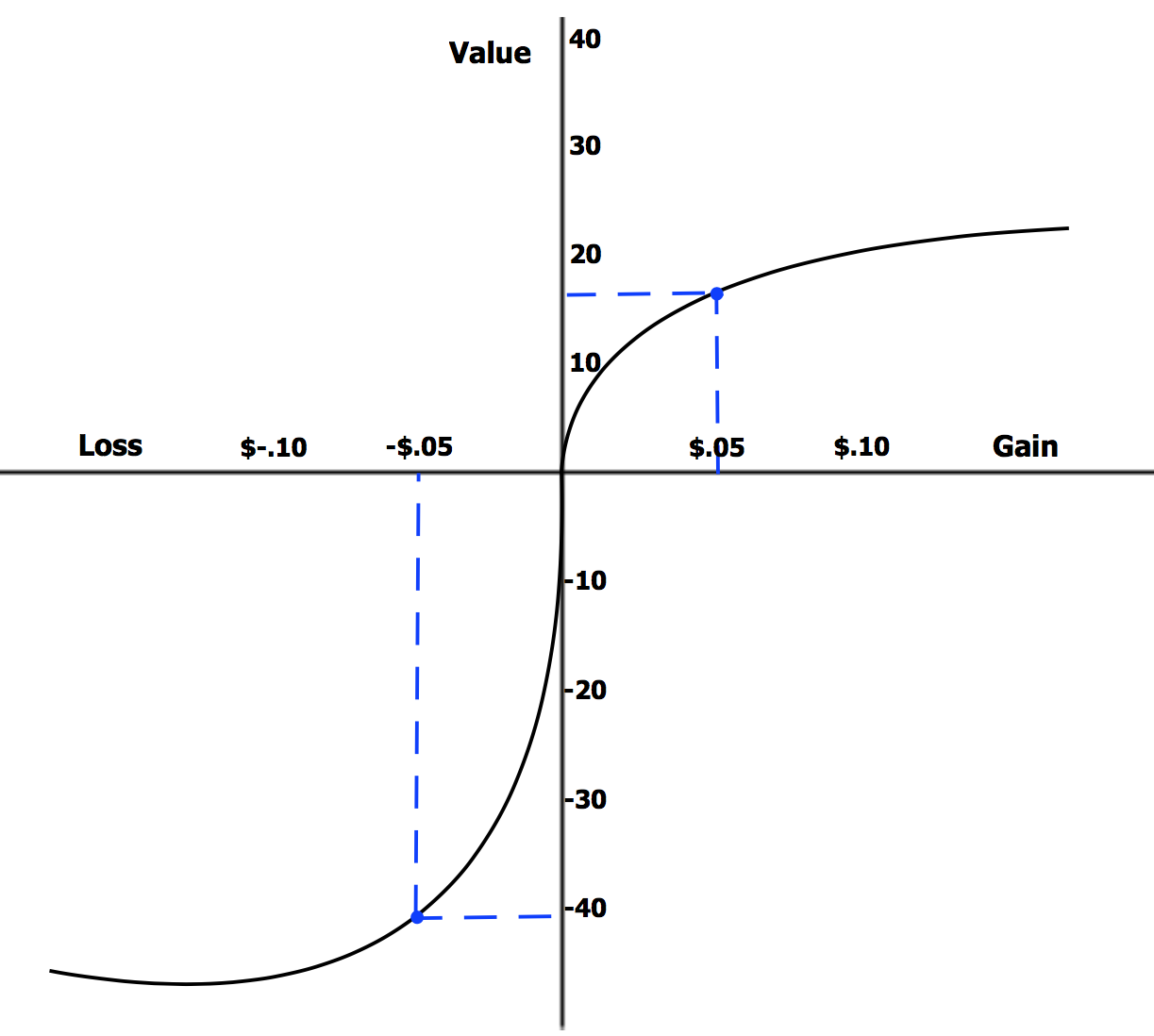
Prospect Theory
Prospect theory is a theory of behavioral economics and behavioral finance that was developed by Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky in 1979. The theory was cited in the decision to award Kahneman the 2002 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics. Based on results from controlled studies, it describes how individuals assess their loss and gain perspectives in an asymmetric manner (see loss aversion). For example, for some individuals, the pain from losing $1,000 could only be compensated by the pleasure of earning $2,000. Thus, contrary to the expected utility theory (which models the decision that perfectly rational agents would make), prospect theory aims to describe the actual behavior of people. In the original formulation of the theory, the term ''prospect'' referred to the predictable results of a lottery. However, prospect theory can also be applied to the prediction of other forms of behaviors and decisions. Overview Prospect theory stems from Loss aversion, where the observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Certainty Effect
The certainty effect is the psychological effect resulting from the reduction of probability from certain to probable . It is an idea introduced in prospect theory. Normally a reduction in the probability of winning a reward (e.g., a reduction from 80% to 20% in the chance of winning a reward) creates a psychological effect such as displeasure to individuals, which leads to the perception of loss from the original probability thus favoring a risk-averse decision. However, the same reduction results in a larger psychological effect when it is done from certainty than from uncertainty. Example illustrated the certainty effect by the following examples. First, consider this example: Which of the following options do you prefer? *A. a sure gain of $30 *B. 80% chance to win $45 and 20% chance to win nothing In this case, 78% of participants chose option A while only 22% chose option B. This demonstrates the typical risk-aversion phenomenon in prospect theory and framing effect bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Theory
Decision theory (or the theory of choice; not to be confused with choice theory) is a branch of applied probability theory concerned with the theory of making decisions based on assigning probabilities to various factors and assigning numerical consequences to the outcome. There are three branches of decision theory: # Normative decision theory: Concerned with the identification of optimal decisions, where optimality is often determined by considering an ideal decision-maker who is able to calculate with perfect accuracy and is in some sense fully rational. # Prescriptive decision theory: Concerned with describing observed behaviors through the use of conceptual models, under the assumption that those making the decisions are behaving under some consistent rules. # Descriptive decision theory: Analyzes how individuals actually make the decisions that they do. Decision theory is closely related to the field of game theory and is an interdisciplinary topic, studied by econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Kahneman
Daniel Kahneman (; he, דניאל כהנמן; born March 5, 1934) is an Israeli-American psychologist and economist notable for his work on the psychology of judgment and decision-making, as well as behavioral economics, for which he was awarded the 2002 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences (shared with Vernon L. Smith). His empirical findings challenge the assumption of human rationality prevailing in modern economic theory. With Amos Tversky and others, Kahneman established a cognitive basis for common human errors that arise from heuristics and biases, and developed prospect theory. In 2011 he was named by '' Foreign Policy'' magazine in its list of top global thinkers. In the same year his book ''Thinking, Fast and Slow'', which summarizes much of his research, was published and became a best seller. In 2015, ''The Economist'' listed him as the seventh most influential economist in the world. He is professor emeritus of psychology and public affairs at Princeton U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amos Tversky
Amos Nathan Tversky ( he, עמוס טברסקי; March 16, 1937 – June 2, 1996) was an Israeli cognitive and mathematical psychologist and a key figure in the discovery of systematic human cognitive bias and handling of risk. Much of his early work concerned the foundations of measurement. He was co-author of a three-volume treatise, ''Foundations of Measurement''. His early work with Daniel Kahneman focused on the psychology of prediction and probability judgment; later they worked together to develop prospect theory, which aims to explain irrational human economic choices and is considered one of the seminal works of behavioral economics. Six years after Tversky's death, Kahneman received the 2002 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for the work he did in collaboration with Amos Tversky. (The prize is not awarded posthumously.) Kahneman told ''The New York Times'' in an interview soon after receiving the honor: "I feel it is a joint prize. We were twinned for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expected Return
The expected return (or expected gain) on a financial investment is the expected value of its return (of the profit on the investment). It is a measure of the center of the distribution of the random variable that is the return. It is calculated by using the following formula: :E \sum_^R_P_ where :: R_ is the return in scenario i; ::P_ is the probability for the return R_ in scenario i; and ::n is the number of scenarios. The expected rate of return is the expected return per currency unit (e.g., dollar) invested. It is computed as the expected return divided by the amount invested. The required rate of return is what an investor would require to be compensated for the risk borne by holding the asset; "expected return" is often used in this sense, as opposed to the more formal, mathematical, sense above. Application Although the above represents what one expects the return to be, it only refers to the long-term average. In the short term, any of the various scenarios could occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allais Paradox
The Allais paradox is a choice problem designed by to show an inconsistency of actual observed choices with the predictions of expected utility theory. Statement of the problem The Allais paradox arises when comparing participants' choices in two different experiments, each of which consists of a choice between two gambles, A and B. The payoffs for each gamble in each experiment are as follows: Several studies involving hypothetical and small monetary payoffs, and recently involving health outcomes, have supported the assertion that when presented with a choice between 1A and 1B, most people would choose 1A. Likewise, when presented with a choice between 2A and 2B, most people would choose 2B. Allais further asserted that it was reasonable to choose 1A alone or 2B alone. However, that the same person (who chose 1A alone or 2B alone) would choose both 1A and 2B together is inconsistent with expected utility theory. According to expected utility theory, the person should choose e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Certainty Effect
The certainty effect is the psychological effect resulting from the reduction of probability from certain to probable . It is an idea introduced in prospect theory. Normally a reduction in the probability of winning a reward (e.g., a reduction from 80% to 20% in the chance of winning a reward) creates a psychological effect such as displeasure to individuals, which leads to the perception of loss from the original probability thus favoring a risk-averse decision. However, the same reduction results in a larger psychological effect when it is done from certainty than from uncertainty. Example illustrated the certainty effect by the following examples. First, consider this example: Which of the following options do you prefer? *A. a sure gain of $30 *B. 80% chance to win $45 and 20% chance to win nothing In this case, 78% of participants chose option A while only 22% chose option B. This demonstrates the typical risk-aversion phenomenon in prospect theory and framing effect bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loaded Question
A loaded question is a form of complex question that contains a controversial assumption (e.g., a presumption of guilt). Such questions may be used as a rhetorical tool: the question attempts to limit direct replies to be those that serve the questioner's agenda. The traditional example is the question "Have you stopped beating your wife?" Whether the respondent answers yes or no, they will admit to having a wife and having beaten her at some time in the past. Thus, these facts are ''presupposed'' by the question, and in this case an entrapment, because it narrows the respondent to a single answer, and the fallacy of many questions has been committed. The fallacy relies upon context for its effect: the fact that a question presupposes something does not in itself make the question fallacious. Only when some of these presuppositions are not necessarily agreed to by the person who is asked the question does the argument containing them become fallacious. Hence, the same question ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loss Aversion
Loss aversion is the tendency to prefer avoiding losses to acquiring equivalent gains. The principle is prominent in the domain of economics. What distinguishes loss aversion from risk aversion is that the utility of a monetary payoff depends on what was previously experienced or was expected to happen. Some studies have suggested that losses are twice as powerful, psychologically, as gains. Loss aversion was first identified by Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman. Loss aversion implies that one who loses $100 will lose more satisfaction than the same person will gain satisfaction from a $100 windfall. In marketing, the use of trial periods and rebates tries to take advantage of the buyer's tendency to value the good more after the buyer incorporates it in the status quo. In past behavioral economics studies, users participate up until the threat of loss equals any incurred gains. Recent methods established by Botond Kőszegi and Matthew Rabin in experimental economics illustrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prospect Theory
Prospect theory is a theory of behavioral economics and behavioral finance that was developed by Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky in 1979. The theory was cited in the decision to award Kahneman the 2002 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics. Based on results from controlled studies, it describes how individuals assess their loss and gain perspectives in an asymmetric manner (see loss aversion). For example, for some individuals, the pain from losing $1,000 could only be compensated by the pleasure of earning $2,000. Thus, contrary to the expected utility theory (which models the decision that perfectly rational agents would make), prospect theory aims to describe the actual behavior of people. In the original formulation of the theory, the term ''prospect'' referred to the predictable results of a lottery. However, prospect theory can also be applied to the prediction of other forms of behaviors and decisions. Overview Prospect theory stems from Loss aversion, where the observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environment), often focusing on negative, undesirable consequences. Many different definitions have been proposed. The international standard definition of risk for common understanding in different applications is “effect of uncertainty on objectives”. The understanding of risk, the methods of assessment and management, the descriptions of risk and even the definitions of risk differ in different practice areas (business, economics, environment, finance, information technology, health, insurance, safety, security etc). This article provides links to more detailed articles on these areas. The international standard for risk management, ISO 31000, provides principles and generic guidelines on managing risks faced by organizations. Definitions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(cropped).jpg)